Navigating the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to the Nepali Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to the Nepali Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to the Nepali Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to the Nepali Map

The Nepali map, a visual representation of the Himalayan nation, is more than just a collection of lines and borders. It embodies the country’s unique geography, its diverse landscapes, and the spirit of its people. Understanding the Nepali map provides invaluable insights into the nation’s history, culture, and present-day challenges. This article aims to offer a comprehensive exploration of the Nepali map, unraveling its complexities and highlighting its significance.
A Tapestry of Terrain:
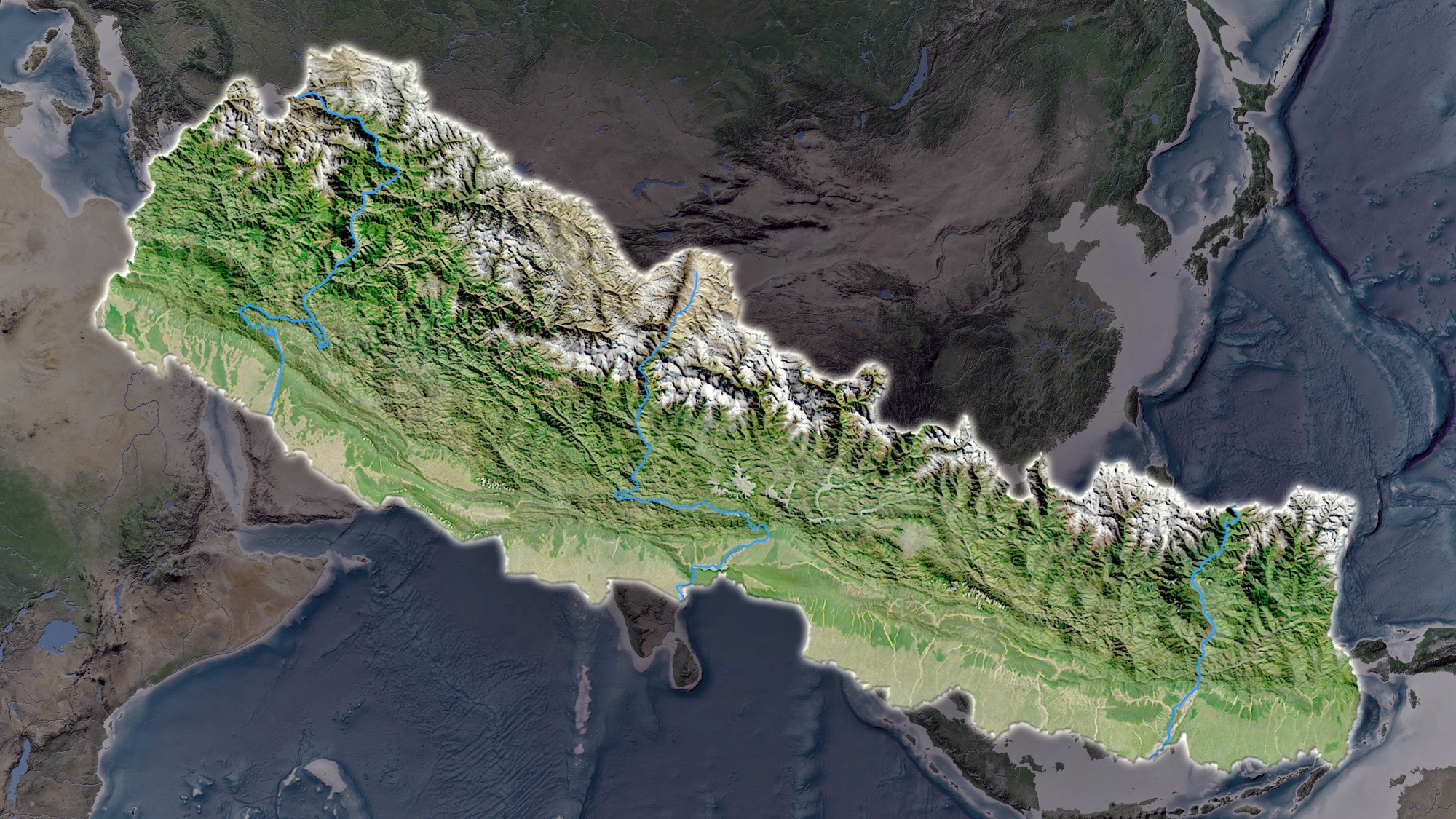
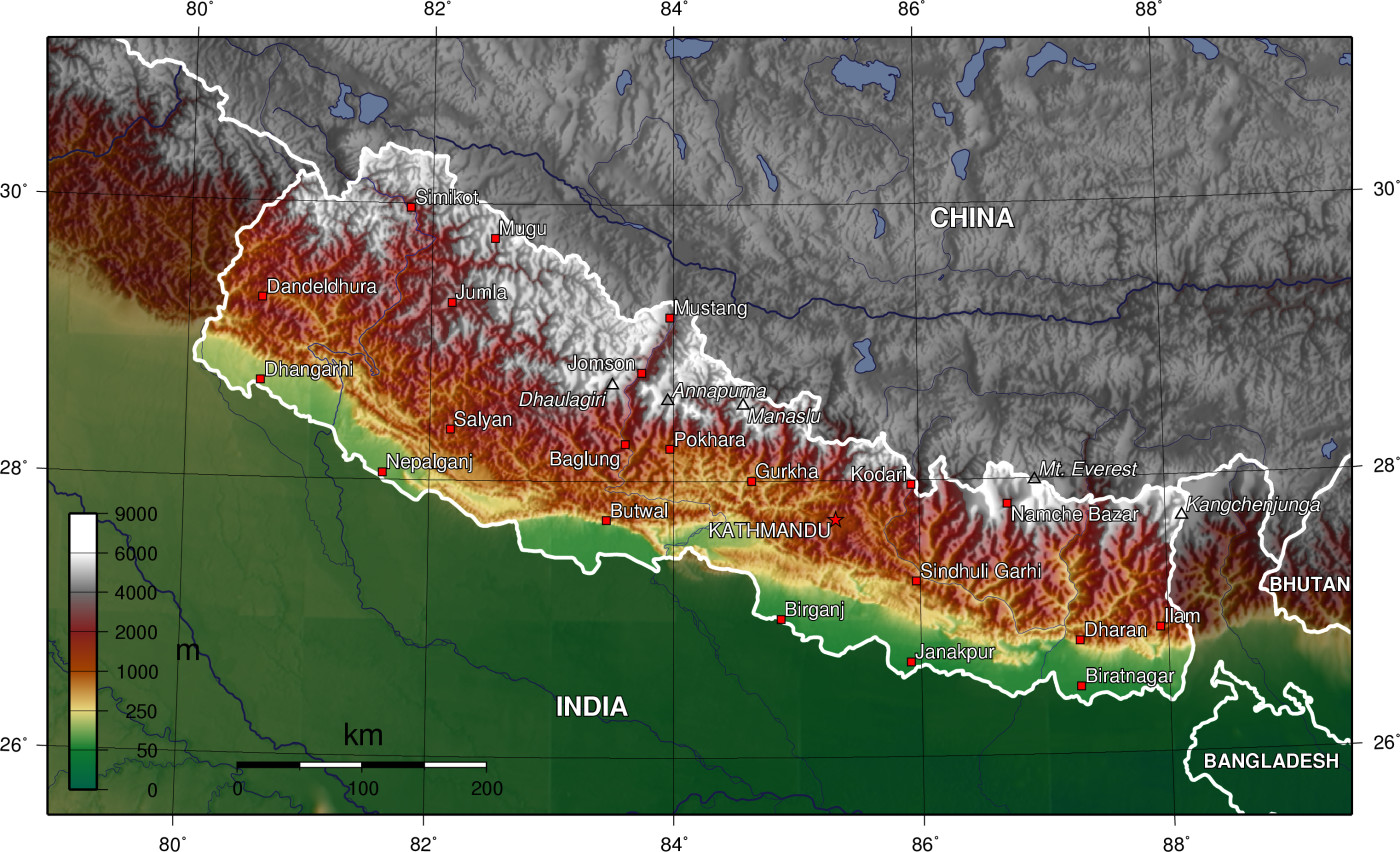
Nepal’s map is a testament to its geographical diversity. The country is sandwiched between two giants, India and China, and its landscape reflects this unique position. The Himalayas, the world’s highest mountain range, dominate the north, culminating in Mount Everest, the tallest peak on Earth. This mountainous terrain transitions southward into the rolling hills of the Mahabharat Range, followed by the fertile plains of the Terai region, bordering India.
Divisions and Demarcations:
The Nepali map is divided into seven provinces, each with its distinct character and identity. These provinces are further subdivided into 77 districts, each with its own administrative and cultural nuances. The map also reveals the country’s intricate network of rivers, including the mighty Karnali, the sacred Bagmati, and the turbulent Kosi. These waterways have played a crucial role in shaping the Nepali landscape and influencing its economy and culture.
Beyond the Borders:
The Nepali map is not merely a geographical representation; it also reflects the country’s rich cultural tapestry. The map reveals the distribution of different ethnic groups, each with its unique traditions, languages, and beliefs. It highlights the importance of preserving Nepal’s diverse cultural heritage and fostering unity amidst its diverse communities.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Nepal’s map also reveals the country’s challenges, particularly those related to its mountainous terrain. Access to remote areas is often difficult, hindering development and economic growth. The map also highlights the vulnerability of the Himalayan region to climate change, posing threats to the delicate ecosystem and the livelihoods of local communities. However, the map also presents opportunities. The country’s diverse landscape and rich cultural heritage offer potential for tourism and sustainable development.
Understanding the Importance:
The Nepali map serves as a vital tool for various purposes:
- Planning and Development: The map provides crucial data for infrastructure development, resource management, and disaster preparedness.
- Tourism and Recreation: The map guides travelers to explore the country’s diverse landscapes, from the majestic Himalayas to the serene Terai plains.
- Education and Awareness: The map fosters understanding of Nepal’s geography, culture, and history, promoting national identity and fostering appreciation for the country’s uniqueness.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What are the highest peaks in Nepal?
A: The highest peaks in Nepal are Mount Everest (8,848.86 m), Lhotse (8,516 m), Kanchenjunga (8,586 m), Makalu (8,485 m), and Cho Oyu (8,188 m).
Q: What is the most densely populated region in Nepal?
A: The Terai region, located in the southern plains, is the most densely populated region in Nepal.
Q: What are the major languages spoken in Nepal?
A: Nepali is the official language of Nepal. However, the country is home to a diverse array of languages, including Maithili, Bhojpuri, Tharu, Tamang, and Gurung, among others.
Q: What are the major religions practiced in Nepal?
A: Hinduism is the dominant religion in Nepal, followed by Buddhism. Other religions practiced in the country include Islam, Christianity, and Sikhism.
Tips for Understanding the Nepali Map:
- Study the physical features: Pay attention to the Himalayas, the Mahabharat Range, and the Terai plains.
- Explore the provinces and districts: Understand the geographical distribution of the country’s administrative divisions.
- Identify major rivers: Learn about the importance of rivers in shaping Nepal’s landscape and culture.
- Research ethnic groups: Discover the diverse cultural heritage of Nepal’s various communities.
- Consider environmental challenges: Recognize the impact of climate change on Nepal’s fragile ecosystem.
Conclusion:
The Nepali map is a powerful visual tool that encapsulates the country’s unique geography, diverse culture, and multifaceted identity. By understanding its complexities and appreciating its significance, we can gain a deeper insight into Nepal’s past, present, and future. The map serves as a guide for development, a source of inspiration for travelers, and a testament to the enduring spirit of the Nepali people. It reminds us that beyond the lines and borders, lies a nation rich in natural beauty, cultural diversity, and boundless potential.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to the Nepali Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!