Understanding the Earth’s Tremors: An Exploration of Earthquake Maps and Their Significance
Related Articles: Understanding the Earth’s Tremors: An Exploration of Earthquake Maps and Their Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Earth’s Tremors: An Exploration of Earthquake Maps and Their Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Earth’s Tremors: An Exploration of Earthquake Maps and Their Significance
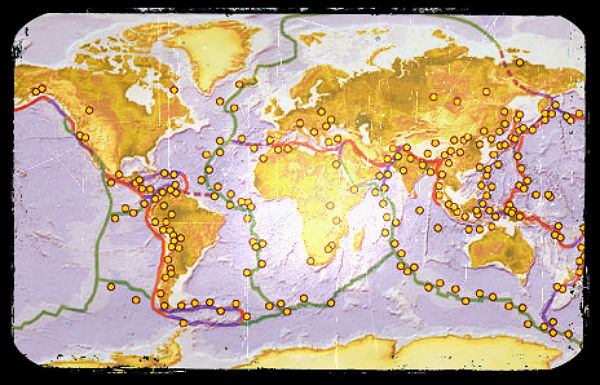
The Earth, despite its seemingly solid exterior, is a dynamic and constantly shifting entity. Deep beneath the surface, tectonic plates, massive slabs of rock, are in perpetual motion, grinding against each other, colliding, and pulling apart. These movements, while imperceptible on the surface, can unleash powerful forces, resulting in seismic events known as earthquakes.
To better understand and prepare for these natural phenomena, scientists and researchers have developed sophisticated tools, including earthquake maps. These visual representations of seismic activity provide valuable insights into the distribution, frequency, and intensity of earthquakes, aiding in preparedness, risk assessment, and scientific research.
Unveiling the Secrets of Seismic Activity: A Look at Earthquake Maps
Earthquake maps are not simply static representations of past events; they are dynamic and constantly evolving tools that provide a wealth of information about the Earth’s seismic activity. They depict:
- Epicenter Locations: Earthquake maps pinpoint the epicenter, the point on the Earth’s surface directly above the earthquake’s origin, providing a precise location for each seismic event.
- Magnitude and Intensity: They illustrate the magnitude of earthquakes, measured on the Richter scale, and the intensity, which describes the effects felt on the surface.
- Fault Lines: Earthquake maps highlight major fault lines, the boundaries between tectonic plates, which are the most common locations for earthquake occurrences.
- Historical Data: These maps often incorporate historical earthquake data, providing a long-term perspective on seismic activity in specific regions.
Types of Earthquake Maps: A Spectrum of Information
There are various types of earthquake maps, each offering unique perspectives on seismic activity:
- Global Earthquake Maps: These maps provide a broad overview of earthquake occurrences worldwide, showcasing the distribution of seismic activity across the globe.
- Regional Earthquake Maps: These maps focus on specific geographic regions, providing detailed information about earthquake occurrences within those areas.
- Fault Line Maps: These maps highlight major fault lines, indicating zones of high seismic activity and potential earthquake risk.
- Seismic Hazard Maps: These maps assess the potential for earthquakes in specific areas, considering factors like fault lines, historical data, and ground conditions.
- Real-time Earthquake Maps: These interactive maps display current earthquake activity, providing updates on ongoing events and their magnitude and location.
The Importance of Earthquake Maps: From Preparedness to Research
Earthquake maps serve as invaluable tools for various purposes, contributing to:
- Disaster Preparedness: They help identify areas at high risk of earthquakes, enabling communities to develop effective disaster preparedness plans, including evacuation routes, emergency shelters, and earthquake-resistant building codes.
- Risk Assessment: They provide a framework for assessing earthquake risk, helping individuals and businesses make informed decisions about insurance, construction, and land use.
- Scientific Research: Earthquake maps serve as vital data sources for scientists studying plate tectonics, seismic wave propagation, and earthquake prediction.
- Public Awareness: They raise awareness about earthquake hazards, promoting public understanding of seismic risks and encouraging preparedness measures.
Exploring the World of Earthquake Maps: Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the best websites for accessing earthquake maps?
A: Numerous reputable websites provide access to real-time and historical earthquake data, including:
- The United States Geological Survey (USGS): https://earthquake.usgs.gov/
- The European-Mediterranean Seismological Centre (EMSC): https://www.emsc-csem.org/
- The International Seismological Centre (ISC): https://www.isc.ac.uk/
Q: How are earthquake magnitudes measured?
A: The magnitude of an earthquake is measured using the Richter scale, a logarithmic scale that assigns a numerical value to the energy released by the earthquake. Each whole number increase on the Richter scale represents a tenfold increase in the amplitude of the seismic waves.
Q: What are the differences between magnitude and intensity?
A: Magnitude refers to the energy released by an earthquake at its source, while intensity measures the effects of the earthquake on the surface. Intensity is typically measured using the Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale, which assigns Roman numerals to describe the severity of ground shaking and damage.
Q: What are the key factors influencing earthquake intensity?
A: The intensity of an earthquake is influenced by several factors, including:
- Magnitude: Larger earthquakes generally have higher intensities.
- Distance from the Epicenter: Intensity decreases with distance from the epicenter.
- Geological Conditions: The type of soil or rock underlying the surface can amplify or dampen seismic waves, affecting intensity.
Q: Are there any tools available for earthquake prediction?
A: While scientists have made significant progress in understanding earthquakes, predicting the exact time, location, and magnitude of an earthquake remains a challenge. However, researchers are continuously developing new tools and methods to improve earthquake forecasting.
Q: What steps can I take to prepare for an earthquake?
A: Preparing for an earthquake involves several steps:
- Secure Heavy Objects: Secure heavy objects that could fall during an earthquake, such as bookshelves, mirrors, and light fixtures.
- Create an Emergency Kit: Prepare an emergency kit with essential supplies, including food, water, first-aid supplies, a flashlight, and a battery-powered radio.
- Develop an Evacuation Plan: Create an evacuation plan for your family, including designated meeting points and escape routes.
- Learn CPR and First Aid: Knowing CPR and first aid can be crucial in an emergency situation.
Navigating Earthquake Maps: Tips for Effective Use
- Understand the Scale: Familiarize yourself with the scale used on the map, whether it’s the Richter scale for magnitude or the Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale for intensity.
- Identify Your Location: Locate your home or workplace on the map to assess your proximity to potential earthquake zones.
- Explore Historical Data: Examine historical earthquake data to understand the frequency and intensity of past events in your area.
- Utilize Interactive Features: Take advantage of interactive features on real-time earthquake maps, such as zooming, panning, and filtering data.
- Stay Informed: Stay informed about earthquake activity by subscribing to alerts and updates from reputable sources like the USGS or EMSC.
Conclusion: Embracing the Earth’s Dynamic Nature
Earthquake maps are not just tools for scientific research; they are essential resources for communities worldwide, enabling informed decision-making, promoting preparedness, and fostering a deeper understanding of the Earth’s dynamic nature. By embracing the information provided by these maps, individuals and communities can better mitigate the risks associated with earthquakes and build resilience in the face of these powerful natural phenomena.


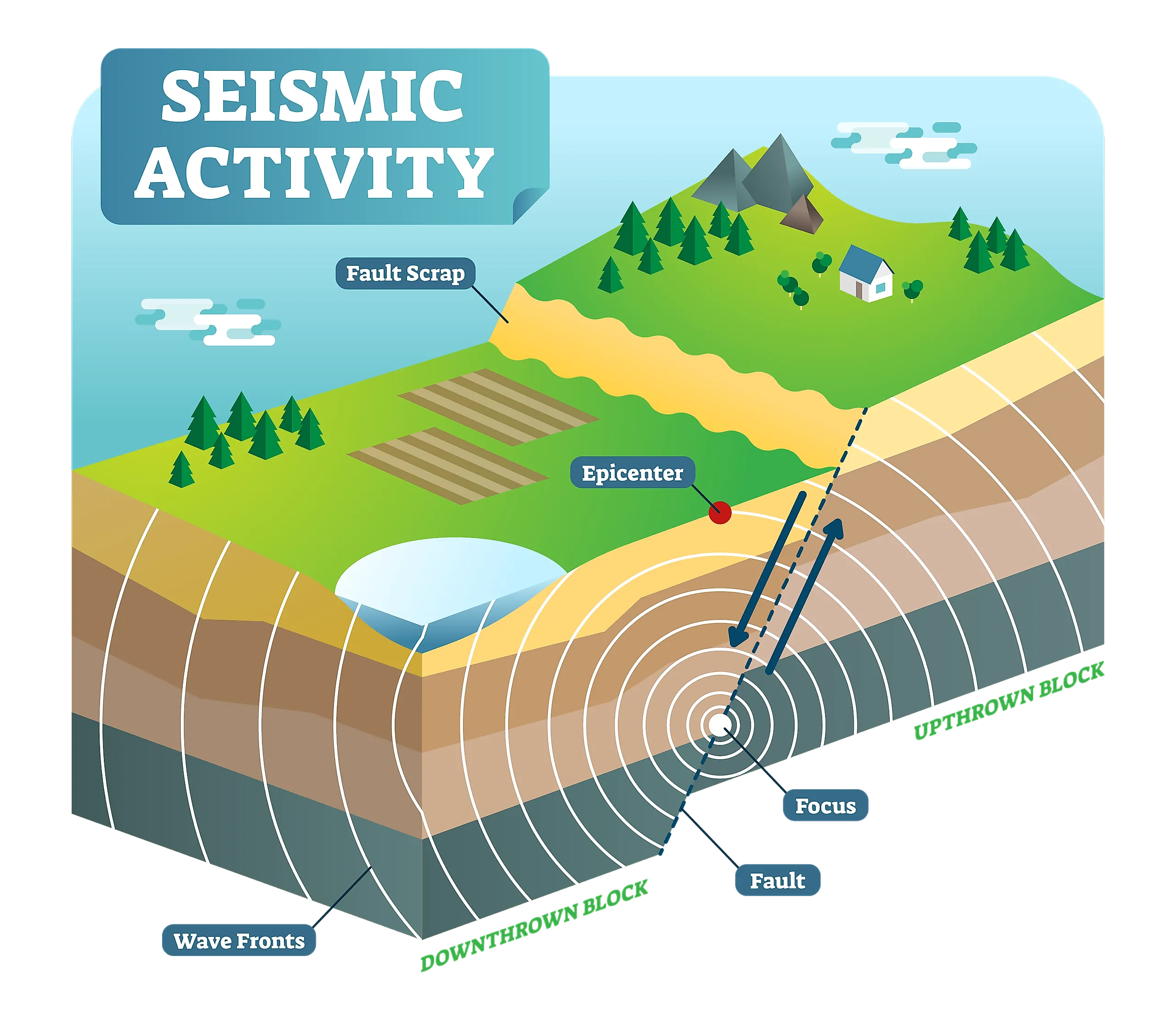



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Earth’s Tremors: An Exploration of Earthquake Maps and Their Significance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!