Stellwagen Bank: A Vital Ecosystem in the Heart of the Atlantic
Related Articles: Stellwagen Bank: A Vital Ecosystem in the Heart of the Atlantic
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Stellwagen Bank: A Vital Ecosystem in the Heart of the Atlantic. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Stellwagen Bank: A Vital Ecosystem in the Heart of the Atlantic
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Stellwagen Bank: A Vital Ecosystem in the Heart of the Atlantic
- 3.1 A Geographical Overview of Stellwagen Bank
- 3.2 Stellwagen Bank’s Remarkable Biodiversity
- 3.3 Stellwagen Bank’s Ecological Importance
- 3.4 Stellwagen Bank: A Legacy of Human Impact
- 3.5 Conservation Efforts and the Future of Stellwagen Bank
- 3.6 FAQs about Stellwagen Bank
- 3.7 Tips for Visiting Stellwagen Bank
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Stellwagen Bank: A Vital Ecosystem in the Heart of the Atlantic
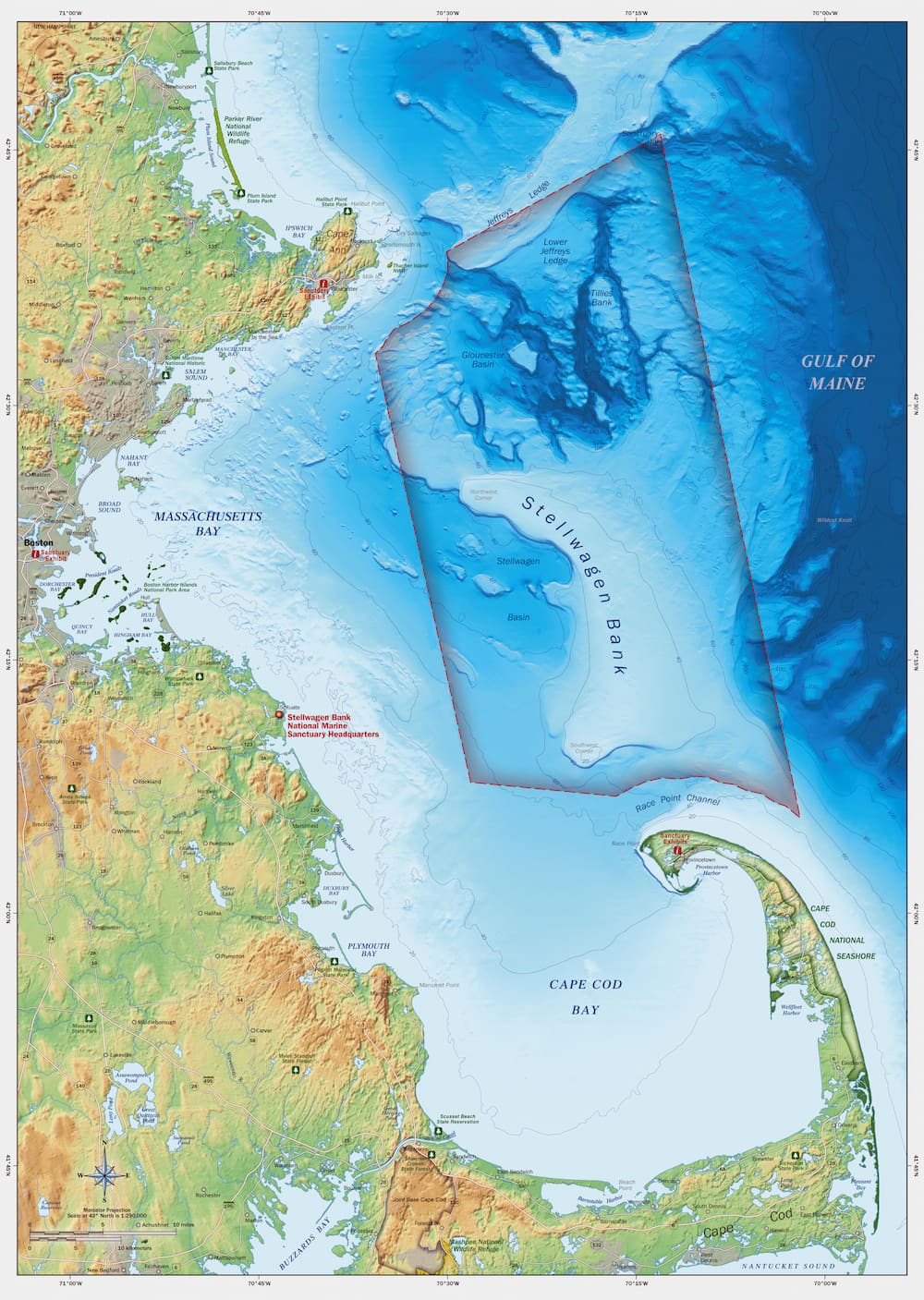
Stellwagen Bank, a submerged plateau located approximately 25 miles southeast of Boston, Massachusetts, is a remarkable marine ecosystem renowned for its rich biodiversity and ecological significance. This underwater haven, stretching over 1,200 square miles, plays a crucial role in the health and productivity of the North Atlantic Ocean, serving as a vital feeding ground, breeding habitat, and nursery for a diverse array of marine life.
A Geographical Overview of Stellwagen Bank
Stellwagen Bank is a product of glacial activity during the last Ice Age. The retreating glaciers carved out a vast underwater plain, leaving behind a shallow, rocky seabed that rises significantly from the surrounding ocean floor. This unique geological formation creates a complex and dynamic environment, characterized by strong currents, tidal flows, and nutrient-rich waters.
The bank’s shallow depths, ranging from 30 to 150 feet, allow sunlight to penetrate the water column, fueling the growth of phytoplankton, the foundation of the marine food web. These microscopic algae form the base of a rich and complex ecosystem, supporting a vast array of marine life, from tiny invertebrates to large whales.
Stellwagen Bank’s Remarkable Biodiversity
Stellwagen Bank is a haven for a remarkable diversity of marine species. Its unique combination of geological features and oceanographic conditions creates a dynamic and productive environment that attracts a wide range of life.
Marine Mammals:
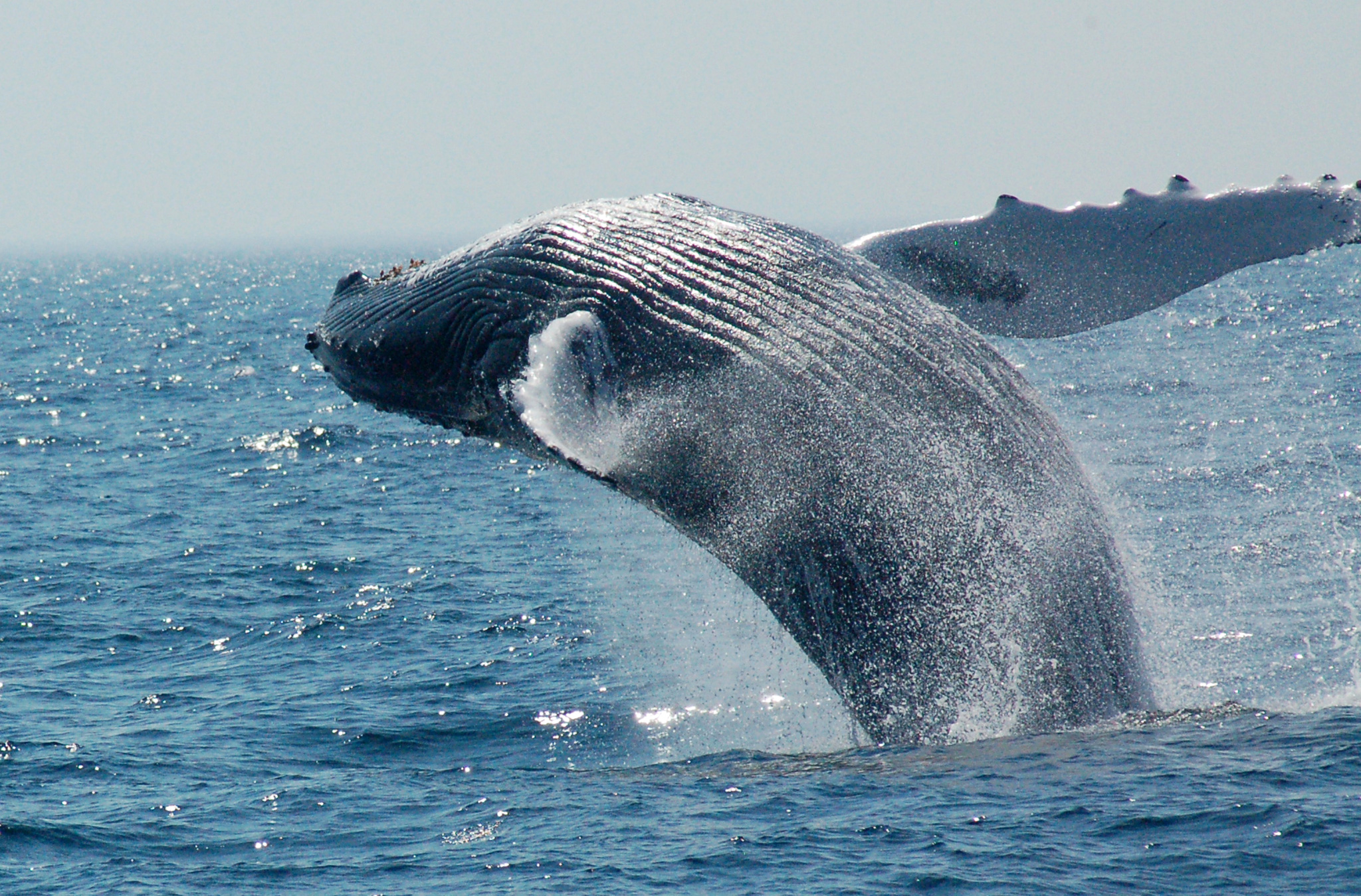
- Whales: Stellwagen Bank is a renowned whale watching destination, hosting a variety of whale species, including humpback whales, fin whales, minke whales, North Atlantic right whales, and sperm whales. These magnificent creatures migrate to the bank during the summer months to feed on abundant prey.
- Dolphins: Several species of dolphins, including common dolphins, Atlantic white-sided dolphins, and harbor porpoises, can be observed in the waters around Stellwagen Bank, often riding the bow waves of boats.
- Seals: Harbor seals and gray seals are common residents of Stellwagen Bank, utilizing the rocky outcroppings and shallow waters as breeding and pupping grounds.
Fish:
- Cod: Stellwagen Bank was once a major cod fishing ground, but overfishing has significantly depleted cod stocks. However, recent conservation efforts are showing signs of recovery.
- Haddock: Stellwagen Bank remains an important habitat for haddock, a commercially valuable fish species.
- Flounder: Various species of flounder, including winter flounder and yellowtail flounder, thrive in the sandy bottom of the bank.
- Swordfish: Swordfish, a large, migratory fish, are known to frequent the waters around Stellwagen Bank, particularly during the summer months.
Seabirds:
- Gulls: A variety of gulls, including herring gulls, great black-backed gulls, and laughing gulls, can be seen soaring overhead and diving for fish in the waters of Stellwagen Bank.
- Puffins: Atlantic puffins, a charismatic seabird with colorful beaks, breed on islands near Stellwagen Bank and forage for fish in its waters.
- Terns: Several species of terns, including common terns, roseate terns, and Arctic terns, are regular visitors to Stellwagen Bank, utilizing the area for feeding and nesting.
Invertebrates:
- Lobsters: Stellwagen Bank is a vital habitat for lobsters, which thrive in the rocky bottom and cold waters.
- Crabs: A variety of crab species, including blue crabs and Jonah crabs, are found in the waters around the bank.
- Scallops: Stellwagen Bank is home to a significant scallop population, which is commercially harvested.
Stellwagen Bank’s Ecological Importance
Stellwagen Bank’s ecological significance extends far beyond its rich biodiversity. Its unique geological features and oceanographic conditions create a complex and dynamic ecosystem that plays a vital role in the health and productivity of the North Atlantic Ocean.
- Feeding Ground: The bank’s shallow depths and abundant phytoplankton provide a rich food source for a wide range of marine life.
- Breeding Habitat: Stellwagen Bank serves as a critical breeding ground for many marine species, including whales, seals, and seabirds.
- Nursery: The bank’s sheltered waters provide a safe haven for young marine animals to grow and mature before venturing into the open ocean.
- Nutrient Cycling: The bank’s strong currents and tidal flows facilitate the transport of nutrients, supporting the growth of phytoplankton and the entire marine food web.
- Carbon Sink: The bank’s abundant marine life and phytoplankton play a crucial role in absorbing atmospheric carbon dioxide, mitigating the effects of climate change.
Stellwagen Bank: A Legacy of Human Impact
Stellwagen Bank has a long history of human interaction, dating back to the early days of European settlement in North America. The bank’s rich fishing grounds attracted fishermen for centuries, leading to the development of a thriving fishing industry. However, overfishing and other human activities have had a significant impact on the bank’s ecosystem.
Overfishing:
- Declining fish stocks: Decades of overfishing have significantly depleted fish populations, including cod, haddock, and flounder.
- Ecosystem imbalance: The decline in fish populations has disrupted the delicate balance of the marine food web, impacting other species that rely on these fish as food sources.
Pollution:
- Runoff from land: Runoff from agricultural and industrial activities can carry pollutants into the ocean, impacting the health of marine life.
- Oil spills: Oil spills can have devastating effects on marine ecosystems, killing wildlife and damaging habitats.
- Plastic pollution: Plastic debris can entangle and suffocate marine animals, and microplastics can be ingested by marine life, potentially causing health problems.
Climate Change:
- Ocean warming: Rising ocean temperatures are impacting the distribution and abundance of marine species, and can lead to coral bleaching and other ecological changes.
- Ocean acidification: The absorption of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere is causing the ocean to become more acidic, which can harm marine life, particularly those with calcium carbonate shells.
Conservation Efforts and the Future of Stellwagen Bank
Recognizing the ecological importance of Stellwagen Bank and the threats it faces, various conservation efforts have been implemented to protect and restore this vital ecosystem.
Stellwagen Bank National Marine Sanctuary:
- Established in 1992, the Stellwagen Bank National Marine Sanctuary protects over 842 square miles of marine habitat, encompassing the bank and surrounding waters.
- The sanctuary prohibits certain activities, such as oil drilling and disposal of hazardous materials, and promotes sustainable fishing practices.
- The sanctuary’s management plan includes research, education, and outreach programs aimed at promoting public awareness of the bank’s ecological importance.
Other Conservation Efforts:
- Fishing regulations: The National Marine Fisheries Service implements fishing regulations to manage fish stocks and protect marine habitats.
- Marine mammal protection: Laws and regulations protect marine mammals, including whales, dolphins, and seals, from harassment, hunting, and other threats.
- Research and monitoring: Ongoing research and monitoring efforts provide valuable data on the health and status of Stellwagen Bank’s ecosystem, informing conservation decisions.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Balancing human activities with conservation: Finding the right balance between human activities and conservation is a major challenge.
- Addressing climate change: Addressing the impacts of climate change on Stellwagen Bank is a crucial priority.
- Public education and engagement: Raising public awareness of the bank’s ecological importance and promoting responsible stewardship is essential for its long-term conservation.
FAQs about Stellwagen Bank
Q: What is Stellwagen Bank and where is it located?
A: Stellwagen Bank is a submerged plateau located approximately 25 miles southeast of Boston, Massachusetts, in the North Atlantic Ocean. It is a shallow, rocky seabed that rises significantly from the surrounding ocean floor.
Q: Why is Stellwagen Bank so important ecologically?
A: Stellwagen Bank is a vital ecosystem, serving as a feeding ground, breeding habitat, and nursery for a diverse array of marine life. Its shallow depths, strong currents, and nutrient-rich waters create a dynamic and productive environment that supports a rich and complex food web.
Q: What are some of the species that live in Stellwagen Bank?
A: Stellwagen Bank is home to a wide variety of marine life, including whales, dolphins, seals, cod, haddock, flounder, swordfish, gulls, puffins, terns, lobsters, crabs, and scallops.
Q: What threats does Stellwagen Bank face?
A: Stellwagen Bank faces various threats, including overfishing, pollution, and climate change. Overfishing has depleted fish stocks, pollution has contaminated the waters, and climate change is altering the ocean’s temperature, acidity, and circulation patterns.
Q: What is being done to protect Stellwagen Bank?
A: Conservation efforts to protect Stellwagen Bank include the establishment of the Stellwagen Bank National Marine Sanctuary, fishing regulations, marine mammal protection laws, and ongoing research and monitoring programs.
Q: How can I help protect Stellwagen Bank?
A: You can help protect Stellwagen Bank by supporting organizations that work to conserve marine ecosystems, reducing your use of plastic, supporting sustainable fishing practices, and advocating for policies that protect the ocean.
Tips for Visiting Stellwagen Bank
- Whale watching tours: Several tour operators offer whale watching trips to Stellwagen Bank, providing an opportunity to observe these magnificent creatures in their natural habitat.
- Responsible boating: If you are boating in the area, be sure to follow all safety regulations and be mindful of marine life.
- Support conservation efforts: Donate to organizations that work to protect Stellwagen Bank and its ecosystem.
- Learn more about the bank: Visit the Stellwagen Bank National Marine Sanctuary website or attend educational programs to learn more about this vital ecosystem.
Conclusion
Stellwagen Bank is a remarkable marine ecosystem that plays a crucial role in the health and productivity of the North Atlantic Ocean. Its rich biodiversity, dynamic environment, and ecological importance make it a treasure to be cherished and protected. By understanding the threats facing Stellwagen Bank and supporting conservation efforts, we can help ensure that this vital ecosystem thrives for generations to come.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Stellwagen Bank: A Vital Ecosystem in the Heart of the Atlantic. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!