Unveiling the Tapestry of Life: Exploring the United States Vegetation Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Tapestry of Life: Exploring the United States Vegetation Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Tapestry of Life: Exploring the United States Vegetation Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Tapestry of Life: Exploring the United States Vegetation Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Tapestry of Life: Exploring the United States Vegetation Map
- 3.1 Mapping the Green Landscape: A Journey Through Diverse Ecosystems
- 3.2 Beyond the Map: Unveiling the Significance of Vegetation Mapping
- 3.3 Navigating the Map: A Glimpse into Key Vegetation Types
- 3.4 Beyond the Basics: Understanding the Dynamics of Vegetation
- 3.5 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about the United States Vegetation Map
- 3.6 Tips for Using the United States Vegetation Map Effectively
- 3.7 Conclusion: A Visual Tapestry of Life and a Guide for the Future
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Tapestry of Life: Exploring the United States Vegetation Map
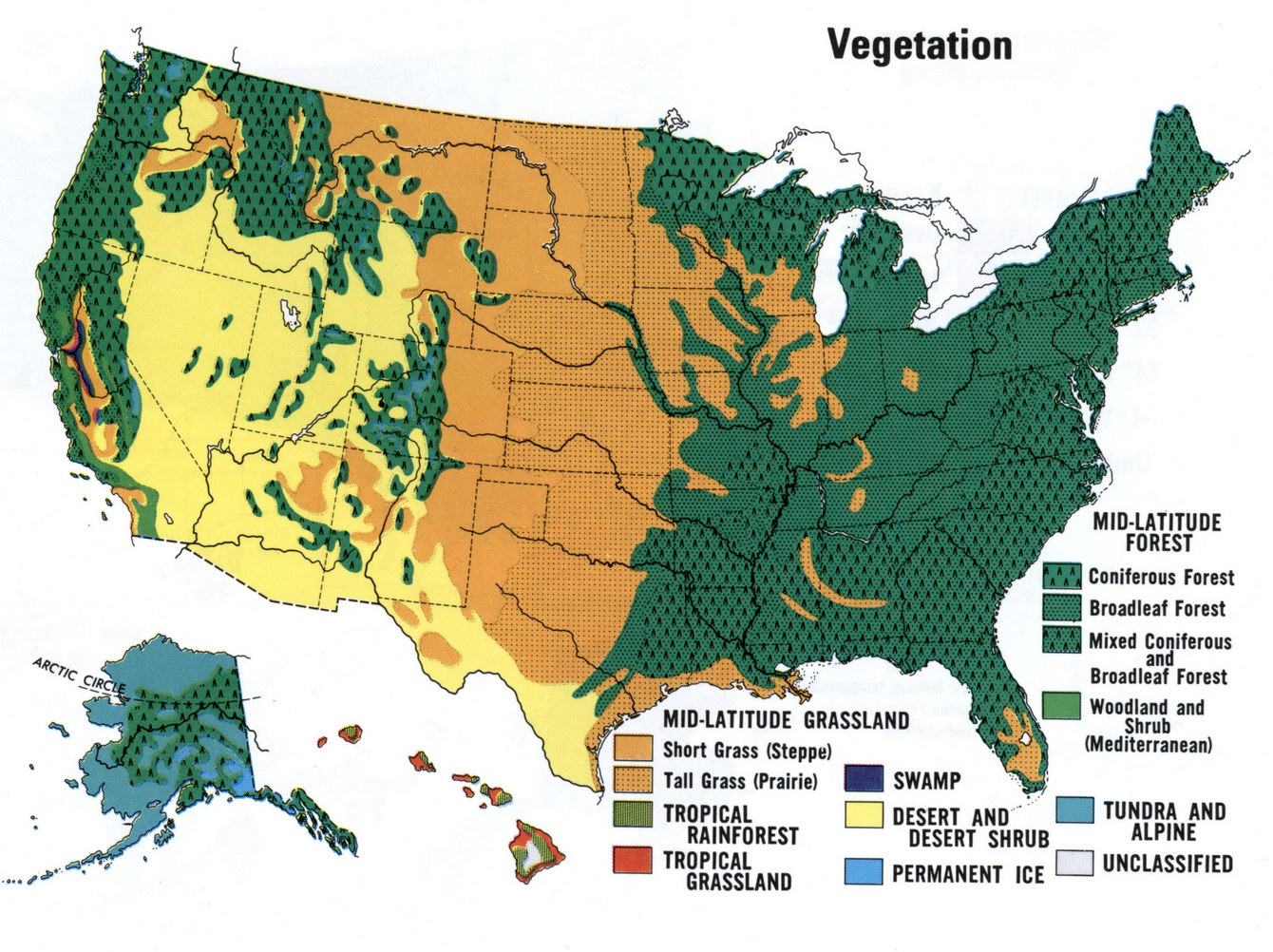
The United States, a vast and diverse land, boasts a rich tapestry of ecosystems, each characterized by unique plant communities. Understanding this intricate web of vegetation is crucial for various purposes, ranging from environmental conservation to resource management and even understanding the impacts of climate change. This intricate picture is vividly captured in the United States Vegetation Map, a powerful tool that provides a comprehensive overview of the country’s diverse plant life.
Mapping the Green Landscape: A Journey Through Diverse Ecosystems
The United States Vegetation Map serves as a visual representation of the country’s vegetation, showcasing the distribution of major plant communities across its landscape. It’s not simply a static image; it’s a dynamic portrayal of the interplay between climate, soil, and topography, all of which influence the types of plants that thrive in a particular region.
The map is a compilation of extensive data gathered through various sources, including:
- Satellite imagery: This provides a broad-scale perspective, allowing scientists to identify major vegetation types and their spatial distribution.
- Aerial photographs: These offer a more detailed view, aiding in the identification of specific plant communities and their boundaries.
- Field surveys: Ground-based observations provide crucial information about the composition and structure of vegetation, including the presence of specific plant species and their abundance.
The resulting map is a vibrant tapestry of colors, each representing a distinct vegetation type. These types range from the towering forests of the Pacific Northwest to the arid deserts of the Southwest, from the lush prairies of the Midwest to the dense swamps of the Southeast.
Beyond the Map: Unveiling the Significance of Vegetation Mapping
The United States Vegetation Map is more than just a visual representation of plant life. It serves as a vital resource for a multitude of purposes, impacting various aspects of our lives:
1. Environmental Conservation:
- Biodiversity assessment: The map provides a baseline for understanding the distribution of plant species and identifying areas with high biodiversity. This information is crucial for prioritizing conservation efforts and protecting vulnerable ecosystems.
- Habitat mapping: By delineating the boundaries of different vegetation types, the map helps in identifying and managing critical habitats for wildlife. This information is crucial for conservation planning and ensuring the long-term survival of endangered species.
- Ecosystem monitoring: The map serves as a benchmark for tracking changes in vegetation patterns over time. These changes can be attributed to various factors, including climate change, land use, and invasive species, providing valuable insights for conservation strategies.
2. Resource Management:
- Forest management: The map assists in understanding the distribution of different forest types, allowing for targeted management practices that promote sustainable forest use and protect valuable timber resources.
- Agricultural planning: The map helps in identifying suitable areas for different agricultural practices, considering factors like soil type, climate, and vegetation. This information is crucial for optimizing crop yields and minimizing environmental impacts.
- Water resource management: The map provides insights into the relationship between vegetation and water availability. This information is valuable for managing water resources, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions.
3. Climate Change Research:
- Carbon sequestration: The map helps in understanding the role of different vegetation types in carbon sequestration, providing valuable information for mitigating climate change.
- Climate change impacts: By monitoring changes in vegetation patterns over time, the map helps in assessing the impacts of climate change on ecosystems and informing adaptation strategies.
- Predicting future vegetation changes: The map, combined with climate models, can be used to predict future changes in vegetation distribution, providing valuable insights for policy decisions and adaptation planning.
4. Public Education and Awareness:
- Visualizing biodiversity: The map offers a compelling visual representation of the vast diversity of plant life in the United States, raising awareness about the importance of conservation.
- Engaging the public: The map can be used in educational programs and outreach initiatives to engage the public in environmental issues and promote responsible stewardship of natural resources.
Navigating the Map: A Glimpse into Key Vegetation Types
The United States Vegetation Map reveals a fascinating array of plant communities, each with its unique characteristics:
1. Forests:
- Deciduous forests: These forests are dominated by trees that shed their leaves in the fall, such as oak, maple, and beech. They are found in the eastern United States and are characterized by distinct seasons.
- Evergreen forests: These forests are dominated by trees that retain their leaves year-round, such as pines, firs, and spruces. They are found in the Pacific Northwest and are associated with cooler, wetter climates.
- Tropical forests: While limited in extent in the United States, these forests are found in southern Florida and are characterized by high biodiversity and a warm, humid climate.
2. Grasslands:
- Tallgrass prairies: These grasslands are dominated by tall grasses and are found in the central United States. They are characterized by rich soils and support a diverse array of wildlife.
- Shortgrass prairies: These grasslands are dominated by shorter grasses and are found in the western United States. They are adapted to drier conditions and are home to unique plant and animal communities.
3. Deserts:
- Sonoran Desert: Located in the southwestern United States, this desert is characterized by cacti, shrubs, and sparse vegetation.
- Mojave Desert: Also located in the southwestern United States, this desert is known for its Joshua trees and other unique plant adaptations.
4. Wetlands:
- Swamps: These wetlands are dominated by trees and are found in the southeastern United States. They are characterized by slow-moving water and support a rich diversity of wildlife.
- Marshes: These wetlands are dominated by grasses and are found along the coasts and in inland areas. They are important for filtering water and providing habitat for birds and other wildlife.
5. Tundra:
- Arctic tundra: Found in Alaska, this biome is characterized by permafrost, low temperatures, and limited vegetation. It is home to specialized plants and animals adapted to harsh conditions.
Beyond the Basics: Understanding the Dynamics of Vegetation
The United States Vegetation Map is a snapshot in time, but the dynamics of vegetation are constantly changing. These changes are influenced by a multitude of factors, including:
- Climate change: Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events are impacting vegetation distribution and composition.
- Land use change: Conversion of forests to agricultural land, urbanization, and other human activities are altering vegetation patterns and impacting ecosystems.
- Invasive species: Non-native plants can outcompete native species, disrupting ecosystems and altering vegetation composition.
- Natural disturbances: Wildfires, hurricanes, and other natural events can significantly alter vegetation patterns, leading to changes in plant communities and ecosystem structure.
Understanding these dynamics is crucial for effective conservation and management strategies. The United States Vegetation Map provides a baseline for monitoring these changes and informing decision-making processes.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about the United States Vegetation Map
1. What is the purpose of the United States Vegetation Map?
The United States Vegetation Map serves as a comprehensive overview of the country’s diverse plant life, providing information on the distribution of major vegetation types and their spatial relationships. This information is vital for environmental conservation, resource management, climate change research, and public education.
2. How is the map created?
The map is created using a combination of data sources, including satellite imagery, aerial photographs, and field surveys. These data are analyzed and integrated to create a detailed representation of vegetation patterns across the United States.
3. What are the different vegetation types represented on the map?
The map depicts a wide range of vegetation types, including forests, grasslands, deserts, wetlands, and tundra. Each type is characterized by unique plant communities and is influenced by factors like climate, soil, and topography.
4. How is the map used in conservation efforts?
The map provides valuable information for identifying areas with high biodiversity, mapping critical habitats for wildlife, and monitoring changes in vegetation patterns over time. This information is crucial for prioritizing conservation efforts and protecting vulnerable ecosystems.
5. What are the implications of climate change for vegetation patterns?
Climate change is altering vegetation distribution and composition, leading to changes in plant communities and ecosystem structure. The map can be used to monitor these changes and inform adaptation strategies.
Tips for Using the United States Vegetation Map Effectively
- Explore the map interactively: Many online resources provide interactive versions of the map, allowing you to zoom in on specific areas and explore different vegetation types in detail.
- Combine the map with other data: The map can be integrated with other data sources, such as climate data, soil maps, and wildlife distribution maps, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of ecological relationships.
- Use the map for educational purposes: The map can be used in classrooms, community centers, and other settings to engage the public in environmental issues and promote responsible stewardship of natural resources.
- Stay informed about updates: The United States Vegetation Map is constantly being updated and refined as new data becomes available. It’s essential to stay informed about the latest versions of the map to access the most accurate information.
Conclusion: A Visual Tapestry of Life and a Guide for the Future
The United States Vegetation Map is a powerful tool for understanding the intricate web of plant life across the country. It provides a visual representation of biodiversity, highlights the importance of conservation, and informs resource management decisions. As we face the challenges of climate change and other environmental threats, the map serves as a vital guide for protecting our natural heritage and ensuring the sustainability of our ecosystems for generations to come. By understanding the dynamics of vegetation and utilizing the map effectively, we can work towards a future where our diverse plant communities thrive and continue to enrich our lives.
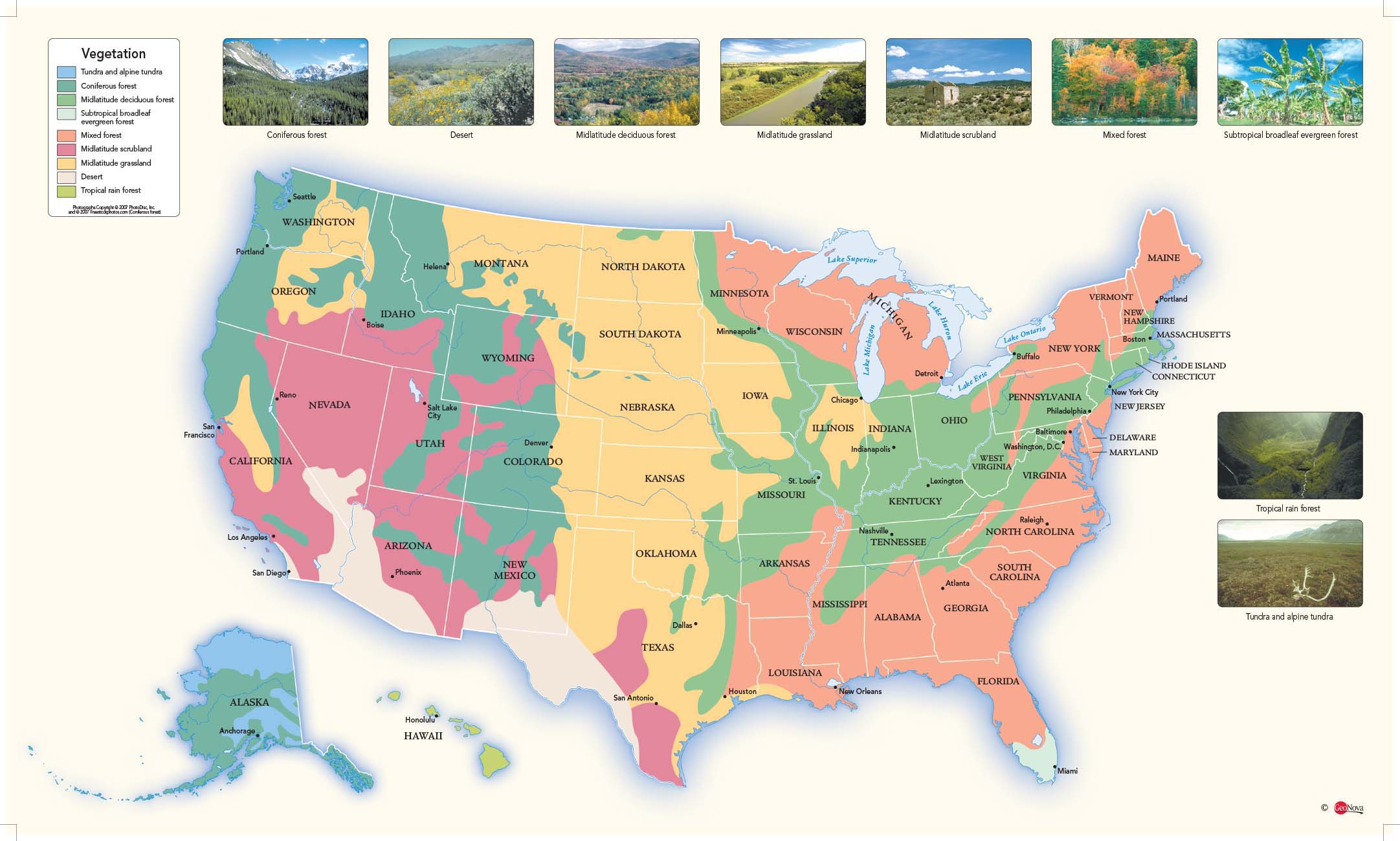



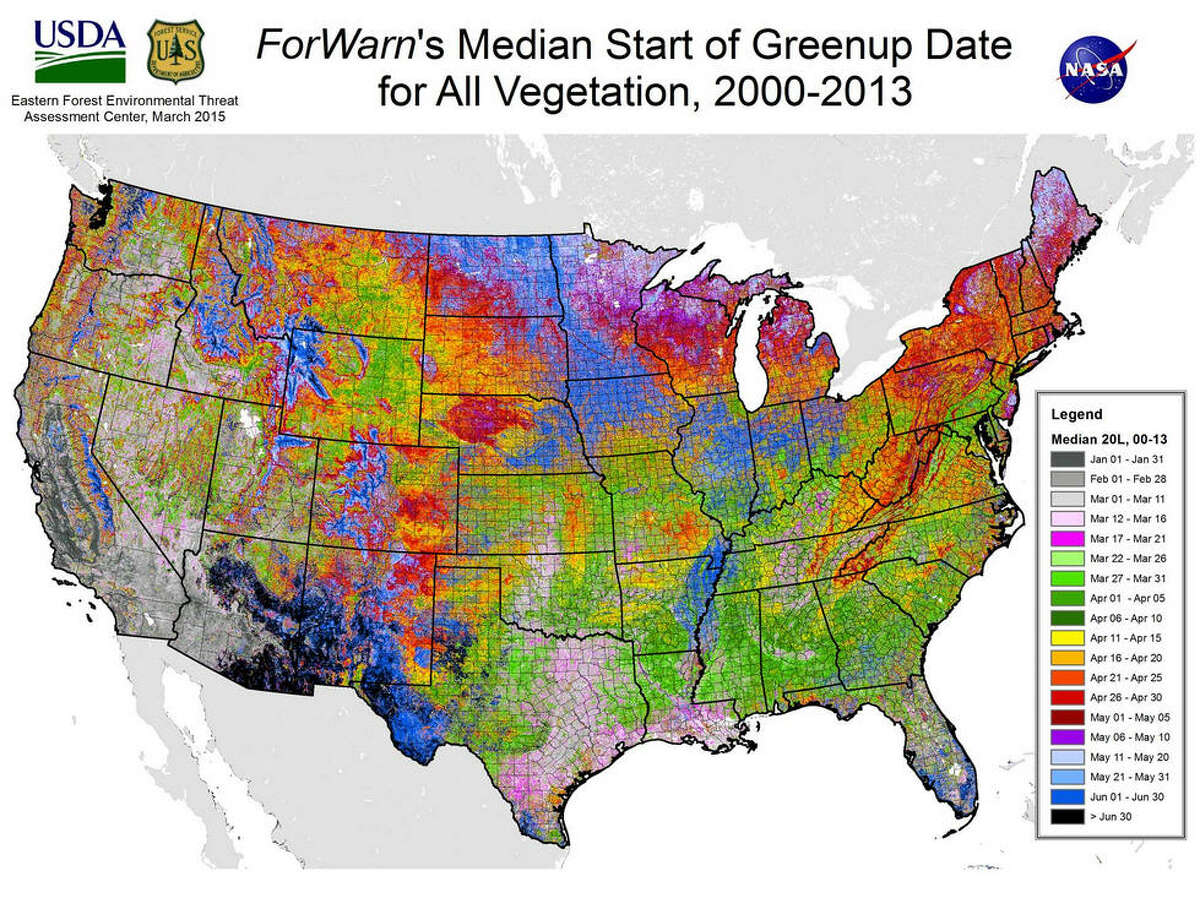

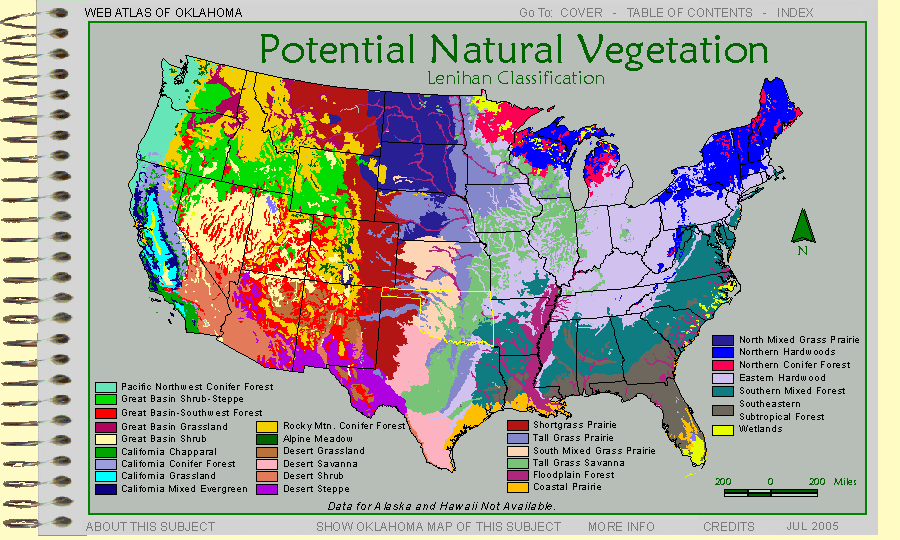

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Tapestry of Life: Exploring the United States Vegetation Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!