Understanding Pennsylvania’s Planting Zones: A Guide to Successful Gardening
Related Articles: Understanding Pennsylvania’s Planting Zones: A Guide to Successful Gardening
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Pennsylvania’s Planting Zones: A Guide to Successful Gardening. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding Pennsylvania’s Planting Zones: A Guide to Successful Gardening
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding Pennsylvania’s Planting Zones: A Guide to Successful Gardening
- 3.1 The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map: A Framework for Success
- 3.2 Pennsylvania’s Diverse Zones: A Closer Look
- 3.3 Navigating the Map: A Practical Guide
- 3.4 The Benefits of Knowing Your Zone: A Foundation for Success
- 3.5 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
- 3.6 Tips for Success: Maximizing Your Gardening Potential
- 3.7 Conclusion: A Foundation for Garden Success
- 4 Closure
Understanding Pennsylvania’s Planting Zones: A Guide to Successful Gardening

Pennsylvania, with its diverse topography and climate, presents a unique challenge for gardeners. Knowing which plants thrive in specific regions is essential for successful cultivation. This is where the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map for Pennsylvania comes into play, offering a crucial tool for navigating the state’s varied growing conditions.
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map: A Framework for Success
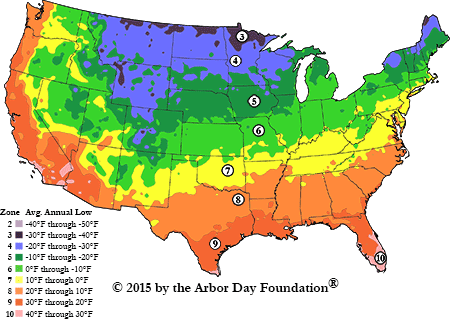
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is a valuable resource for gardeners, providing a standardized system to categorize regions based on their average annual minimum winter temperatures. Each zone represents a 10-degree Fahrenheit range, with higher numbers signifying warmer climates. This map serves as a guide for selecting plants that can withstand the coldest temperatures in a particular area.
Pennsylvania’s Diverse Zones: A Closer Look
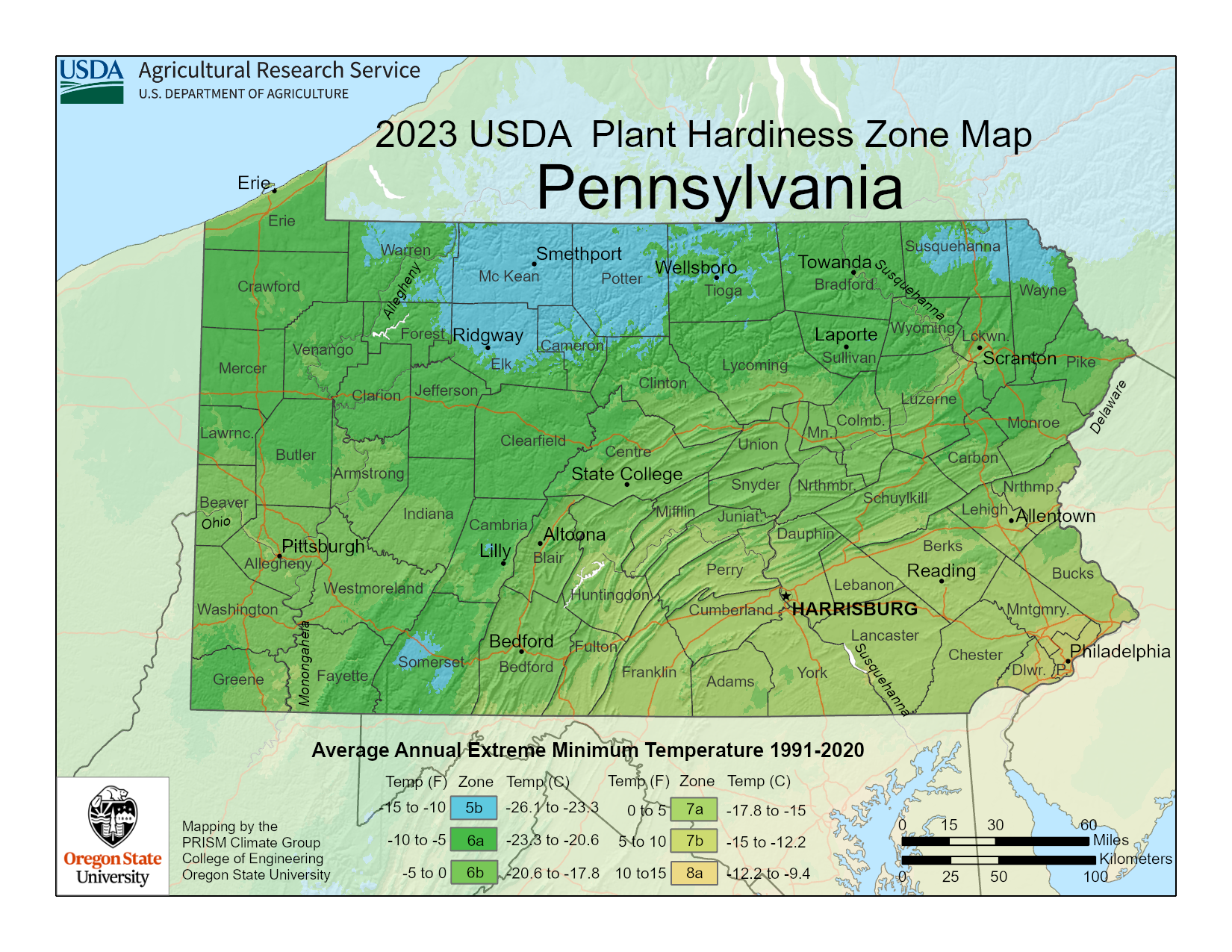
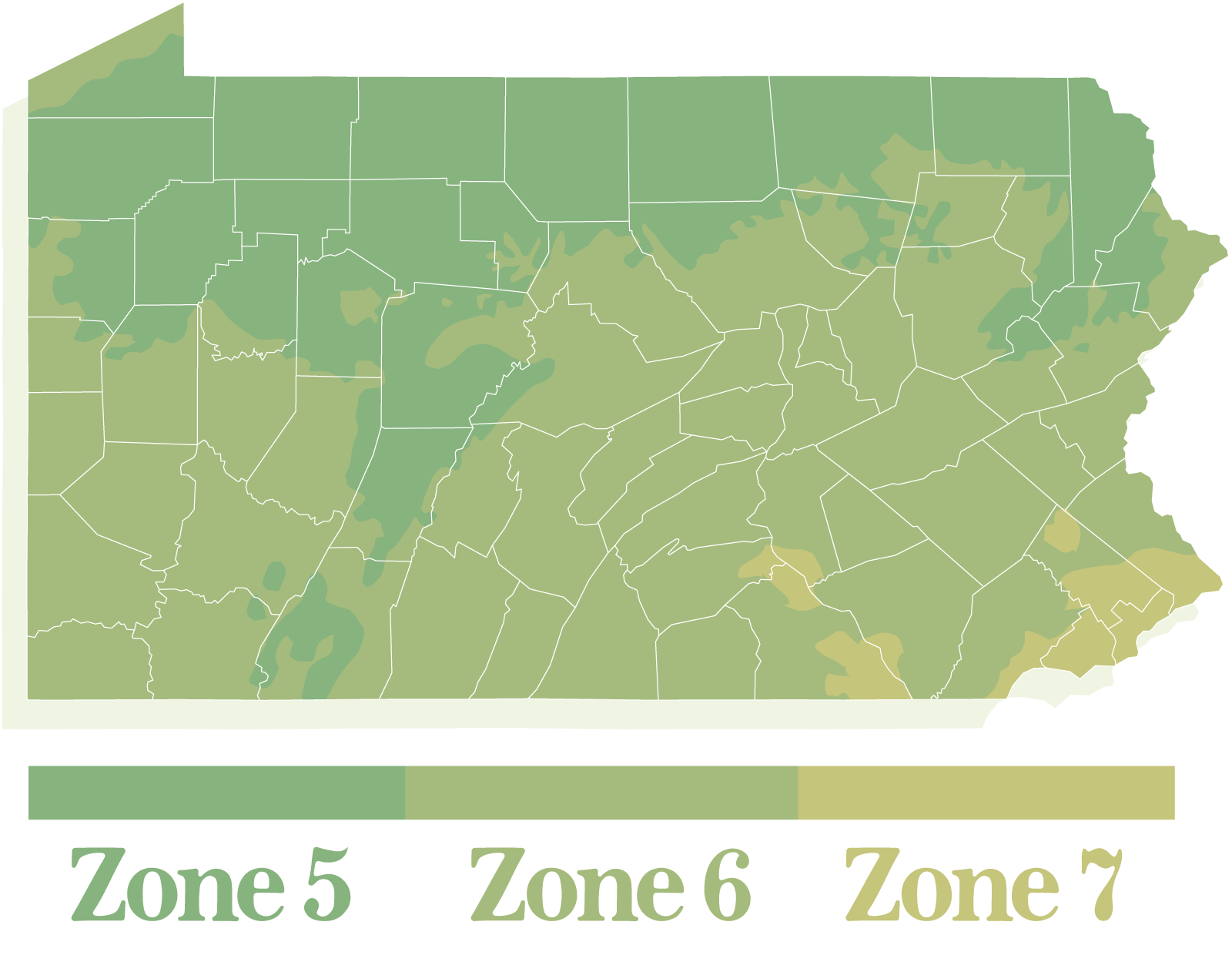
Pennsylvania, spanning from the Appalachian Mountains to the Delaware River, exhibits a significant range in its hardiness zones. The state is divided into six distinct zones, each with specific characteristics that influence plant growth and survival.
-
Zone 4: The northernmost region of Pennsylvania, encompassing areas like Erie and Scranton, falls within Zone 4. This zone experiences average minimum winter temperatures between -30 and -20 degrees Fahrenheit. While challenging for many plants, Zone 4 still offers opportunities for hardy varieties like spruce, fir, and certain deciduous trees.
-
Zone 5: Moving southward, the state transitions to Zone 5, encompassing areas like Williamsport, Harrisburg, and Pittsburgh. This zone boasts average minimum winter temperatures between -20 and -10 degrees Fahrenheit. Zone 5 supports a wider variety of plants, including popular choices like lilac, hydrangea, and many varieties of fruit trees.
-
Zone 6: The southernmost regions of Pennsylvania, including Philadelphia, Allentown, and Lancaster, fall within Zone 6. This zone enjoys warmer winters, with average minimum temperatures ranging from -10 to 0 degrees Fahrenheit. Zone 6 is ideal for growing a wider array of plants, including roses, perennials, and even some subtropical varieties.
Navigating the Map: A Practical Guide
Understanding the specific zone for your location in Pennsylvania is crucial for successful gardening. The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map offers a comprehensive visual representation of the state’s diverse zones.
-
Online Resources: Numerous online resources, including the USDA website and gardening websites, offer interactive maps and tools to determine your specific zone. Simply enter your zip code or address to obtain accurate information.
-
Local Garden Centers: Visiting local garden centers and nurseries can provide valuable insights into the best plants for your specific zone. Experts can offer personalized recommendations based on your location and gardening goals.
The Benefits of Knowing Your Zone: A Foundation for Success
Utilizing the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map for Pennsylvania provides numerous benefits for gardeners:
-
Increased Success Rates: By selecting plants suited to your specific zone, you significantly increase the chances of successful growth and survival. This eliminates the risk of investing in plants that may not thrive in your local climate.
-
Cost Savings: Choosing plants that are well-adapted to your region reduces the need for additional care, such as winter protection, and minimizes the risk of plant loss. This translates to cost savings in the long run.
-
Reduced Environmental Impact: Planting appropriate species for your zone promotes biodiversity and reduces the need for excessive watering or fertilization, contributing to a healthier environment.
-
Enhanced Aesthetics: By selecting plants that thrive in your specific zone, you can create a vibrant and visually appealing garden that flourishes throughout the year.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: How often is the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map updated?
A: The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is periodically updated to reflect changes in climate patterns. However, the map is generally considered a reliable guide for long-term planning.
Q: What are the differences between plant hardiness zones and microclimates?
A: While plant hardiness zones provide a general overview of regional climate, microclimates refer to localized variations in temperature, humidity, and other factors within a specific area. Factors like proximity to water bodies, elevation, and urban heat islands can influence microclimates.
Q: Can I grow plants outside my designated zone?
A: While it’s possible to grow plants outside their designated zone, it requires extra care and effort. You may need to provide additional protection during extreme weather events, such as winter cover or shade during hot summers.
Q: How does climate change affect plant hardiness zones?
A: Climate change is causing shifts in average temperatures, potentially impacting plant hardiness zones. As temperatures rise, some areas may shift to higher zones, while others may remain relatively stable.
Tips for Success: Maximizing Your Gardening Potential
-
Consider Microclimates: Within your zone, consider microclimates within your garden. Areas near buildings or facing south may experience warmer temperatures than other sections.
-
Consult Local Resources: Contact local garden clubs, master gardeners, or extension services for specific advice on plant selection and care for your region.
-
Start Small: Begin with a few plants that are known to thrive in your zone. Observe their growth and adapt your planting choices accordingly.
-
Embrace Variety: Explore the diverse plant options within your zone to create a vibrant and visually appealing garden.
Conclusion: A Foundation for Garden Success
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map for Pennsylvania provides a valuable framework for successful gardening in the state. By understanding your specific zone and selecting plants well-suited to your local climate, you can significantly increase your chances of creating a flourishing and rewarding garden. Embrace the diversity of Pennsylvania’s zones, learn from local resources, and enjoy the beauty and bounty that your garden has to offer.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Pennsylvania’s Planting Zones: A Guide to Successful Gardening. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!