Unraveling the Tapestry of Time: The Oldest Maps of China and Their Enduring Legacy
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of Time: The Oldest Maps of China and Their Enduring Legacy
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of Time: The Oldest Maps of China and Their Enduring Legacy. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Tapestry of Time: The Oldest Maps of China and Their Enduring Legacy

The history of China, a civilization spanning millennia, is intricately woven with the art of cartography. Maps have served as vital tools for navigating vast landscapes, understanding territorial boundaries, and recording the evolution of human settlements. Delving into the oldest maps of China offers a unique window into the past, revealing the ingenuity of ancient cartographers and the profound impact of their creations on the course of Chinese history.
Tracing the Earliest Cartographic Footprints:
While definitive evidence is scarce, the earliest known Chinese maps can be traced back to the Shang Dynasty (1600-1046 BCE). Archaeological discoveries have unearthed fragments of pottery and oracle bones inscribed with simple depictions of geographical features. These rudimentary maps, though lacking in detail, provide a glimpse into the nascent development of cartographic knowledge in ancient China.
The Emergence of Detailed Maps:
The Zhou Dynasty (1046-256 BCE) witnessed a significant advancement in cartography. The emergence of bronzeware production led to the creation of elaborately crafted maps etched onto bronze vessels. These maps, often depicting specific regions or cities, were not only functional but also served as prestigious objects, reflecting the increasing importance of cartography in the social and cultural landscape of the time.
The Flourishing of Cartography in the Han Dynasty (206 BCE – 220 CE):
The Han Dynasty marked a golden age for Chinese cartography. The development of papermaking and printing technologies facilitated the creation and dissemination of maps on a larger scale. The "Yu Gong" section of the "Classic of Rites", compiled during this period, is considered a landmark work in Chinese cartography. This comprehensive geographical treatise provides detailed descriptions of various regions, their resources, and the distribution of populations.
The Rise of the "World Map" in the Tang Dynasty (618-907 CE):
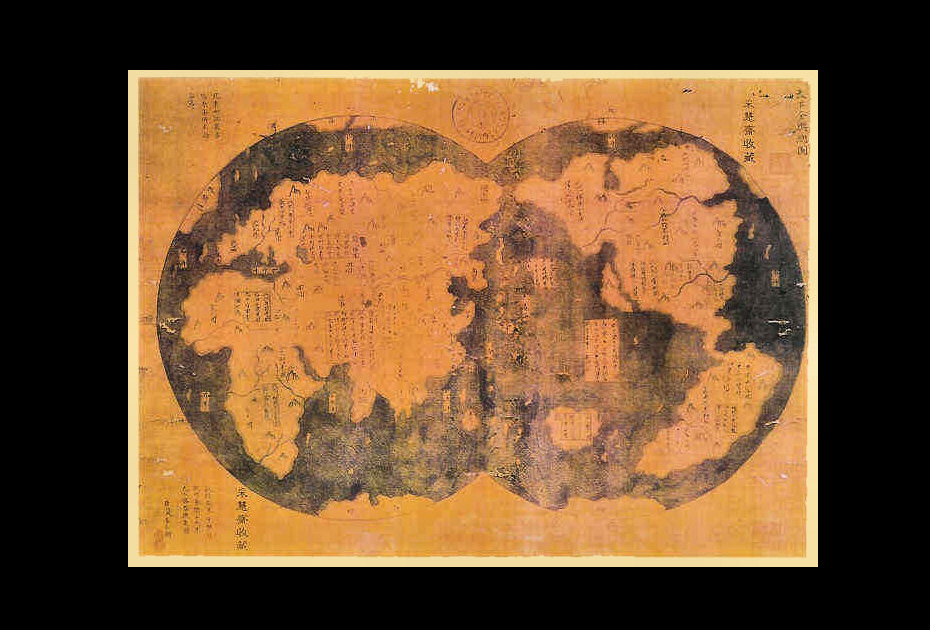
The Tang Dynasty witnessed the emergence of elaborate "world maps," showcasing the vastness of the known world from a Chinese perspective. These maps, often incorporating elements of mythology and cosmology, reflected the growing influence of China on the global stage. The "Dunhuang Map", a monumental map discovered in the Mogao Caves of Dunhuang, is a prime example of this period’s cartographic achievements.
The Evolution of Maps in the Song Dynasty (960-1279 CE):
The Song Dynasty, a period marked by technological innovation and cultural flourishing, saw further advancements in cartography. The invention of the "compass" revolutionized navigation, leading to the creation of more precise and accurate maps. The "Yu Ji Tu", a comprehensive map of the Song Dynasty, stands as a testament to the meticulousness and detail achieved by cartographers of this era.
The Impact of the Mongol Empire (1271-1368 CE):
The Mongol conquest of China had a significant impact on cartography. The Yuan Dynasty (1271-1368 CE), established by Kublai Khan, fostered a cosmopolitan environment that encouraged the exchange of knowledge and ideas. This led to the creation of maps that incorporated geographical information from across the vast Mongol Empire, including regions beyond China’s traditional borders.
The Ming Dynasty (1368-1644 CE) and the "Great Ming Map":
The Ming Dynasty witnessed the creation of the monumental "Great Ming Map", a vast and detailed map that encompassed the entirety of the Ming Empire. This map, spanning over 300 scrolls, was a testament to the ambitious cartographic project undertaken during this period. It served as a valuable tool for administration, navigation, and military planning.
The Qing Dynasty (1644-1912 CE) and the Rise of Modern Cartography:
The Qing Dynasty saw a gradual transition towards modern cartographic techniques. The introduction of European cartographic methods, coupled with advancements in surveying and printing technologies, led to the creation of more accurate and scientifically sound maps. The "Kangxi Map", a comprehensive map of China compiled during the reign of Emperor Kangxi, stands as a landmark achievement of this period.
The Enduring Legacy of Ancient Chinese Maps:
The oldest maps of China serve as invaluable historical documents, offering insights into the past that extend beyond mere geographical information. They reveal the evolving understanding of the world, the changing political landscape, and the cultural values of each era. These maps are not merely static representations of physical space but rather dynamic reflections of the human experience, reflecting the ingenuity, ambition, and interconnectedness of generations past.
FAQs: The Oldest Maps of China
1. What is the earliest known map of China?
While definitive evidence is scarce, the earliest known Chinese maps can be traced back to the Shang Dynasty (1600-1046 BCE). These early maps, often depicted on pottery and oracle bones, were rudimentary but provide a glimpse into the nascent development of cartography.
2. What are the key features of the "Yu Gong" section of the "Classic of Rites"?
The "Yu Gong," compiled during the Han Dynasty, is a comprehensive geographical treatise that provides detailed descriptions of various regions, their resources, and the distribution of populations. It stands as a landmark work in Chinese cartography, offering valuable insights into the socio-economic conditions of the time.
3. How did the Mongol Empire influence cartography in China?
The Yuan Dynasty (1271-1368 CE), established by Kublai Khan, fostered a cosmopolitan environment that encouraged the exchange of knowledge and ideas. This led to the creation of maps that incorporated geographical information from across the vast Mongol Empire, including regions beyond China’s traditional borders.
4. What is the significance of the "Great Ming Map"?
The "Great Ming Map," compiled during the Ming Dynasty, encompassed the entirety of the Ming Empire. This monumental map, spanning over 300 scrolls, was a testament to the ambitious cartographic project undertaken during this period and served as a valuable tool for administration, navigation, and military planning.
5. How did the Qing Dynasty contribute to the evolution of cartography?
The Qing Dynasty saw a gradual transition towards modern cartographic techniques. The introduction of European cartographic methods, coupled with advancements in surveying and printing technologies, led to the creation of more accurate and scientifically sound maps. The "Kangxi Map," a comprehensive map of China compiled during the reign of Emperor Kangxi, stands as a landmark achievement of this period.
Tips for Understanding and Appreciating the Oldest Maps of China:
- Context is Key: Understanding the historical context in which a map was created is crucial for interpreting its significance and accuracy. Consider the political, social, and technological factors that influenced the map’s creation.
- Beyond the Lines: Maps are not merely visual representations of geographical features but also convey cultural and ideological perspectives. Look beyond the lines and symbols to understand the messages and ideas embedded within the map.
- Comparison and Contrast: Comparing and contrasting different maps from different periods can reveal the evolution of cartographic knowledge and the changing understanding of the world.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: Engage with other disciplines, such as history, archaeology, and art history, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the maps’ context and significance.
- Appreciate the Craft: Recognize the skill and ingenuity of ancient cartographers who, using limited tools and resources, created maps that provided vital information and shaped our understanding of the world.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of the Oldest Maps of China
The oldest maps of China are more than just pieces of paper; they are windows into the past, offering glimpses into the ingenuity, ambition, and cultural values of ancient civilizations. These maps, meticulously crafted by skilled cartographers, reveal the evolution of human understanding of the world, the changing political landscape, and the enduring connection between humans and their environment. By studying and appreciating these historical treasures, we gain a deeper understanding of our own place in the world and the interconnectedness of human history.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of Time: The Oldest Maps of China and Their Enduring Legacy. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!