Unveiling the Secrets of the Savanna: A Comprehensive Guide to the Biome Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of the Savanna: A Comprehensive Guide to the Biome Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of the Savanna: A Comprehensive Guide to the Biome Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of the Savanna: A Comprehensive Guide to the Biome Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Secrets of the Savanna: A Comprehensive Guide to the Biome Map
- 3.1 Defining the Savanna Biome: A Landscape of Contrasts
- 3.2 The Importance of the Savanna Biome Map
- 3.3 Constructing the Savanna Biome Map: A Multifaceted Approach
- 3.4 Applications of the Savanna Biome Map: A Tool for Conservation and Management
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the Savanna Biome Map
- 3.6 Tips for Using Savanna Biome Maps
- 3.7 Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Understanding and Protecting a Vital Ecosystem
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Secrets of the Savanna: A Comprehensive Guide to the Biome Map
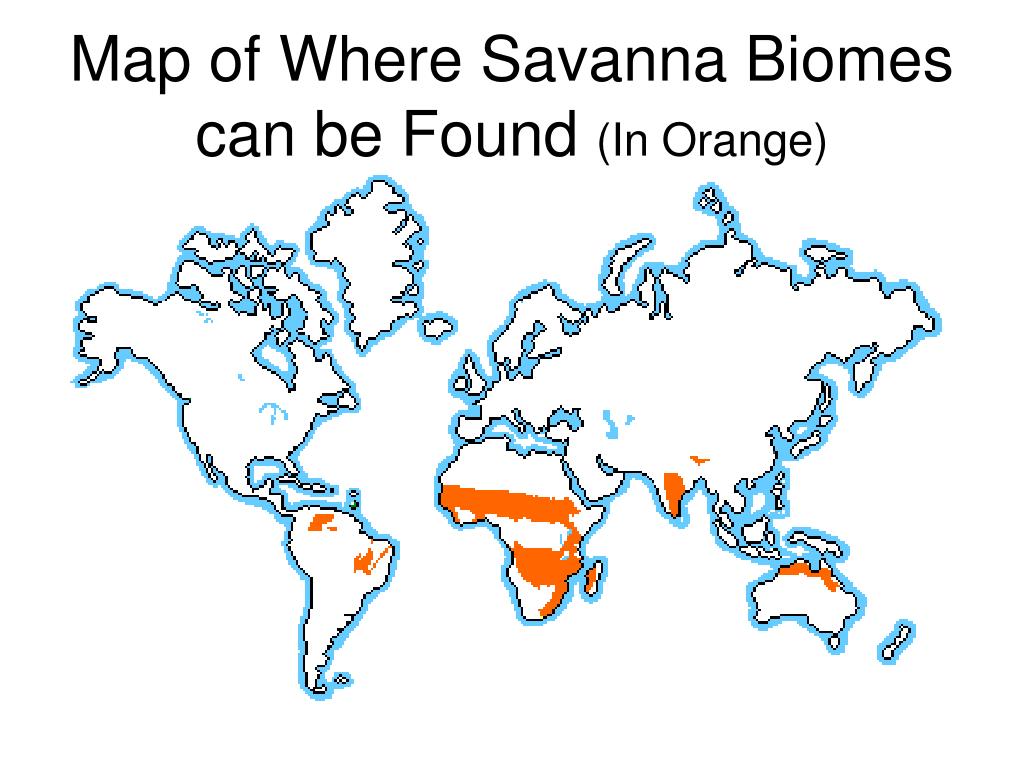
The savanna, a vast expanse of grassland dotted with scattered trees, occupies a significant portion of the Earth’s surface. This biome, characterized by its distinct climate, vegetation, and diverse wildlife, is a vital component of the global ecosystem. Understanding the distribution and characteristics of savannas is crucial for conservation efforts, sustainable resource management, and scientific research. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of the savanna biome map, exploring its significance, construction, and applications.
Defining the Savanna Biome: A Landscape of Contrasts
The savanna biome is defined by a unique combination of factors, including:
- Climate: Savannas experience a distinct wet and dry season, with rainfall concentrated in a specific period. The dry season can be harsh, characterized by low humidity and the threat of wildfires.
- Vegetation: Grasslands dominate the savanna landscape, with scattered trees and shrubs providing pockets of shade and habitat. The type of vegetation varies depending on rainfall patterns and soil conditions.
- Wildlife: Savannas are renowned for their diverse and abundant wildlife, including large mammals like lions, elephants, giraffes, and zebras, as well as a variety of birds, reptiles, and insects.
The Importance of the Savanna Biome Map
The savanna biome map serves as a crucial tool for understanding and managing this vital ecosystem. It provides a visual representation of the global distribution of savannas, highlighting key features such as:
- Geographic boundaries: The map delineates the precise locations of savanna biomes across continents, offering a clear understanding of their extent.
- Vegetation patterns: Different types of savanna vegetation, such as tall-grass, short-grass, and acacia woodlands, are depicted on the map, providing insights into the variations within the biome.
- Climate data: The map can incorporate climate data, such as rainfall patterns and temperature fluctuations, offering a deeper understanding of the factors driving savanna ecosystems.
- Biodiversity hotspots: Areas with high levels of biodiversity are often highlighted on the map, identifying regions requiring special conservation attention.
Constructing the Savanna Biome Map: A Multifaceted Approach
The creation of a savanna biome map involves a complex process that combines various data sources and analytical techniques:
- Remote sensing: Satellite imagery and aerial photographs provide detailed information on vegetation cover, land use, and other environmental factors.
- Field surveys: Direct observations and measurements in the field are essential for validating and refining data collected through remote sensing.
- Climate models: Computer simulations are used to predict future changes in climate patterns, providing valuable insights for understanding the potential impact on savanna ecosystems.
- Species distribution models: These models analyze the relationship between environmental factors and the distribution of specific plant and animal species, helping to map biodiversity hotspots.
Applications of the Savanna Biome Map: A Tool for Conservation and Management
The savanna biome map has numerous applications across various fields, including:
- Conservation planning: The map helps identify areas of high conservation value, guiding efforts to protect endangered species and preserve biodiversity.
- Sustainable resource management: It assists in the management of natural resources, ensuring their sustainable use and preventing overexploitation.
- Climate change mitigation: The map provides data for understanding the potential impacts of climate change on savanna ecosystems, enabling informed decision-making for adaptation and mitigation strategies.
- Scientific research: The map serves as a valuable tool for scientists studying the ecology, biodiversity, and evolution of savanna ecosystems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the Savanna Biome Map
1. What are the major savanna regions of the world?
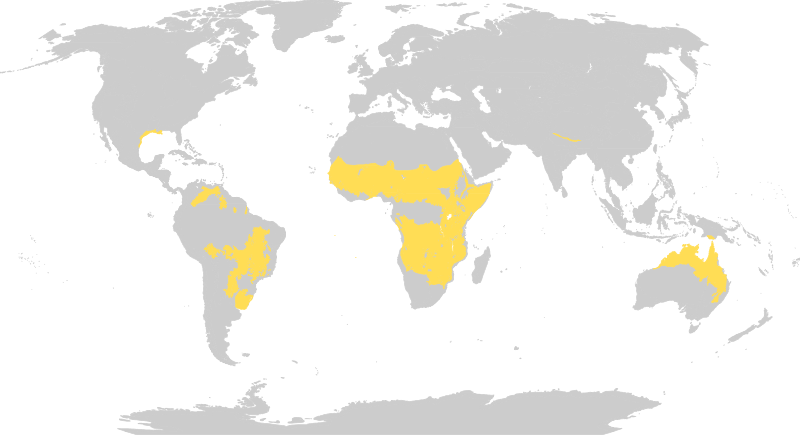
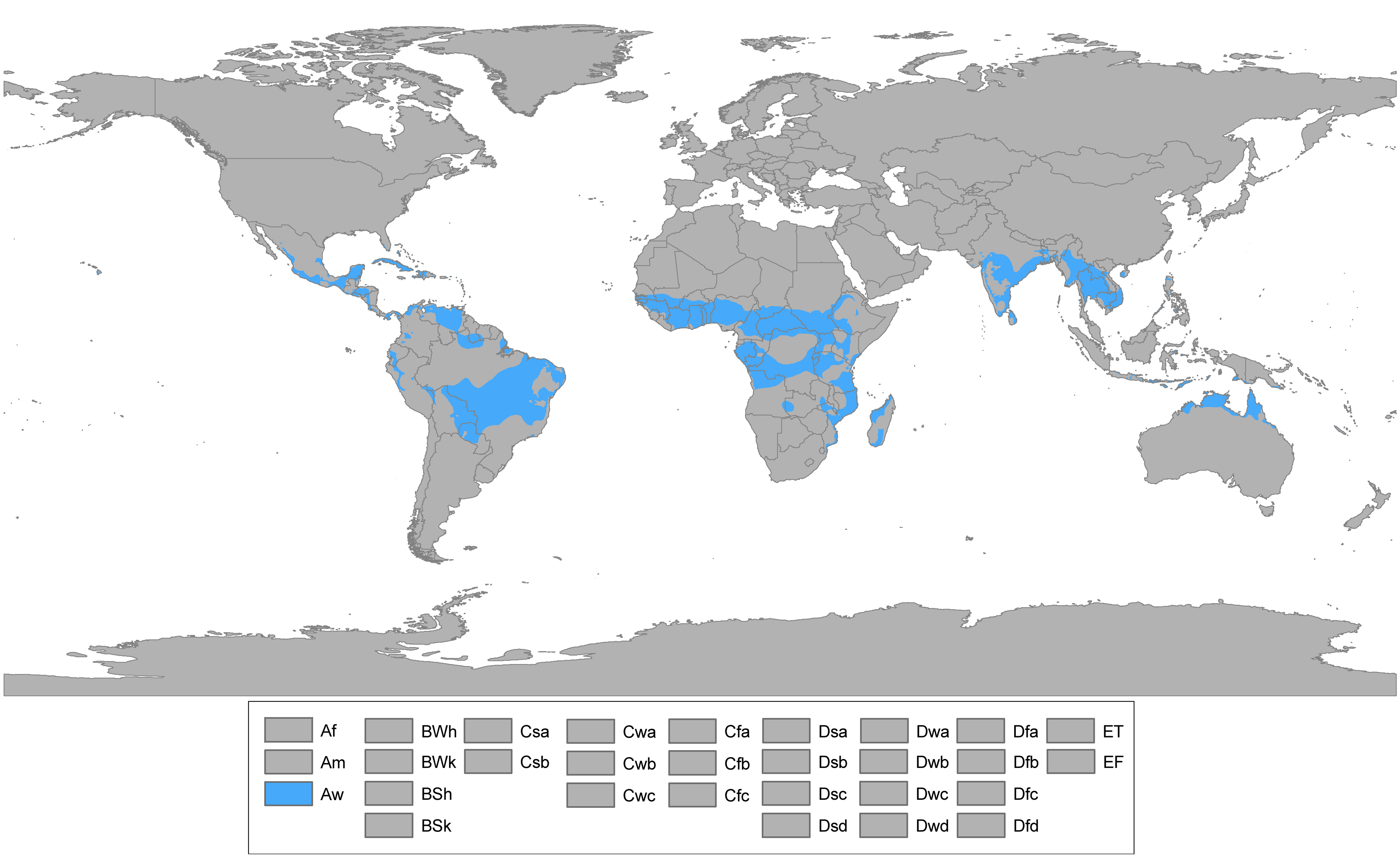
The savanna biome is found on all continents except Antarctica, with major regions located in:
- Africa: The African savanna is the largest and most well-known, stretching across vast areas of eastern and southern Africa.
- South America: The cerrado region of Brazil is a significant savanna biome, characterized by its unique plant and animal life.
- Australia: The Australian savanna is characterized by its diverse flora and fauna, including unique species found nowhere else.
- Asia: Savannas occur in parts of India, Southeast Asia, and southern China.
- North America: The tallgrass prairie of North America is a remnant of a once vast savanna ecosystem.
2. How do savanna biome maps help protect endangered species?
By identifying areas of high biodiversity and the distribution of endangered species, savanna biome maps provide crucial information for conservation efforts. This data helps prioritize areas for protection, establish protected areas, and develop targeted conservation strategies.
3. How can savanna biome maps be used to manage wildfires?
Savanna ecosystems are prone to wildfires, which can be both destructive and beneficial. The map provides valuable information about fire-prone areas, allowing for targeted fire management strategies to mitigate risks and promote healthy ecosystems.
4. What are the challenges in creating accurate savanna biome maps?
Creating accurate savanna biome maps is a complex task that faces numerous challenges, including:
- Data availability: Access to reliable and comprehensive data, especially for remote areas, can be limited.
- Spatial resolution: The resolution of available data can affect the accuracy of the map, especially for small-scale features.
- Dynamic nature of ecosystems: Savanna ecosystems are dynamic and constantly changing, making it difficult to capture their precise state at any given time.
Tips for Using Savanna Biome Maps
- Understand the map’s limitations: Be aware of the data sources, methods used, and potential inaccuracies in the map.
- Consider multiple sources: Combine information from different maps and data sources to gain a more complete picture.
- Consult with experts: Seek advice from experts in savanna ecology and conservation for interpretation and application of the map.
- Stay informed: Keep abreast of advancements in mapping technologies and new data sources to ensure you are using the most up-to-date information.
Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Understanding and Protecting a Vital Ecosystem
The savanna biome map is a powerful tool for understanding, managing, and protecting this vital ecosystem. It provides a visual representation of the global distribution of savannas, highlighting key features, biodiversity hotspots, and areas requiring conservation attention. By leveraging the information provided by the map, researchers, conservationists, and policymakers can make informed decisions to ensure the long-term health and sustainability of savanna ecosystems for generations to come.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of the Savanna: A Comprehensive Guide to the Biome Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!