Unveiling Spatial Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Tableau Map Visualization
Related Articles: Unveiling Spatial Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Tableau Map Visualization
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Spatial Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Tableau Map Visualization. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling Spatial Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Tableau Map Visualization
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling Spatial Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Tableau Map Visualization
- 3.1 The Power of Spatial Data Visualization
- 3.2 Understanding the Building Blocks of Tableau Maps
- 3.3 The Advantages of Tableau Map Visualization
- 3.4 Applications of Tableau Map Visualization
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions about Tableau Map Visualization
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Tableau Map Visualization
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unveiling Spatial Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Tableau Map Visualization
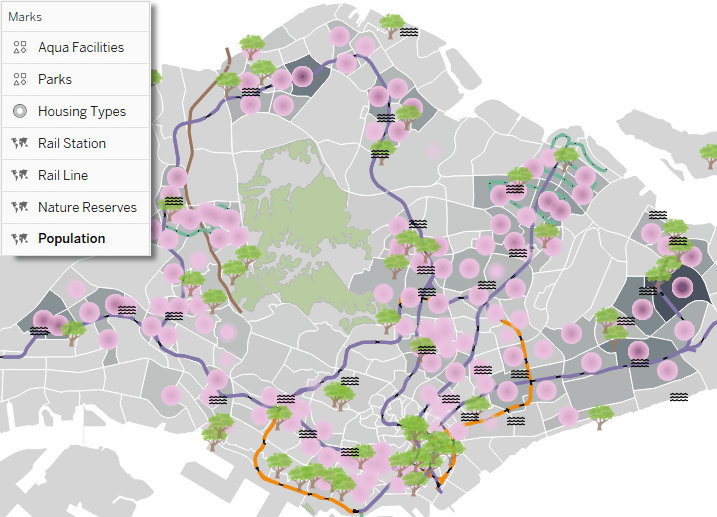
In the realm of data visualization, maps hold a unique power. They provide a natural and intuitive way to understand spatial relationships, patterns, and trends. Tableau, a leading data visualization platform, empowers users to harness this power through its robust map visualization capabilities. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of Tableau map visualization, exploring its functionality, benefits, and applications.
The Power of Spatial Data Visualization
Map visualization in Tableau goes beyond simply plotting data points on a map. It enables users to:
- Visualize geographic distributions: Identify areas of high or low concentration for various metrics, such as sales, customer demographics, or disease prevalence.
- Explore spatial relationships: Analyze how data points interact with each other based on their geographic location, revealing clusters, outliers, and potential correlations.
- Create interactive maps: Allow users to zoom in, pan, and filter data on the map, enabling deeper exploration and customized insights.
- Present compelling narratives: Leverage maps to effectively communicate complex data stories, making them more engaging and accessible to audiences.
Understanding the Building Blocks of Tableau Maps
Tableau offers a range of tools and features to create effective map visualizations. Here’s a breakdown of key elements:
1. Geographic Data: The foundation of any Tableau map is the underlying geographic data. This can be:
- Geocoded Data: Data with latitude and longitude coordinates, enabling direct plotting on a map.
- Spatial Data: Data associated with geographic shapes, such as countries, states, counties, or zip codes.
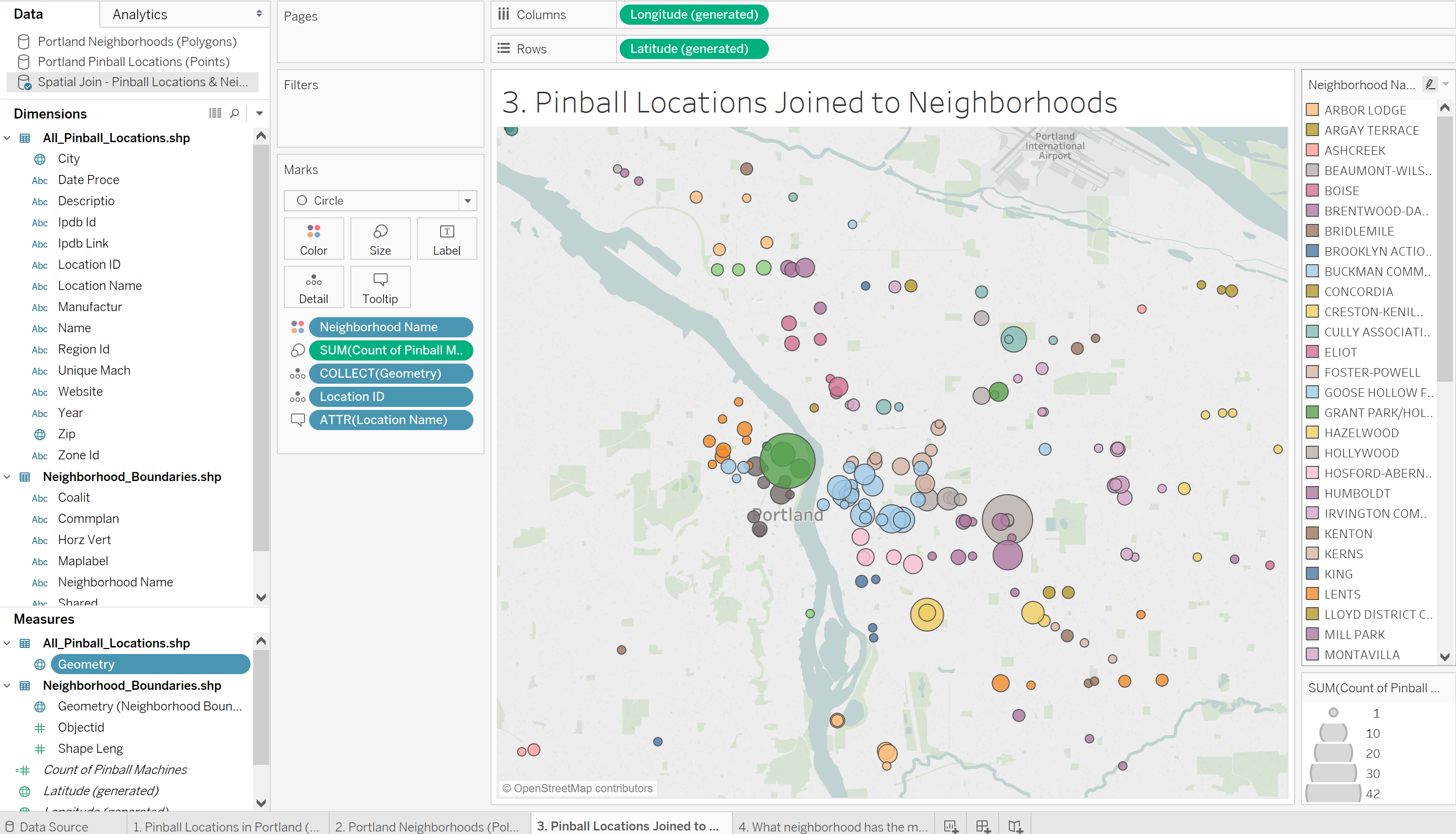
- Shapefiles: Geospatial data files containing geographic boundaries and attributes, often used for creating custom maps.
2. Map Types: Tableau provides a variety of map types, each suited for different visualization needs:
- Choropleth Maps: Represent data values using color gradients across geographic regions, highlighting areas with high or low values.
- Symbol Maps: Use different symbols to represent data points, allowing for visual differentiation based on size, color, or shape.
- Heat Maps: Show data density using a gradient of colors, revealing areas of high concentration.
- Bubble Maps: Represent data values with circles of varying sizes, providing a visual indication of relative magnitude.
3. Map Layers: Tableau allows users to create layers on their maps, providing context and depth to the visualization. This includes:
- Base Maps: Background maps providing geographic context, such as roads, water bodies, or political boundaries.
- Data Layers: Layers displaying the actual data, using different map types as described above.
- Overlay Layers: Additional layers for showcasing supplementary information, such as images, labels, or annotations.
4. Interactive Elements: Tableau empowers users to create interactive maps, enabling users to explore data dynamically:
- Filtering: Users can filter data based on geographic regions, values, or other criteria, revealing specific patterns or insights.
- Tooltips: Display detailed information about data points when hovering over them, providing context and additional data.
- Drill Down: Zoom in on specific regions of the map to explore data at a more granular level.
- Legends: Provide clear explanations of the colors, symbols, or other visual elements used in the map.
The Advantages of Tableau Map Visualization
The power of Tableau map visualization lies in its ability to unlock valuable insights from spatial data. Here are some key benefits:
- Enhanced Data Understanding: Visualizing data geographically provides a more intuitive understanding of spatial relationships, patterns, and trends.
- Improved Decision Making: Maps help identify areas of opportunity, risk, or impact, enabling data-driven decisions based on location-specific information.
- Effective Communication: Maps provide a visually compelling way to communicate complex data stories, making them more engaging and accessible to audiences.
- Data Exploration: Tableau’s interactive map features allow users to explore data dynamically, revealing hidden patterns and uncovering new insights.
- Increased Efficiency: Visualizing data on a map can streamline analysis and decision-making processes, saving time and resources.
Applications of Tableau Map Visualization
Tableau map visualization finds applications across various domains, empowering data-driven insights in a variety of industries:
- Business: Analyze sales performance by region, identify high-potential customer segments, and optimize marketing campaigns based on geographic targeting.
- Healthcare: Track disease outbreaks, monitor patient demographics, and optimize resource allocation based on spatial patterns.
- Finance: Analyze investment opportunities, assess risk factors, and monitor market trends across different geographic regions.
- Government: Track population density, monitor infrastructure development, and assess the impact of policies on different communities.
- Education: Analyze student demographics, assess school performance, and identify areas requiring targeted interventions.
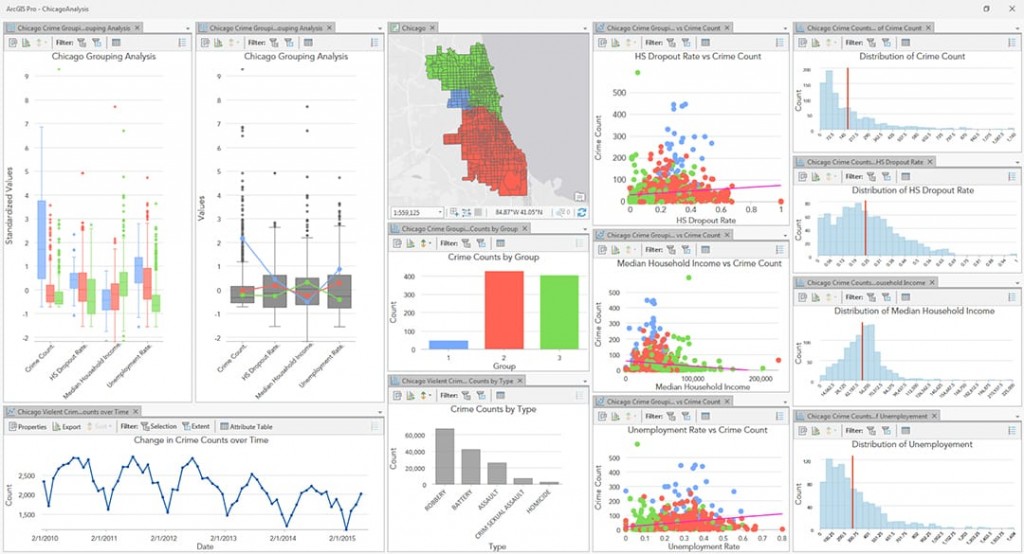
- Environmental Science: Track environmental changes, analyze pollution patterns, and monitor the impact of climate change on different regions.
Frequently Asked Questions about Tableau Map Visualization
1. What are the different map projections available in Tableau?
Tableau offers a variety of map projections, including Mercator, Albers, and Winkel Tripel. The choice of projection depends on the specific data and visualization requirements.
2. How can I create custom maps in Tableau?
Tableau allows users to create custom maps using shapefiles, enabling the visualization of specific geographic areas or boundaries not available in the default map library.
3. How can I incorporate external data into my Tableau maps?
Tableau supports connecting to various data sources, including databases, spreadsheets, and web services. Users can join external data with geographic data to create rich map visualizations.
4. What are some best practices for creating effective Tableau maps?
- Choose the appropriate map type: Select a map type that best represents the data and communicates the intended message.
- Use clear and concise labeling: Ensure that map labels are legible and provide relevant information.
- Apply appropriate color schemes: Use color palettes that are visually appealing and easy to interpret.
- Optimize for different screen sizes: Ensure that maps are responsive and display well on various devices.
- Consider accessibility: Design maps that are accessible to users with disabilities.
5. How can I share my Tableau map visualizations with others?
Tableau offers various options for sharing map visualizations, including publishing to Tableau Server or Tableau Public, embedding in websites, or exporting as images or interactive dashboards.
Tips for Effective Tableau Map Visualization
- Start with a clear objective: Determine the specific insights you want to communicate through your map visualization.
- Choose the right data: Ensure that the data used is relevant, accurate, and appropriate for the map type chosen.
- Experiment with different map types: Explore different map types to find the one that best represents your data and conveys your message effectively.
- Use color strategically: Choose colors that are visually appealing and clearly differentiate between data points.
- Keep it simple: Avoid overcrowding the map with too much information. Focus on highlighting key insights.
- Tell a story: Use the map to communicate a narrative and guide the audience through the data.
- Test and refine: Iterate on your map visualizations to ensure they are clear, engaging, and effective in communicating your message.
Conclusion
Tableau map visualization empowers users to unlock the power of spatial data, revealing hidden patterns, trends, and insights that would otherwise remain obscured. By leveraging the platform’s robust features and tools, users can create compelling and informative maps that facilitate data-driven decision making, enhance communication, and drive innovation across various industries. As data becomes increasingly geographically diverse, Tableau map visualization plays a crucial role in transforming spatial insights into actionable knowledge, shaping a future driven by data-informed decisions.
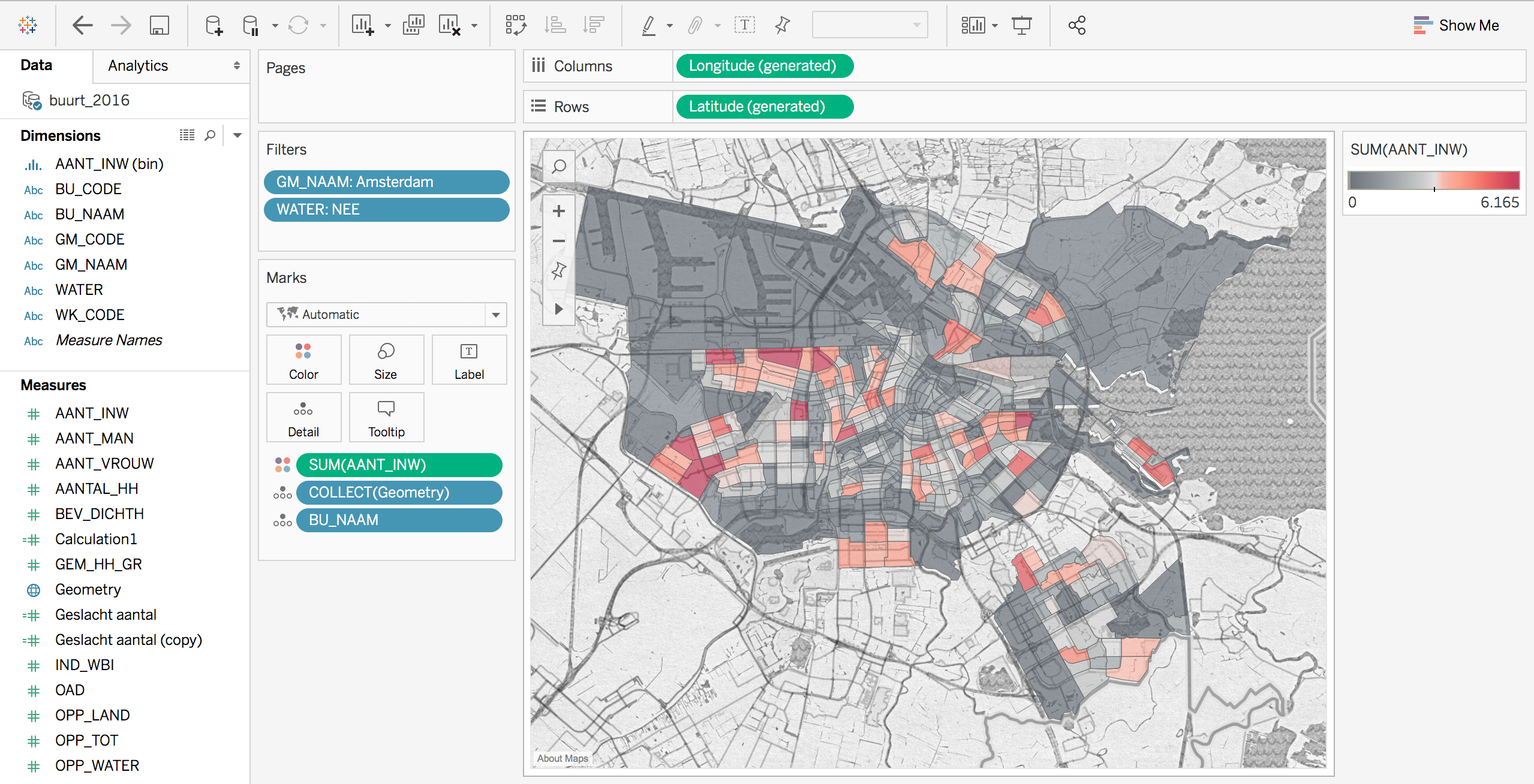
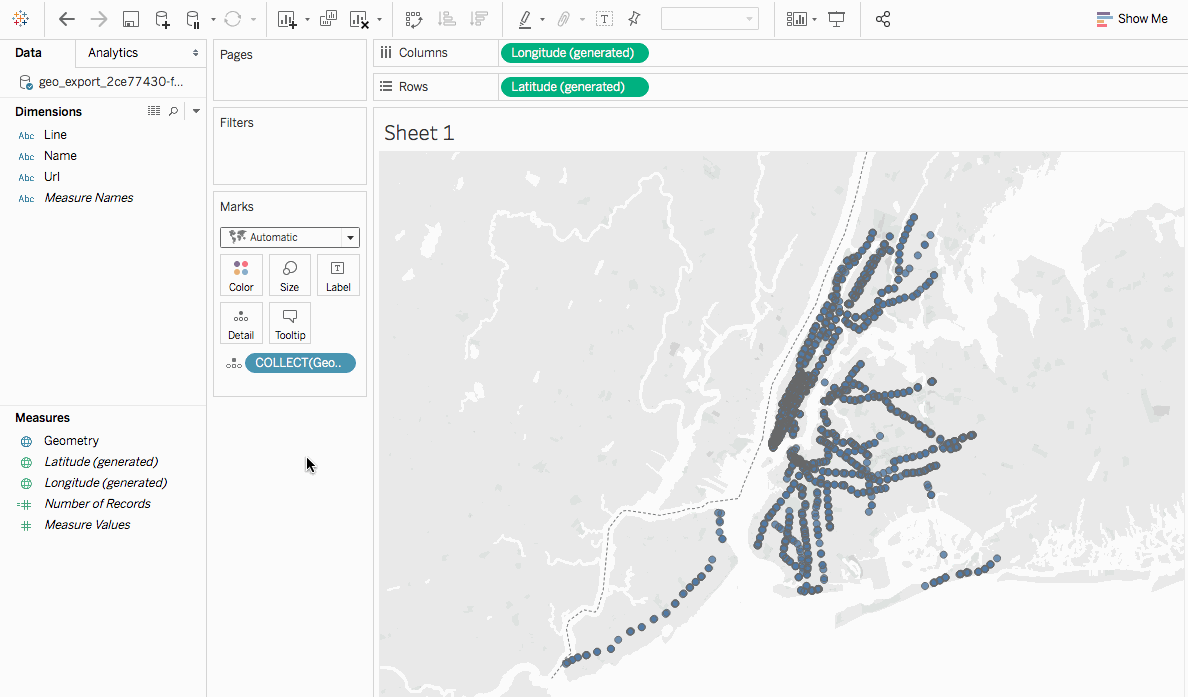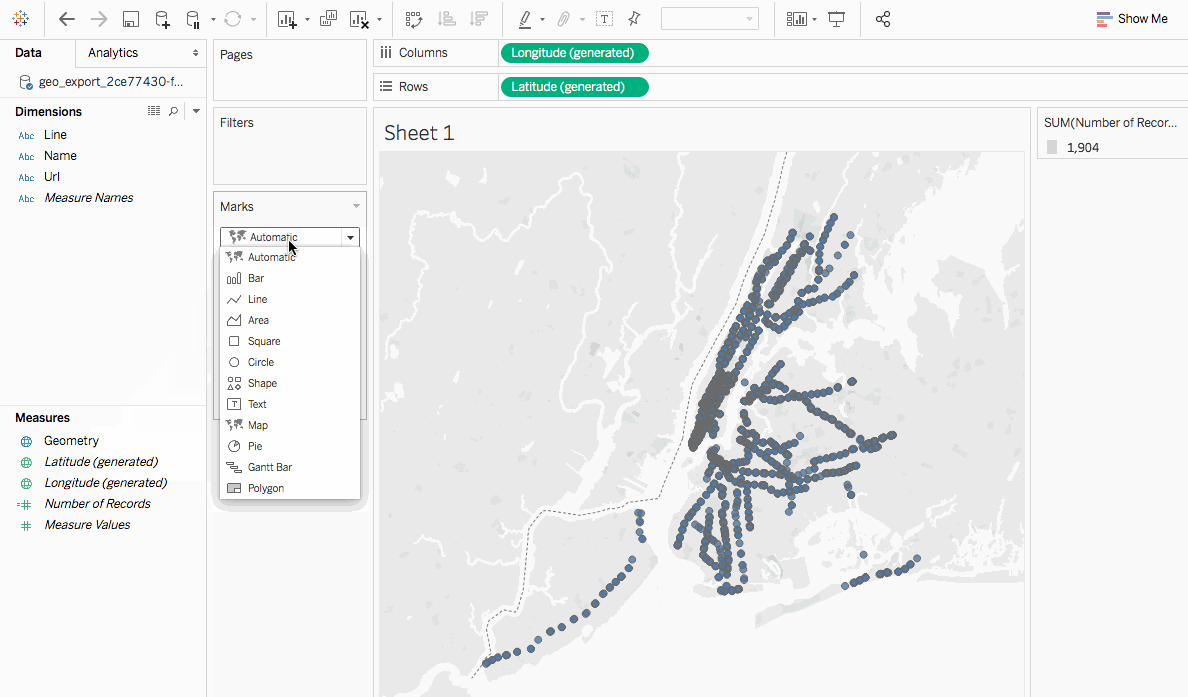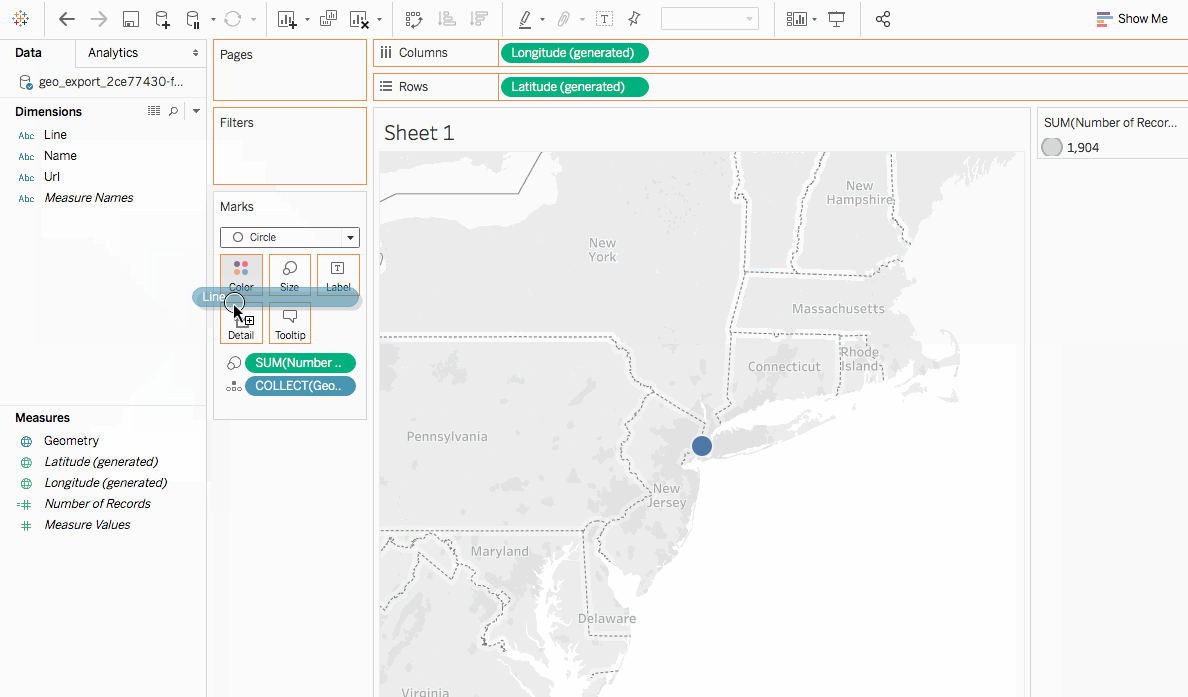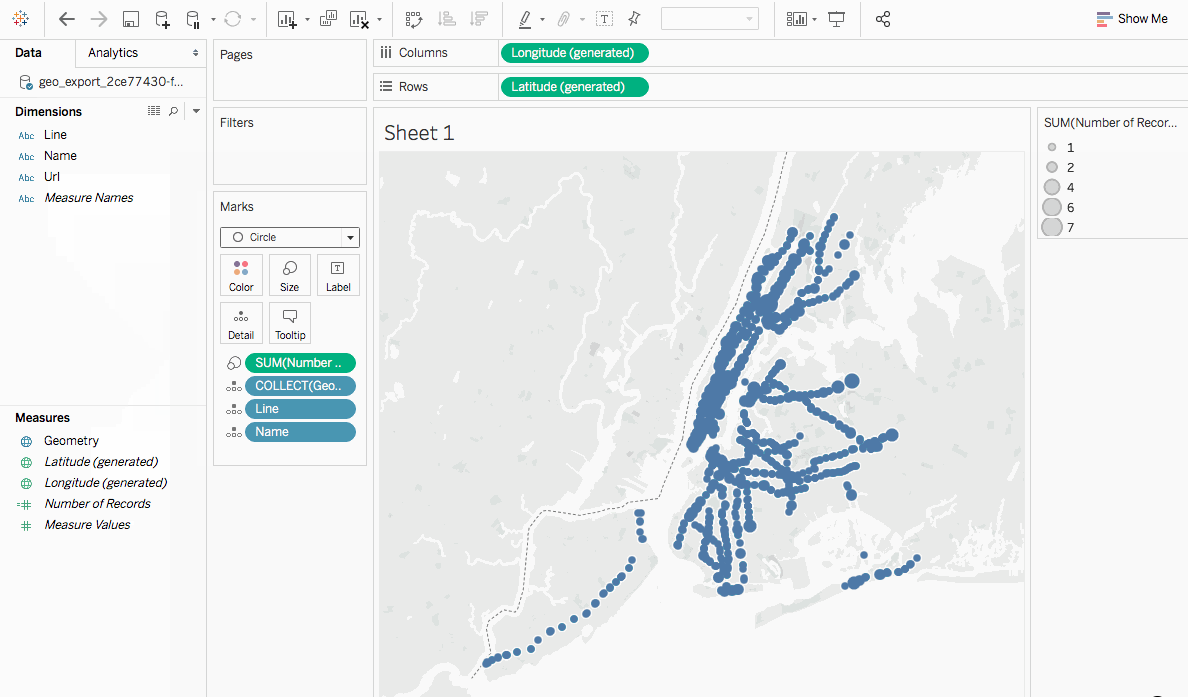



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Spatial Insights: A Comprehensive Guide to Tableau Map Visualization. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!