Navigating the Web of Knowledge: A Comprehensive Guide to Linked Data and Knowledge Graphs
Related Articles: Navigating the Web of Knowledge: A Comprehensive Guide to Linked Data and Knowledge Graphs
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Web of Knowledge: A Comprehensive Guide to Linked Data and Knowledge Graphs. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Web of Knowledge: A Comprehensive Guide to Linked Data and Knowledge Graphs
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Web of Knowledge: A Comprehensive Guide to Linked Data and Knowledge Graphs
- 3.1 Understanding Linked Data: Connecting the Dots of Information
- 3.2 The Power of Knowledge Graphs: Organizing Information in a Structured Way
- 3.3 Benefits of Linked Data and Knowledge Graphs: A Deeper Dive
- 3.4 Real-World Applications of Linked Data and Knowledge Graphs
- 3.5 Challenges and Opportunities: The Future of Linked Data and Knowledge Graphs
- 3.6 FAQs about Linked Data and Knowledge Graphs
- 3.7 Tips for Working with Linked Data and Knowledge Graphs
- 3.8 Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Linked Data and Knowledge Graphs
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Web of Knowledge: A Comprehensive Guide to Linked Data and Knowledge Graphs

The internet has revolutionized the way we access and share information. However, the vast amount of data available online often presents a challenge: how to navigate this sea of knowledge effectively and efficiently? This is where linked data and knowledge graphs come into play, offering a powerful solution to organize and connect information in a structured and meaningful way.
Understanding Linked Data: Connecting the Dots of Information
Linked data, a key component of the Semantic Web, is a way to structure data on the web in a way that allows machines to understand and interpret it. This is achieved by linking data points across different sources using unique identifiers called URIs (Uniform Resource Identifiers). These links create a web of interconnected data, enabling machines to follow relationships and discover new information.
Imagine a simple scenario: you’re looking for information about the Eiffel Tower. A traditional search engine might return a list of websites containing the keywords "Eiffel Tower." However, with linked data, you could start with a URI representing the Eiffel Tower and follow the links to discover information about its architect, construction date, height, and even related tourist attractions.
The Power of Knowledge Graphs: Organizing Information in a Structured Way
Knowledge graphs, built upon the principles of linked data, represent a powerful tool for organizing and understanding information. They are essentially structured databases that capture relationships between entities, allowing machines to reason about the information they contain.
Imagine a knowledge graph about cities. It would include entities like cities, countries, populations, and landmarks. Each entity would have properties associated with it, and relationships would connect these entities. For example, the entity "Paris" would be connected to the entity "France" through the relationship "located in," and to the entity "Eiffel Tower" through the relationship "contains."
Benefits of Linked Data and Knowledge Graphs: A Deeper Dive
The use of linked data and knowledge graphs offers numerous benefits, transforming the way we interact with information:
-
Improved Data Discoverability: By connecting data points across various sources, linked data makes it easier to discover relevant information. Imagine a researcher looking for scientific articles on a specific topic. Linked data could help them find relevant articles even if they don’t know the exact keywords or search terms.
-
Enhanced Data Integration: Linked data facilitates the integration of data from different sources, creating a unified view of information. This is particularly useful for organizations with data spread across multiple systems.
-
Increased Data Accessibility: Linked data promotes open data access and sharing, making information available to a wider audience. This can foster collaboration and innovation, allowing researchers, developers, and businesses to leverage data in new ways.
-
Facilitated Data Analysis: Knowledge graphs provide a structured representation of information, making it easier to analyze data and extract insights. This can be valuable for researchers, businesses, and policymakers seeking to understand complex relationships and patterns within data.
-
Automated Reasoning and Machine Learning: Knowledge graphs enable machines to reason about information, making it possible to automate tasks like data analysis, information retrieval, and even decision-making. This is particularly relevant for artificial intelligence and machine learning applications.
Real-World Applications of Linked Data and Knowledge Graphs
The applications of linked data and knowledge graphs are vast and diverse, impacting various sectors:
-
Scientific Research: Linking data across different scientific disciplines can accelerate research and foster collaboration. Researchers can easily find related data, identify trends, and make new discoveries.
-
Healthcare: Knowledge graphs can be used to manage patient records, track disease outbreaks, and develop personalized treatments. Linking medical data can improve patient care and outcomes.
-
Business Intelligence: By analyzing linked data, businesses can gain valuable insights into customer behavior, market trends, and competitor activities. This information can inform strategic decisions and drive growth.
-
Government and Public Services: Knowledge graphs can be used to improve public services, such as transportation planning, disaster management, and social welfare programs. Linking data from different government agencies can streamline services and improve efficiency.
-
Education: Knowledge graphs can be used to create interactive learning experiences, providing students with a deeper understanding of complex topics. Linking educational content with real-world data can make learning more engaging and relevant.
Challenges and Opportunities: The Future of Linked Data and Knowledge Graphs
Despite the numerous benefits, implementing linked data and knowledge graphs presents some challenges:
-
Data Quality and Standardization: Ensuring data quality and consistency across various sources is crucial for building reliable knowledge graphs. Establishing standards and best practices for data representation is essential.
-
Scalability and Performance: Handling large volumes of data and complex relationships can be challenging, requiring efficient storage and retrieval mechanisms. Optimizing knowledge graph infrastructure for scalability and performance is critical.
-
Privacy and Security: Linking data raises concerns about privacy and security. Ensuring data is handled responsibly and protecting sensitive information is paramount.
-
Interoperability and Data Exchange: Establishing standards and protocols for data exchange between different systems is crucial for enabling interoperability and collaboration.
Despite these challenges, the future of linked data and knowledge graphs is promising. Ongoing research and development are addressing these challenges, leading to advancements in:
-
Semantic Web Technologies: New technologies are being developed to improve data interoperability, enhance data quality, and facilitate automated reasoning.
-
Knowledge Graph Construction and Maintenance: Tools and techniques are being developed to automate the construction and maintenance of large-scale knowledge graphs, making them more accessible and scalable.
-
Data Governance and Privacy: Frameworks and policies are being developed to ensure responsible data governance and protect privacy in linked data environments.
FAQs about Linked Data and Knowledge Graphs
Q: What is the difference between linked data and knowledge graphs?
A: Linked data is a foundational principle for structuring data on the web using URIs and linking relationships. Knowledge graphs are specific implementations of linked data, representing information in a structured database with entities, properties, and relationships.
Q: How can I access linked data?
A: Several platforms and tools provide access to linked data. Some popular examples include:
- DBpedia: A knowledge graph extracted from Wikipedia, offering structured information about real-world entities.
- Freebase: A large-scale knowledge graph developed by Google, containing information about people, places, and concepts.
- Linked Open Data Cloud: A collection of linked data datasets from various sources, covering diverse topics.
Q: What are some examples of linked data applications?
A: Linked data finds applications in various domains, including:
- Semantic search: Using linked data to improve search results by understanding the meaning of queries and retrieving relevant information from multiple sources.
- Personalized recommendations: Leveraging linked data to provide personalized recommendations based on user preferences and past interactions.
- Data integration and analysis: Combining data from different sources using linked data to gain a holistic view of information and extract valuable insights.
Q: What are the future trends in linked data and knowledge graphs?
A: Future trends include:
- Increased adoption: Linked data and knowledge graphs are expected to become increasingly prevalent in various sectors, driving innovation and transforming how we interact with information.
- Artificial intelligence integration: Knowledge graphs are playing a crucial role in artificial intelligence and machine learning applications, enabling machines to reason about information and make more informed decisions.
- Data governance and ethics: As linked data becomes more widespread, establishing robust data governance frameworks and ethical guidelines will be essential for responsible data sharing and use.
Tips for Working with Linked Data and Knowledge Graphs
- Start with a clear objective: Define your goals and identify the specific information you need from linked data sources.
- Choose the right tools and platforms: Select tools and platforms that best suit your needs and provide the necessary functionality for working with linked data.
- Ensure data quality: Verify the accuracy and reliability of data sources before incorporating them into your knowledge graphs.
- Understand the underlying relationships: Pay attention to the relationships between entities in linked data and knowledge graphs to gain a deeper understanding of the information.
- Collaborate and share knowledge: Engage with the linked data community and share your knowledge and experiences to foster innovation and collaboration.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Linked Data and Knowledge Graphs
Linked data and knowledge graphs represent a paradigm shift in how we manage and interact with information. They offer a powerful solution to organize, connect, and reason about data, enabling us to unlock new insights and drive innovation in various fields. By embracing these technologies, we can navigate the vast web of knowledge more effectively, making information more accessible, understandable, and actionable for everyone. As these technologies continue to evolve, they promise to transform the way we live, work, and learn, ushering in a new era of knowledge-driven discovery and collaboration.


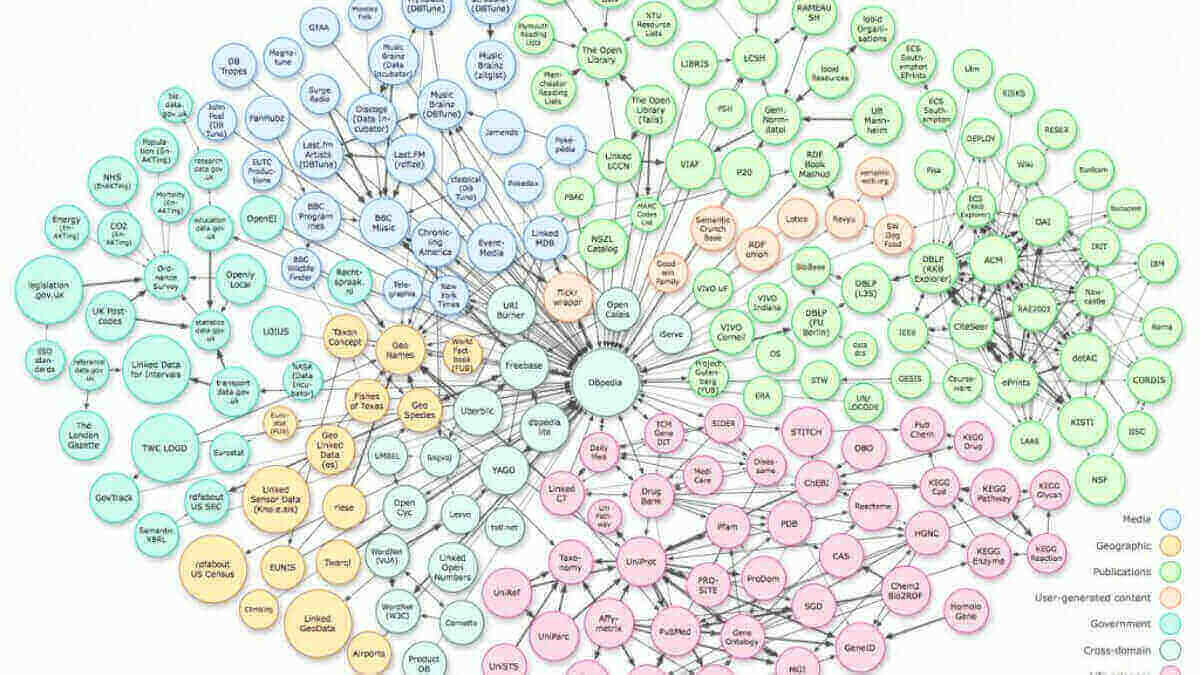

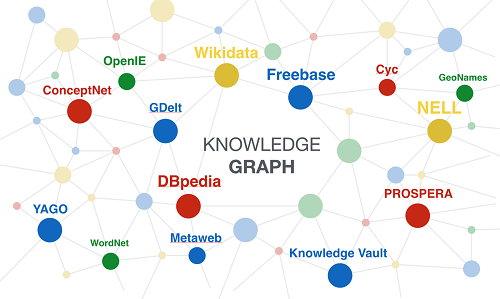

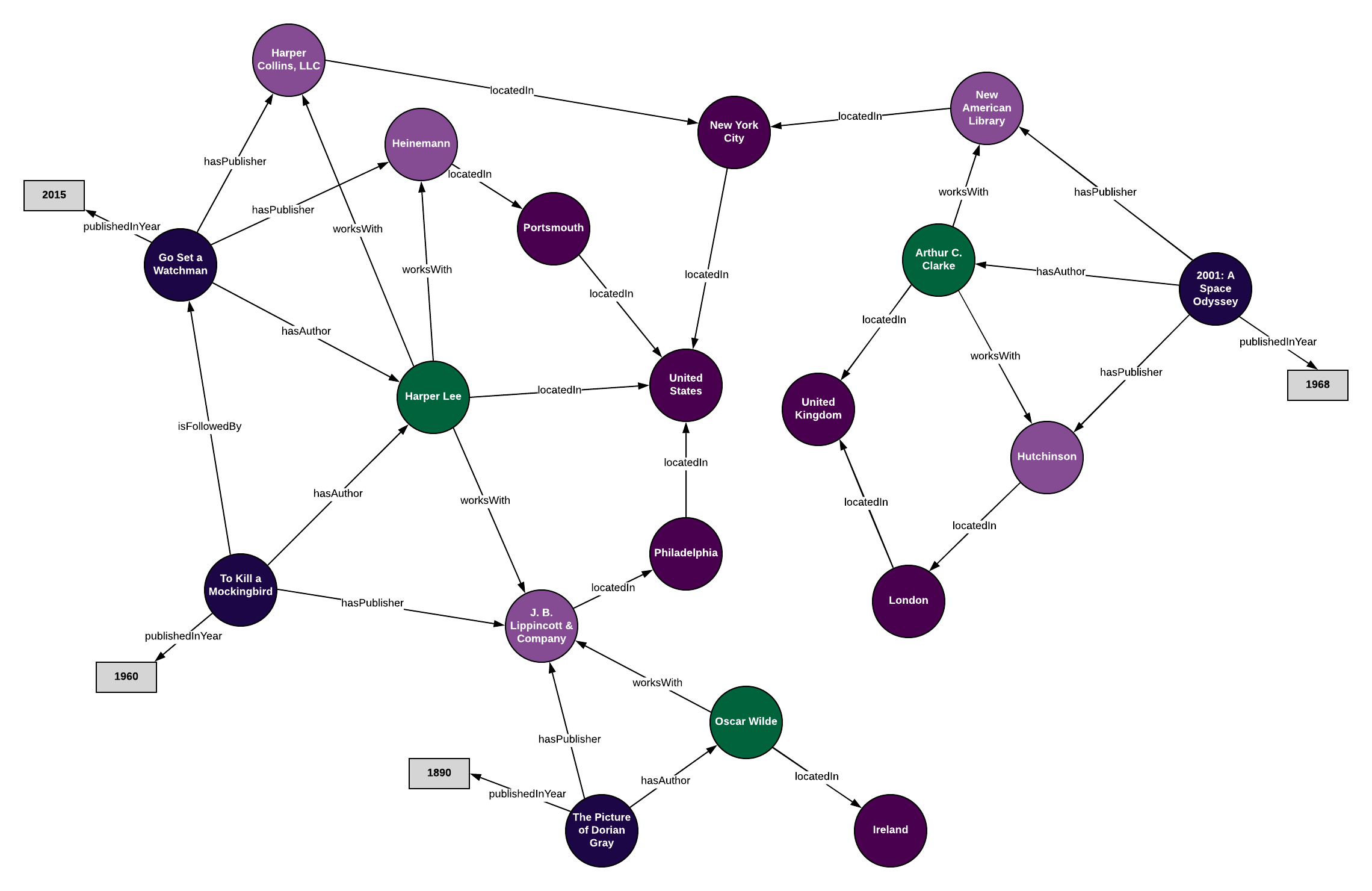
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Web of Knowledge: A Comprehensive Guide to Linked Data and Knowledge Graphs. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!