Understanding the Significance of Second Grade MAP Test Scores: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Significance of Second Grade MAP Test Scores: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Significance of Second Grade MAP Test Scores: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Significance of Second Grade MAP Test Scores: A Comprehensive Guide

The second grade is a crucial stage in a child’s educational journey. This is the year when foundational skills in reading, writing, and mathematics solidify, setting the stage for future academic success. Standardized assessments, such as the Measures of Academic Progress (MAP) test, play a pivotal role in evaluating student progress and identifying areas for support. This guide will delve into the importance of second-grade MAP test scores, their interpretation, and their implications for student learning.
The MAP Test: A Snapshot of Student Progress
The MAP test is a computer-adaptive assessment that measures student growth in reading, language usage, and mathematics. It is designed to provide a detailed picture of a student’s current academic standing and their potential for future learning. Unlike traditional standardized tests that focus on a single point in time, MAP tests are administered multiple times throughout the school year, allowing educators to track student progress and identify areas requiring additional support.
Understanding Second Grade MAP Test Scores
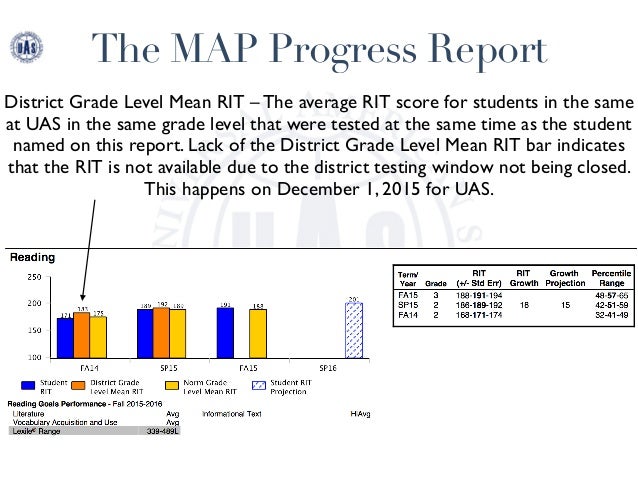
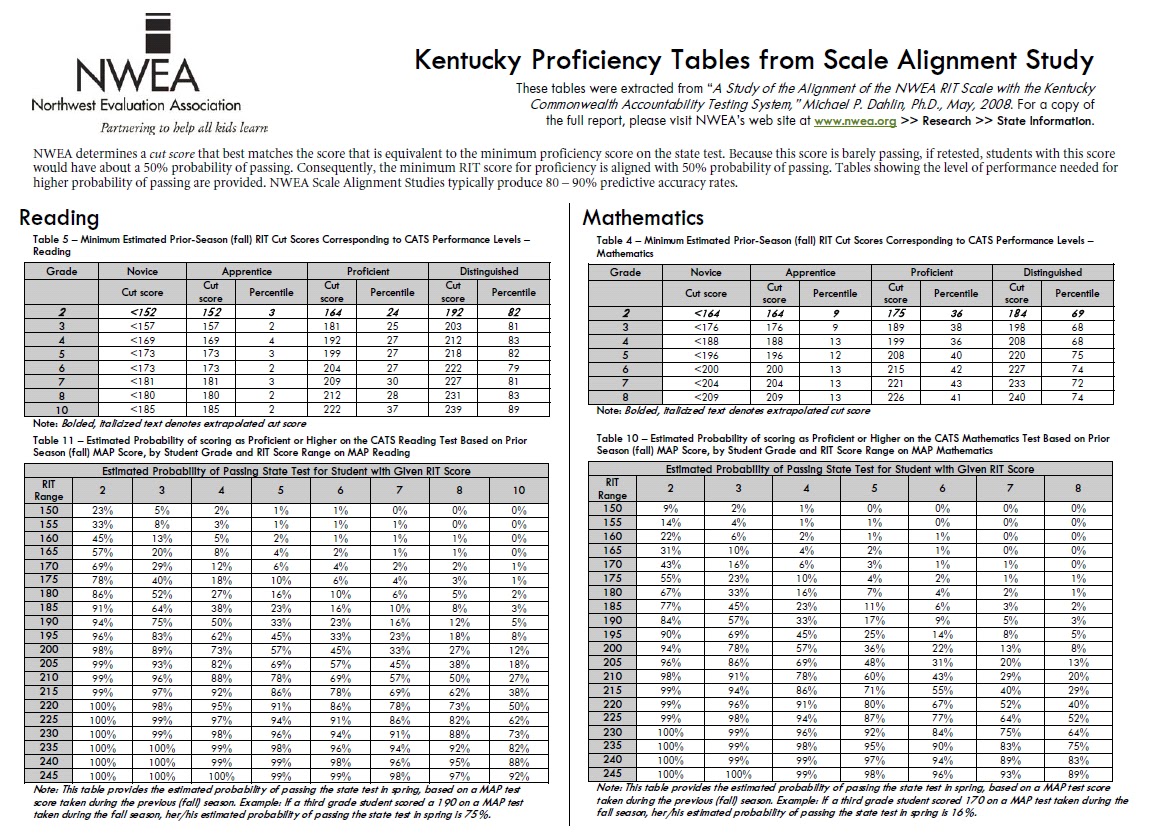
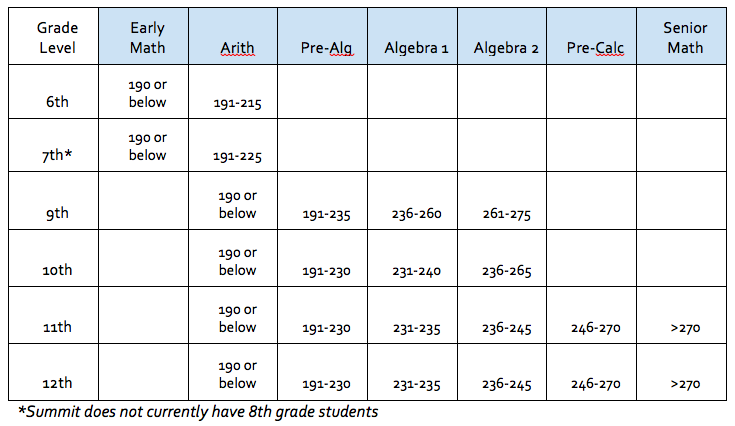
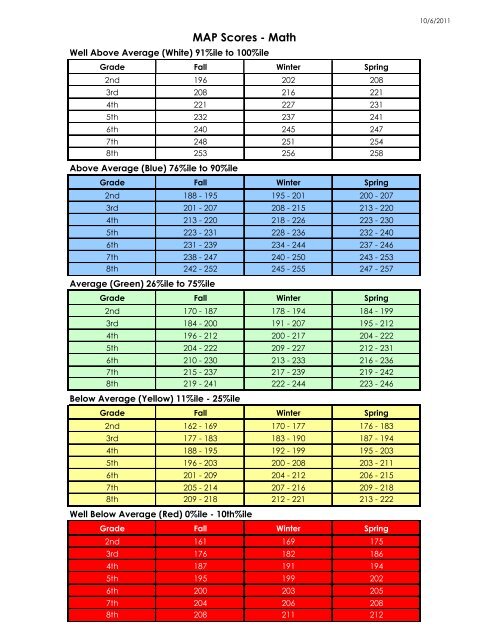
Second-grade MAP test scores are reported as RIT scores, which represent a student’s estimated grade level in a particular subject. These scores are based on a national norm, meaning they reflect the average performance of students across the country at that grade level. A higher RIT score indicates a higher level of academic achievement.
The Importance of Second Grade MAP Test Scores
Second-grade MAP test scores hold significant importance for several reasons:
- Early Identification of Learning Gaps: These scores provide educators with valuable insights into a student’s strengths and weaknesses, allowing for early intervention and targeted support. By identifying learning gaps early on, educators can implement individualized strategies to help students catch up and reach their full potential.
- Personalized Learning Plans: MAP test scores can inform the development of personalized learning plans that cater to each student’s unique needs. By analyzing the data, educators can tailor instruction, provide additional practice, and select appropriate learning resources to address individual learning styles and areas for improvement.
- Monitoring Student Growth: Regular MAP testing allows educators to track student progress over time and identify areas where students are excelling or struggling. This ongoing monitoring enables teachers to adjust their teaching strategies and provide appropriate support to ensure that all students are making adequate progress.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: MAP test scores provide valuable data that informs decision-making at the classroom, school, and district levels. Educators can use this data to evaluate the effectiveness of instructional programs, identify areas for improvement, and allocate resources effectively.
- Parental Communication: MAP test scores provide a clear and objective measure of student performance that can be shared with parents. This communication fosters open dialogue about a child’s academic progress, enabling parents to actively participate in their child’s education and provide necessary support.
Interpreting Second Grade MAP Test Scores
Interpreting second-grade MAP test scores requires careful consideration of several factors:
- RIT Score Range: The RIT score range for second grade typically falls between 150 and 200, with higher scores indicating higher levels of achievement.
- Growth Over Time: It is essential to consider student growth over time, rather than focusing solely on a single score. Tracking a student’s progress across multiple testing periods provides a more comprehensive picture of their development.
- Comparison to National Norms: Comparing a student’s RIT score to national norms helps to understand their performance relative to other students in the same grade level.
- Individual Student Factors: It is crucial to consider individual student factors such as prior academic experience, learning disabilities, and language proficiency when interpreting MAP test scores.
FAQs Regarding Second Grade MAP Test Scores
1. What if my child scores below the national average on the MAP test?
If your child scores below the national average, it is important to discuss the results with their teacher. The teacher can provide further insight into your child’s performance and develop a personalized plan to address any areas of weakness.
2. How can I help my child prepare for the MAP test?
Encourage your child to read regularly, practice math skills, and engage in activities that promote critical thinking and problem-solving. You can also work with your child on test-taking strategies, such as time management and eliminating incorrect answers.
3. What are some strategies for improving my child’s MAP test scores?
- Targeted Intervention: Work with your child’s teacher to identify specific areas requiring additional support and implement targeted interventions.
- Increased Practice: Provide your child with regular opportunities to practice reading, writing, and math skills.
- Engaging Learning Experiences: Create a stimulating learning environment that encourages your child’s curiosity and fosters a love of learning.
- Positive Reinforcement: Encourage and praise your child’s efforts and progress, creating a positive and supportive learning environment.
4. How often are MAP tests administered?
MAP tests are typically administered three times per year: fall, winter, and spring. This allows educators to monitor student progress and adjust instruction accordingly.
5. What are the implications of a low MAP test score?
A low MAP test score may indicate a need for additional support and intervention. It is essential to work with your child’s teacher to develop a personalized plan to address any learning gaps and ensure academic success.
Tips for Supporting Second Grade Students with MAP Test Scores
- Open Communication: Foster open communication with your child’s teacher, discussing their performance and any concerns you may have.
- Positive Attitude: Create a positive and supportive learning environment at home, encouraging your child’s efforts and celebrating their achievements.
- Active Participation: Encourage your child to actively participate in their learning, asking questions and seeking clarification when needed.
- Real-World Applications: Connect learning to real-world situations, making it more engaging and relevant for your child.
- Learning Resources: Utilize various learning resources, such as books, online games, and educational apps, to supplement classroom instruction.
Conclusion
Second-grade MAP test scores play a crucial role in assessing student progress and identifying areas for support. By understanding the importance of these scores and working collaboratively with educators, parents and teachers can ensure that all students have the opportunity to reach their full potential. By providing targeted support and creating a supportive learning environment, we can empower second-grade students to develop the foundational skills they need for lifelong success.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Significance of Second Grade MAP Test Scores: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!