The Power of Visualizing Data: Exploring the Significance of Maps with Pins
Related Articles: The Power of Visualizing Data: Exploring the Significance of Maps with Pins
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Power of Visualizing Data: Exploring the Significance of Maps with Pins. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Power of Visualizing Data: Exploring the Significance of Maps with Pins
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Power of Visualizing Data: Exploring the Significance of Maps with Pins
- 3.1 Understanding the Essence of Maps with Pins
- 3.2 Benefits of Utilizing Maps with Pins
- 3.3 Applications of Maps with Pins
- 3.4 Examples of Maps with Pins
- 3.5 FAQs About Maps with Pins
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Use of Maps with Pins
- 3.7 Conclusion: The Power of Visualizing Data Through Maps with Pins
- 4 Closure
The Power of Visualizing Data: Exploring the Significance of Maps with Pins
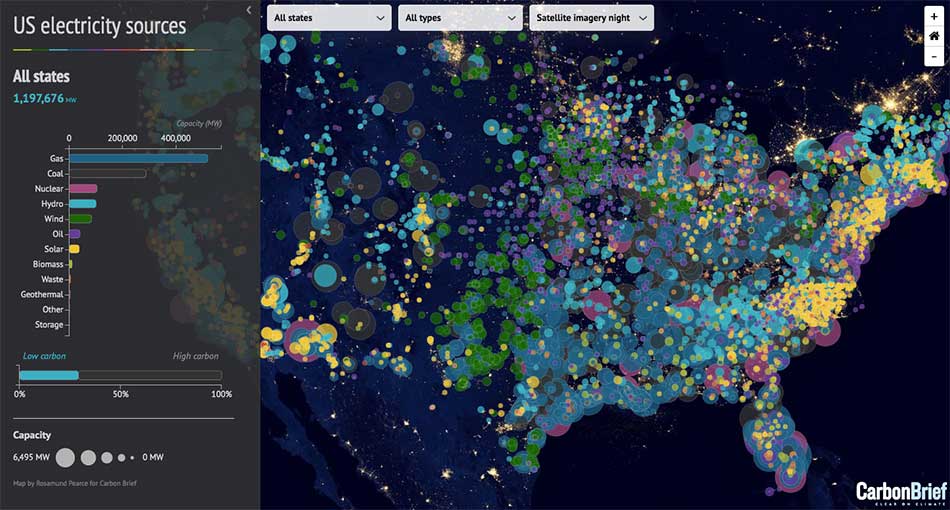
Maps have long served as powerful tools for navigating the physical world, guiding us from one location to another. In the digital age, however, maps have evolved beyond simple navigation, becoming dynamic platforms for visualizing and analyzing data. Among these innovations, maps with pins, often referred to as "pin maps" or "marker maps," have emerged as a particularly versatile and insightful tool.
Understanding the Essence of Maps with Pins
At its core, a map with pins is a visual representation of data points overlaid on a geographical map. Each pin represents a specific location, and its attributes, such as color, size, or icon, can convey additional information about the data point. This simple yet effective approach allows for the creation of visually engaging and informative representations of diverse datasets.
Benefits of Utilizing Maps with Pins
The use of maps with pins offers numerous benefits across various fields and applications:
1. Data Visualization and Exploration: Maps with pins provide a clear and intuitive way to visualize spatial data, enabling users to quickly identify patterns, trends, and outliers. This visual representation facilitates data exploration, allowing users to gain insights that might be missed when looking at data in tabular format.
2. Location-Based Analysis: By associating data points with specific locations, maps with pins enable location-based analysis. This allows users to analyze data patterns based on geographic factors such as proximity, distance, or regional characteristics.
3. Communication and Storytelling: Maps with pins are excellent tools for communicating complex data in a simple and engaging manner. The visual nature of these maps makes it easier for audiences to understand and remember information, particularly when dealing with spatial data.
4. Decision-Making and Planning: By providing a clear visual understanding of data distribution, maps with pins can support informed decision-making and planning. This is particularly relevant in fields such as urban planning, resource management, and disaster response.
5. Trend Identification and Forecasting: Maps with pins can be used to track changes in data over time, allowing users to identify trends and patterns. This information can be used to predict future outcomes and make informed decisions.
Applications of Maps with Pins
The versatility of maps with pins has led to their widespread adoption across diverse industries and applications:
1. Business and Marketing: Businesses use maps with pins to visualize customer locations, identify market potential, track sales performance, and optimize marketing campaigns.
2. Real Estate: Real estate professionals use maps with pins to showcase property listings, identify market trends, and analyze neighborhood demographics.
3. Healthcare: Healthcare organizations use maps with pins to track disease outbreaks, identify healthcare access disparities, and optimize resource allocation.
4. Education: Educators use maps with pins to teach geography, history, and social studies concepts, providing students with a visual understanding of spatial relationships.
5. Environmental Science: Environmental scientists use maps with pins to track pollution levels, monitor deforestation, and assess the impact of climate change.
6. Emergency Response: Emergency responders use maps with pins to track the location of incidents, manage resources, and coordinate rescue efforts.
7. Social Sciences: Social scientists use maps with pins to analyze demographic data, identify social inequalities, and study spatial patterns of human behavior.
Examples of Maps with Pins
1. Customer Location Visualization: A business can use a map with pins to visualize the locations of its customers, highlighting areas with high customer concentration. This information can be used to optimize marketing campaigns, identify potential new markets, and plan store locations.
2. Disease Outbreak Tracking: Public health officials can use a map with pins to track the spread of a disease, identifying areas with high infection rates and implementing targeted interventions.
3. Real Estate Market Analysis: Real estate agents can use a map with pins to visualize property listings, highlighting areas with high demand and identifying potential investment opportunities.
4. Environmental Monitoring: Environmental scientists can use a map with pins to track pollution levels in different locations, identifying areas with high pollution and implementing remediation strategies.
FAQs About Maps with Pins
Q: What software can be used to create maps with pins?
A: There are numerous software options available for creating maps with pins, ranging from free online tools to professional mapping software. Some popular options include:
- Google Maps: A widely used platform offering various customization options for creating maps with pins.
- Leaflet: A free and open-source JavaScript library for creating interactive maps.
- Mapbox: A platform for creating custom maps with advanced features and data visualization capabilities.
- ArcGIS: A comprehensive Geographic Information System (GIS) software for professional mapping and analysis.
Q: How can I customize the appearance of pins on a map?
A: Most mapping software allows for customization of pin appearance, enabling users to:
- Change pin color: Represent different data categories or values using distinct colors.
- Adjust pin size: Use pin size to indicate the magnitude of data values.
- Select pin icons: Use icons to represent specific categories or data points.
- Add labels and tooltips: Provide additional information about each pin by adding labels or tooltips.
Q: What are some common data types used with maps with pins?
A: Maps with pins can be used to represent various data types, including:
- Location Data: GPS coordinates, addresses, or place names.
- Categorical Data: Data that can be grouped into distinct categories, such as types of businesses, disease classifications, or political districts.
- Numerical Data: Quantitative data, such as population density, sales figures, or pollution levels.
- Temporal Data: Data that changes over time, such as crime rates, traffic patterns, or weather conditions.
Q: What are the limitations of using maps with pins?
A: While maps with pins offer numerous benefits, they also have some limitations:
- Data Density: Maps with pins can become cluttered when representing a large number of data points, making it difficult to identify individual points or patterns.
- Spatial Bias: Maps with pins can be biased towards areas with higher data density, potentially underrepresenting areas with fewer data points.
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of maps with pins depends on the quality of the underlying data. Inaccurate data can lead to misleading conclusions.
Tips for Effective Use of Maps with Pins
1. Choose the Right Software: Select mapping software that meets your specific needs and provides the necessary customization options.
2. Use Clear and Concise Labels: Ensure that labels are legible and provide clear and concise information about each pin.
3. Use Consistent Color Schemes: Employ a consistent color scheme to represent different data categories, ensuring clarity and visual appeal.
4. Consider Data Density: Avoid overcrowding the map with too many pins, especially in areas with high data density.
5. Use Interactive Features: Leverage interactive features such as zoom, pan, and filtering to enhance user experience and data exploration.
6. Provide Contextual Information: Include additional information such as legends, scales, and data sources to provide context and enhance understanding.
7. Use Data Visualization Best Practices: Adhere to data visualization principles to create effective and informative maps with pins.
Conclusion: The Power of Visualizing Data Through Maps with Pins
Maps with pins have emerged as a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing spatial data, offering numerous benefits across diverse fields. By leveraging the power of visual representation, these maps provide a clear and engaging way to explore data patterns, identify trends, and support informed decision-making. As technology continues to evolve, maps with pins are likely to play an increasingly important role in our understanding of the world and the data that shapes it.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Visualizing Data: Exploring the Significance of Maps with Pins. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!