Unveiling the Global Tapestry of Temperature: A Comprehensive Look at Average Temperature Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Global Tapestry of Temperature: A Comprehensive Look at Average Temperature Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Global Tapestry of Temperature: A Comprehensive Look at Average Temperature Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Global Tapestry of Temperature: A Comprehensive Look at Average Temperature Maps
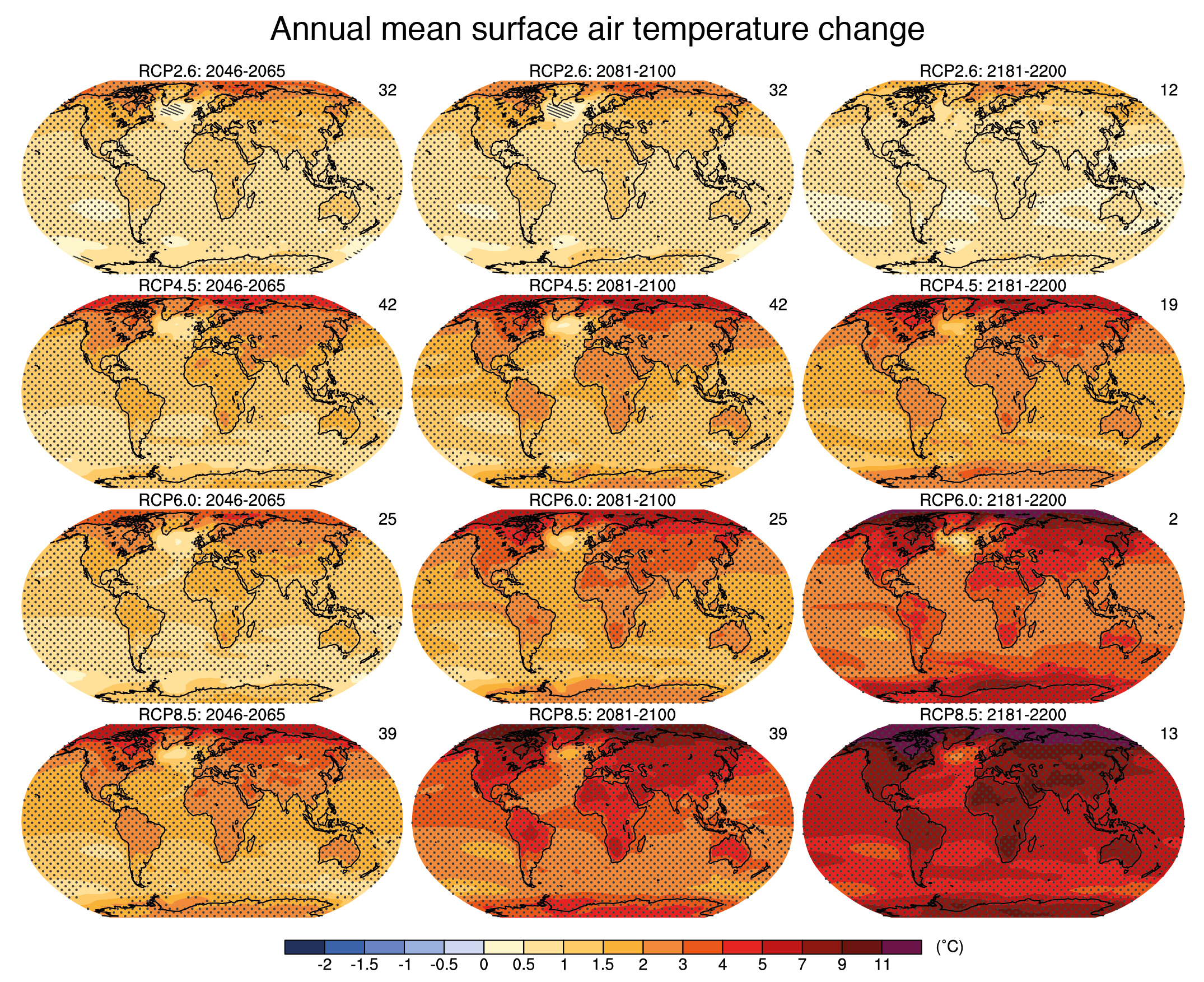
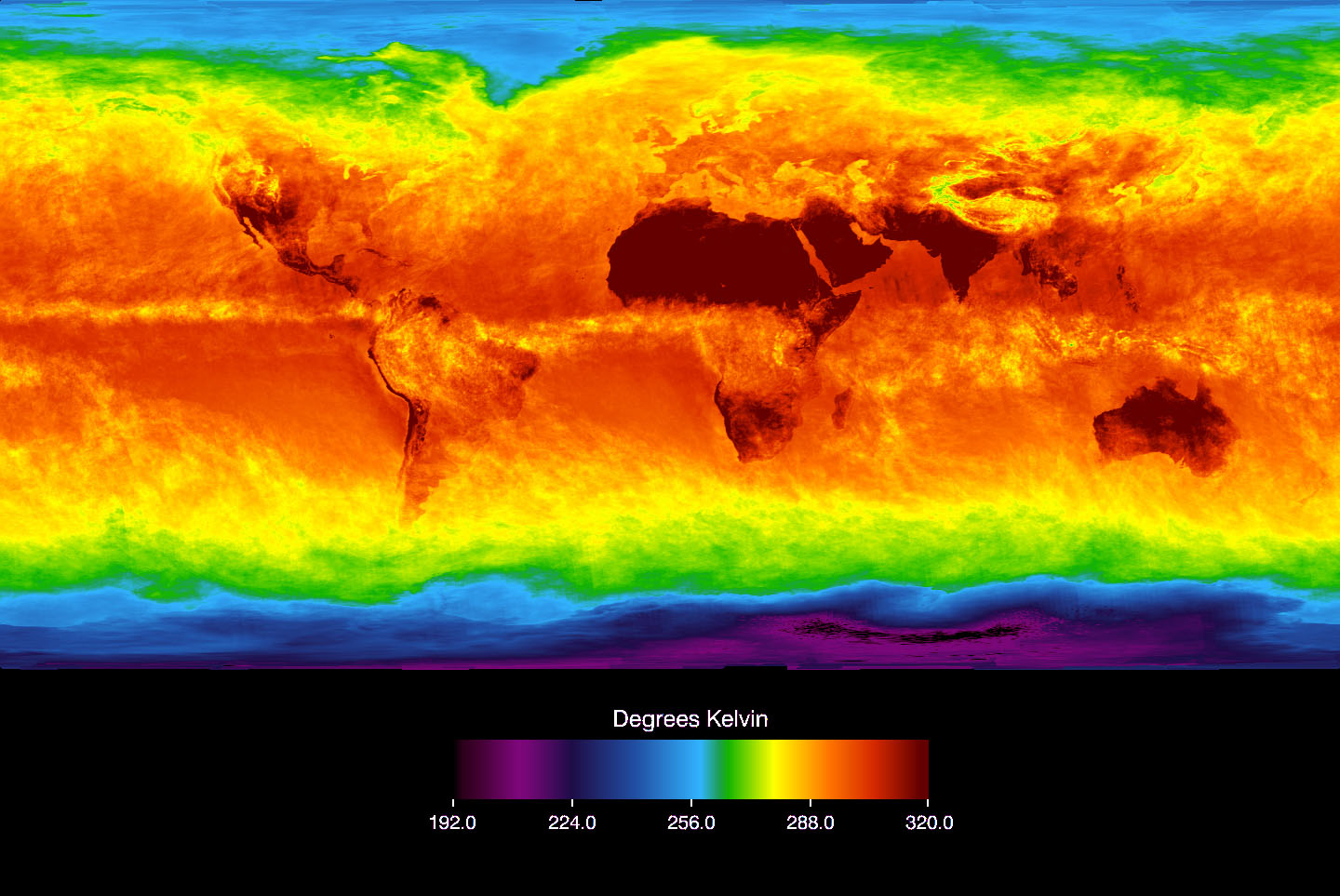
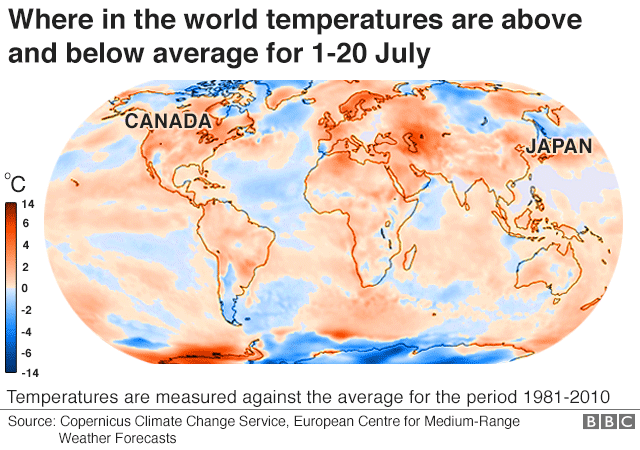
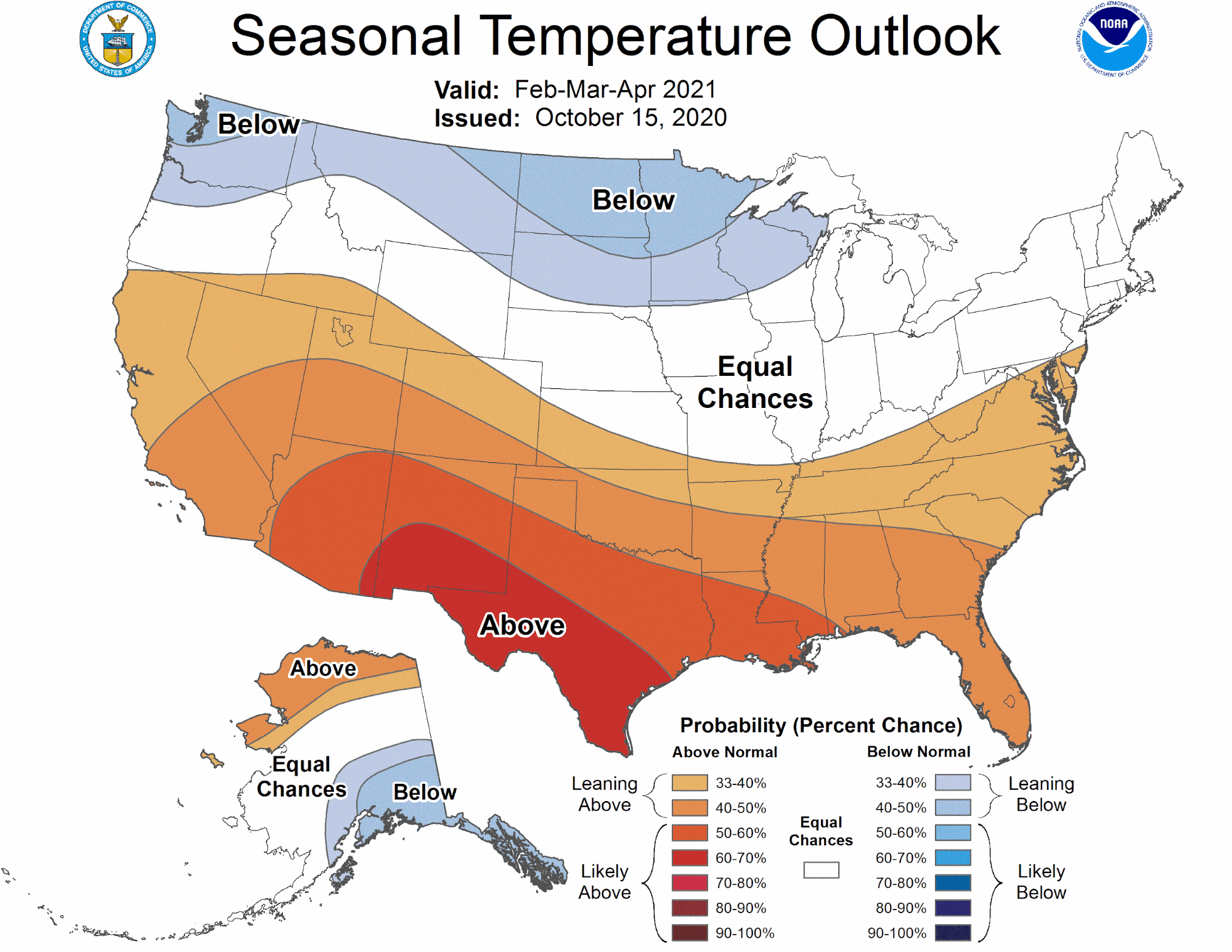
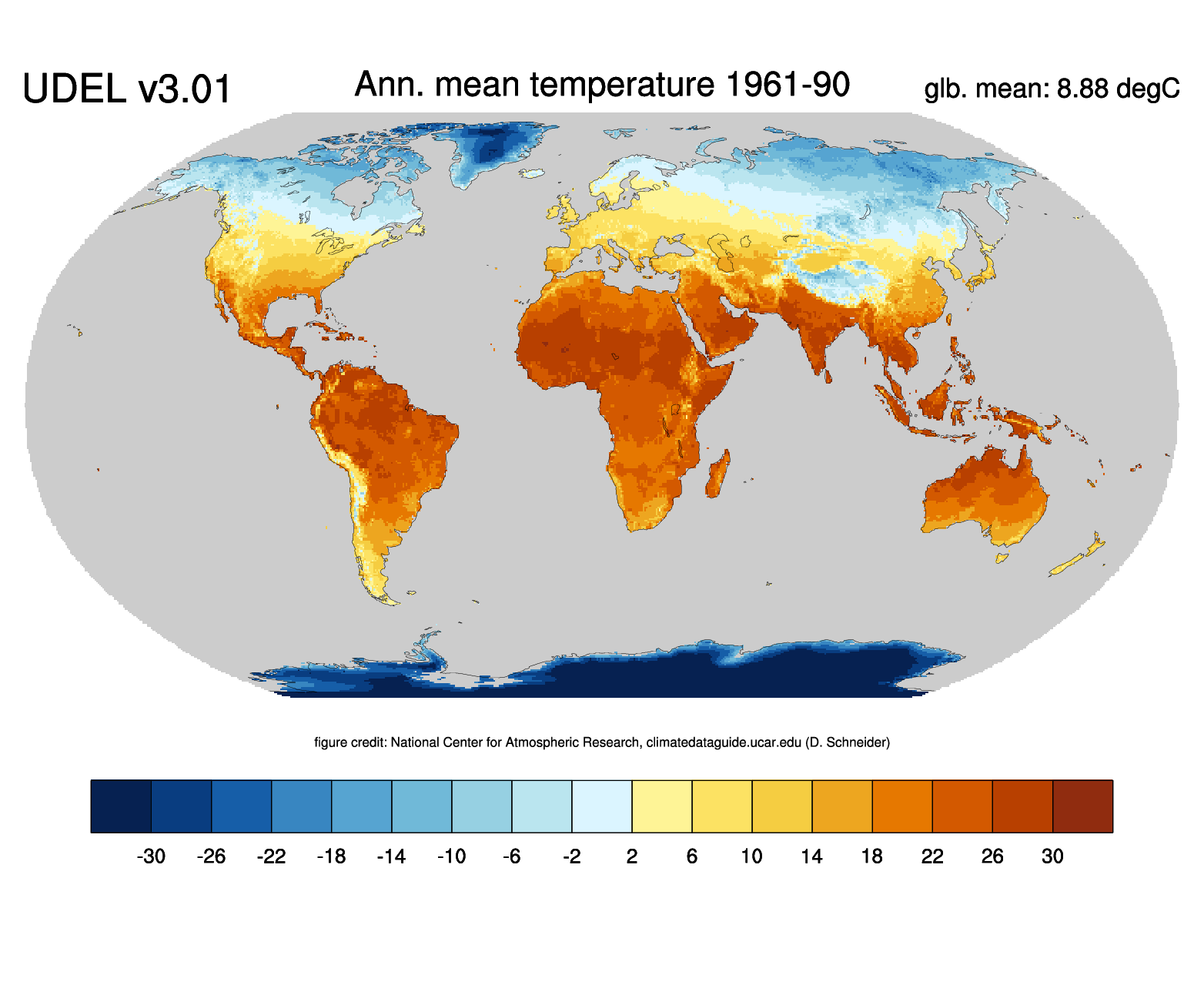
Our planet Earth, a vibrant and dynamic sphere, pulsates with a myriad of climates, each unique and contributing to the intricate tapestry of life. Understanding the distribution of temperature across the globe is paramount to comprehending the intricate interplay of weather patterns, ecological systems, and human societies. This is where average temperature maps, powerful visual tools, come into play.
Delving into the Essence of Average Temperature Maps
Average temperature maps, often referred to as global temperature maps, represent a snapshot of Earth’s thermal landscape. They depict the average temperature for a specific period, usually a year or a month, across different regions of the globe. These maps are meticulously constructed using data gathered from numerous meteorological stations, satellites, and climate models. They provide a valuable visual representation of the global temperature distribution, highlighting areas of warmth and cold, and revealing the intricate interplay of factors influencing these variations.
Factors Shaping the Global Temperature Landscape
The average temperature map is not a static entity but rather a dynamic reflection of the complex interplay of several factors, including:
-
Latitude: The Earth’s spherical shape and its tilt on its axis lead to unequal distribution of solar radiation. Regions closer to the equator receive more direct sunlight, resulting in higher temperatures, while regions closer to the poles experience colder temperatures due to less direct sunlight.
-
Altitude: As altitude increases, air pressure decreases, resulting in a decrease in temperature. This explains why mountainous regions generally experience lower temperatures than surrounding lowlands.
-
Ocean Currents: Ocean currents act as conveyor belts, transporting heat from warmer regions to colder regions. This influences the temperature distribution along coastlines and contributes to the formation of unique microclimates.
-
Landmasses and Water Bodies: Land heats up and cools down faster than water. This difference in heat capacity leads to temperature variations between continental and oceanic regions. Coastal areas tend to experience milder temperatures due to the moderating influence of the ocean.
-
Cloud Cover: Clouds reflect incoming solar radiation, reducing the amount of heat reaching the Earth’s surface. This leads to cooler temperatures in areas with significant cloud cover.
-
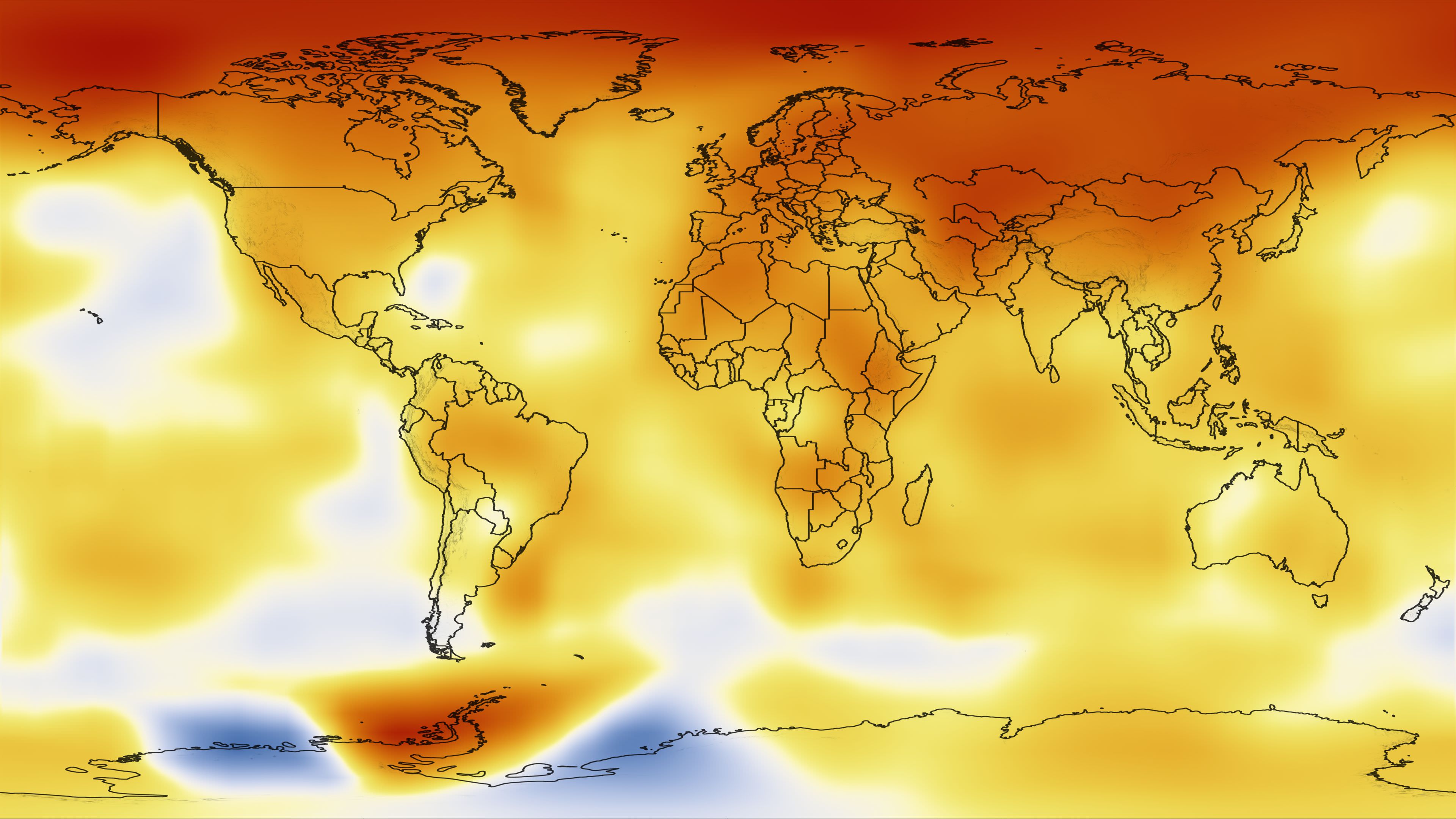
Human Activities: Human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, contribute to the release of greenhouse gases, leading to a gradual warming of the planet. This phenomenon, known as climate change, is altering the average temperature patterns across the globe, leading to more extreme weather events and shifts in regional climates.
The Significance of Average Temperature Maps
Average temperature maps serve as vital tools for various disciplines and applications, including:
-
Climate Science: These maps provide crucial insights into long-term temperature trends, helping scientists understand the dynamics of climate change, its impacts on various ecosystems, and the development of mitigation strategies.
-
Meteorology: Meteorologists rely on average temperature maps to analyze weather patterns, predict future weather conditions, and issue warnings for extreme weather events.
-
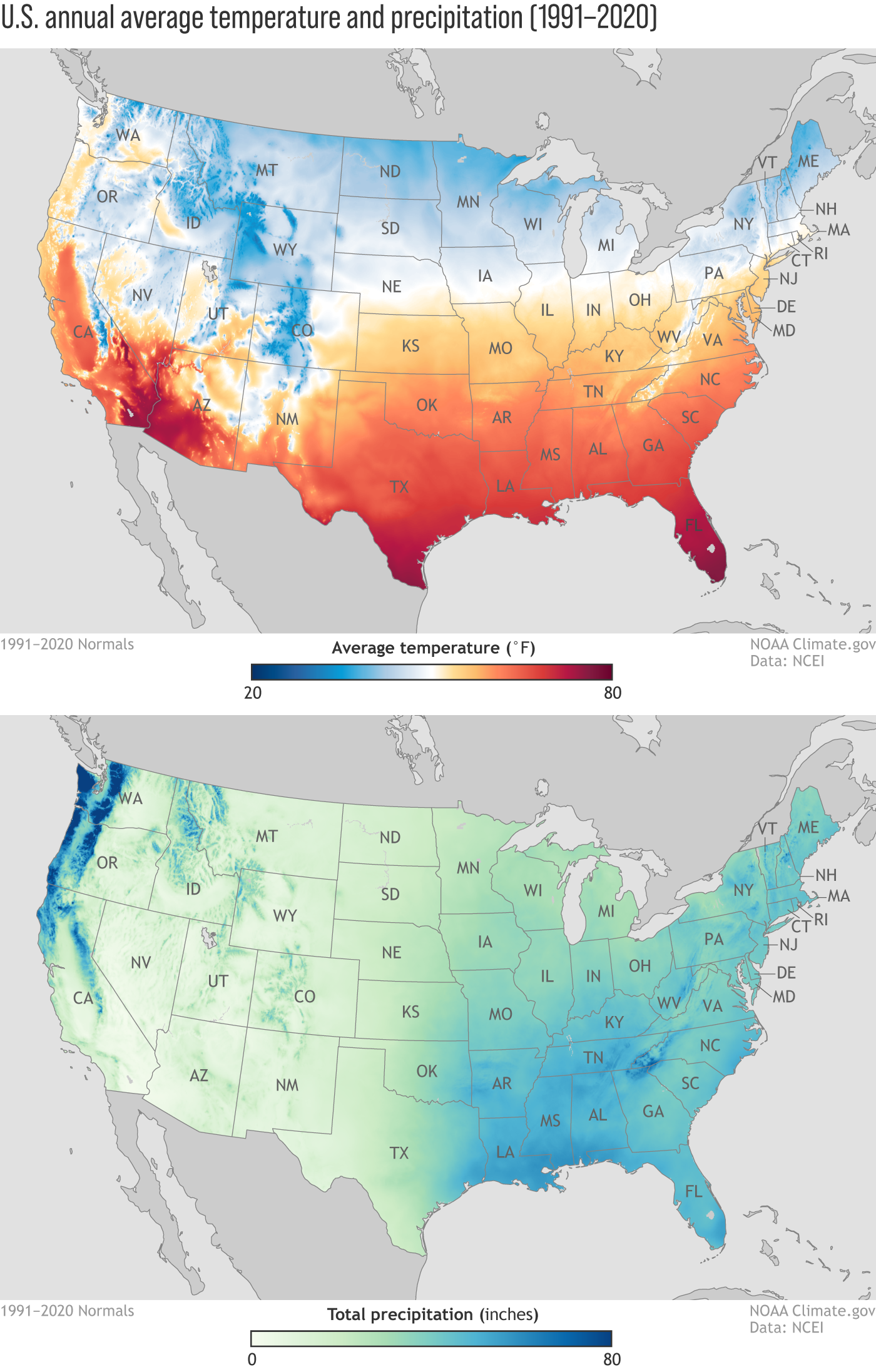
Agriculture: Farmers utilize these maps to determine suitable growing seasons and crop varieties for their regions, optimizing agricultural practices for maximum yield and resilience.
-
Urban Planning: Planners use average temperature maps to assess the urban heat island effect, a phenomenon where urban areas experience higher temperatures than surrounding rural areas due to the presence of concrete and asphalt. This information helps in developing sustainable urban designs that minimize heat stress and improve livability.
-
Public Health: Average temperature maps are essential for understanding the spread of infectious diseases, as temperature plays a crucial role in the survival and transmission of pathogens. This knowledge is crucial for public health initiatives aimed at disease prevention and control.
-
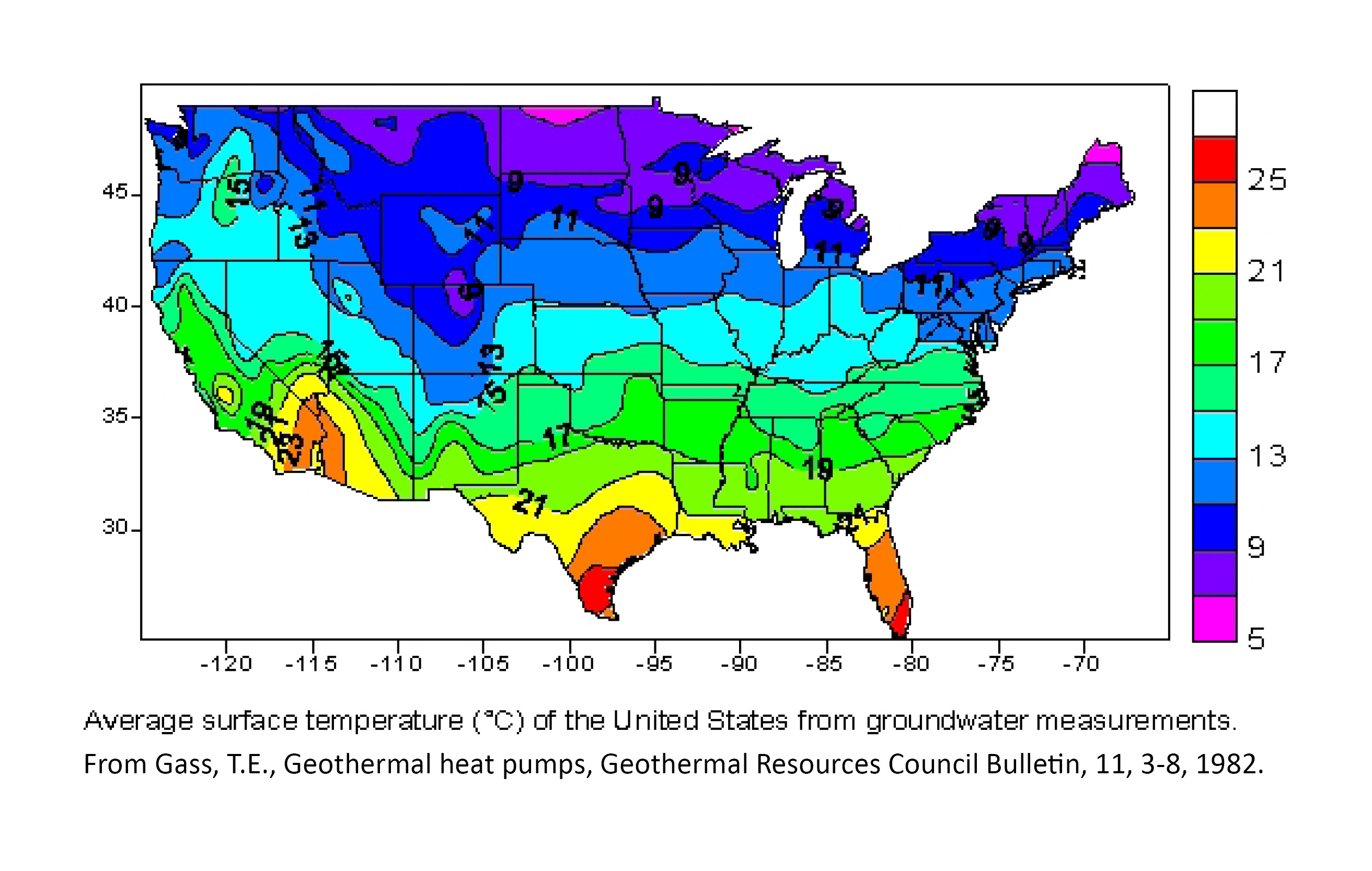
Resource Management: Understanding the distribution of temperature helps in managing water resources, as temperature influences evaporation rates and precipitation patterns. This information is critical for optimizing water use and ensuring sustainable water management practices.
-
Tourism and Recreation: Average temperature maps are valuable for tourism and recreation industries, helping travelers choose destinations based on their preferred temperature range and climate conditions.
Understanding the Nuances of Average Temperature Maps
While average temperature maps offer a valuable representation of global temperature patterns, it’s crucial to understand their limitations:
-
Spatial Resolution: The accuracy of these maps depends on the density and distribution of meteorological stations and data sources. Regions with limited data coverage may have less accurate temperature representations.
-
Temporal Resolution: Average temperature maps typically represent data for a specific period, usually a year or a month. They do not capture short-term variations in temperature, such as daily fluctuations or extreme weather events.
-
Averaging Effects: Average temperature maps represent mean values, masking the variability of temperature within a region. This can lead to misinterpretations, as a single average value might not accurately reflect the actual temperature range experienced in a specific location.
FAQs about Average Temperature Maps
Q: How are average temperature maps created?
A: Average temperature maps are created using a combination of data from meteorological stations, satellites, and climate models. These data sources provide information on temperature measurements at different locations and time periods. The data is then processed and analyzed using statistical methods to create a map representing the average temperature for a specific period.
Q: What are the different types of average temperature maps?
A: There are various types of average temperature maps, including:
-
Annual average temperature maps: These maps depict the average temperature for a specific year, providing a comprehensive overview of the global temperature distribution.
-
Monthly average temperature maps: These maps show the average temperature for a particular month, allowing for the analysis of seasonal temperature variations.
-
Historical average temperature maps: These maps depict the average temperature over a specific period, such as decades or centuries, helping to understand long-term temperature trends.
-
Projected average temperature maps: These maps utilize climate models to predict future average temperature scenarios based on different emission scenarios and climate change projections.
Q: What are the benefits of using average temperature maps?
A: Average temperature maps offer numerous benefits, including:
-
Understanding climate patterns: They provide a visual representation of the global temperature distribution, revealing patterns and variations across different regions.
-
Assessing climate change impacts: They help to track long-term temperature trends, identifying areas experiencing significant warming or cooling and assessing the potential impacts of climate change.
-
Supporting decision-making: They provide valuable information for various sectors, including agriculture, urban planning, public health, and resource management, enabling informed decision-making.
Q: What are the limitations of average temperature maps?
A: While average temperature maps provide valuable insights, they have limitations, including:
-
Spatial resolution: The accuracy of these maps depends on the density and distribution of data sources. Areas with limited data coverage may have less accurate temperature representations.
-
Temporal resolution: Average temperature maps represent data for a specific period, not capturing short-term variations in temperature.
-
Averaging effects: Average temperature maps represent mean values, masking the variability of temperature within a region.
Tips for Interpreting Average Temperature Maps
-
Consider the time period: Understand the period for which the average temperature is calculated, as it can influence the data interpretation.
-
Pay attention to the units: Ensure you understand the units used to represent temperature (Celsius, Fahrenheit, etc.) to interpret the data accurately.
-
Look for patterns: Analyze the map for patterns in temperature distribution, identifying areas of high and low temperatures, and potential factors contributing to these variations.
-
Compare with other data: Combine average temperature maps with other data sources, such as precipitation maps, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of climate patterns.
Conclusion
Average temperature maps serve as invaluable tools for comprehending the global thermal landscape, revealing the intricate interplay of factors shaping Earth’s climate and highlighting the dynamic nature of our planet. By providing a visual representation of average temperature patterns, these maps empower us to understand the complexities of climate change, its impact on various ecosystems, and the need for informed decision-making to mitigate its effects and ensure a sustainable future for our planet.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Global Tapestry of Temperature: A Comprehensive Look at Average Temperature Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!