Understanding the Landscape of Representation: A Comprehensive Look at Wisconsin’s 2000 Senate District Map
Related Articles: Understanding the Landscape of Representation: A Comprehensive Look at Wisconsin’s 2000 Senate District Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Landscape of Representation: A Comprehensive Look at Wisconsin’s 2000 Senate District Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Landscape of Representation: A Comprehensive Look at Wisconsin’s 2000 Senate District Map

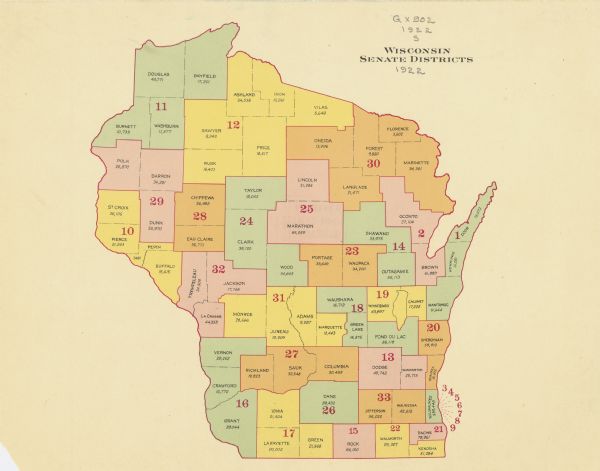
The 2000 map of Wisconsin Senate districts offers a fascinating snapshot of the state’s political landscape at the turn of the century. It is a visual representation of how the state was divided into 33 distinct districts, each electing a senator to the Wisconsin State Senate. While the map is now outdated, it holds significant historical and political value, providing insights into the dynamics of representation and the evolution of political boundaries.
The Significance of the Map:
The 2000 map, like all district maps, played a crucial role in shaping the political landscape of Wisconsin. It determined which communities were grouped together for representation, influencing the political voice and priorities of each district. This map, like its predecessors and successors, was a product of a complex process involving political considerations, demographic trends, and legal requirements. Understanding the map’s origins and its impact on the state’s political landscape is essential for grasping the evolution of representation in Wisconsin.
Key Features of the Map:
The 2000 map of Wisconsin Senate districts exhibits several key features that are worth noting:
- Geographic Boundaries: The map clearly delineates the boundaries of each district, outlining the specific areas represented by each senator. These boundaries often follow natural features like rivers and lakes, but also incorporate urban and rural areas, reflecting the diverse nature of Wisconsin’s communities.
- Population Distribution: The map reflects the uneven distribution of population across the state. Some districts encompass densely populated urban areas, while others cover vast rural territories. This disparity in population density directly impacted the size and influence of each district.
- Political Leanings: The 2000 map, while not a direct indicator of political leanings, offers a glimpse into the potential voting patterns and political affiliations of each district. By analyzing the demographic makeup of each district, one can infer general political trends and historical voting patterns.
Delving Deeper into the Map’s Context:
To truly understand the map’s significance, it is essential to consider the historical context surrounding its creation and the subsequent political developments it influenced.
- Redistricting Process: The 2000 map was a product of the redistricting process, which occurs every ten years following the US Census. This process involves redrawing district boundaries to ensure equal representation based on population changes and demographic shifts. The redistricting process is often politically charged, as it can influence the outcome of elections and the balance of power within the state legislature.
- Political Landscape in 2000: The 2000 map reflected the political landscape of the time, characterized by a growing partisan divide and increasing focus on gerrymandering. Gerrymandering, the manipulation of district boundaries to favor a specific political party, was a significant issue in the 2000s, with accusations of partisan bias in redistricting efforts across the country.
- Impact on Representation: The 2000 map, like all district maps, had a direct impact on the representation of different communities and interests within the state legislature. It determined which communities were grouped together, influencing the priorities and concerns addressed by their elected representatives.
The Evolving Landscape of Representation:
The 2000 map is a historical artifact, a snapshot of the political landscape at a specific moment in time. Since then, the map has been revised multiple times, reflecting changes in population distribution, evolving political dynamics, and legal challenges to redistricting practices.
Understanding the 2000 map is crucial for appreciating the evolution of representation in Wisconsin and the ongoing challenges and debates surrounding redistricting. It highlights the complex interplay of demographics, politics, and legal frameworks in shaping the political landscape and ensuring fair and equitable representation for all communities.
FAQs about the 2000 Map of Wisconsin Senate Districts:
Q: How often are Wisconsin Senate district maps redrawn?
A: The maps are redrawn every ten years following the US Census, which is conducted every decade.
Q: What are the criteria for drawing Senate district boundaries?
A: The boundaries must adhere to legal requirements, including the principle of "one person, one vote," which means districts must have roughly equal populations. Additionally, the districts should be geographically contiguous and compact.
Q: How does the redistricting process impact the political landscape?
A: The redistricting process can significantly influence the outcome of elections and the balance of power within the state legislature. By strategically drawing district boundaries, political parties can attempt to create districts that favor their candidates.
Q: What are the challenges associated with redistricting?
A: Redistricting is a complex and often contentious process, fraught with challenges such as gerrymandering, political bias, and the need to balance competing interests.
Tips for Analyzing the 2000 Map:
- Consider the historical context: The 2000 map reflects the political landscape of the time, with its own unique set of challenges and priorities.
- Examine the demographic makeup of each district: By analyzing the population distribution, one can infer general political trends and historical voting patterns.
- Compare the 2000 map with subsequent maps: This comparison highlights the evolution of representation in Wisconsin and the impact of redistricting on the political landscape.
- Research the redistricting process and its legal framework: Understanding the legal requirements and political considerations involved in redistricting is crucial for interpreting the map’s significance.
Conclusion:
The 2000 map of Wisconsin Senate districts provides a valuable window into the state’s political landscape at the turn of the century. It highlights the importance of redistricting in shaping representation and the ongoing challenges associated with ensuring fair and equitable representation for all communities. While the map itself is now outdated, its historical and political significance remains relevant, offering insights into the evolution of the state’s political landscape and the ongoing debate surrounding redistricting practices.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Landscape of Representation: A Comprehensive Look at Wisconsin’s 2000 Senate District Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!