Navigating the Roanoke River: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Geography and Significance
Related Articles: Navigating the Roanoke River: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Geography and Significance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Roanoke River: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Geography and Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Roanoke River: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Geography and Significance

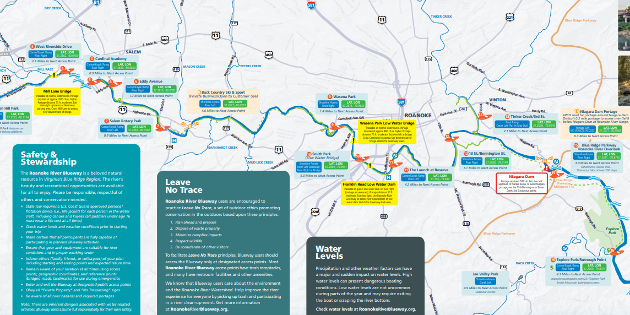
The Roanoke River, a vital waterway coursing through the heart of Virginia and North Carolina, holds a rich history and ecological significance. Understanding the river’s geography through maps is crucial for appreciating its impact on the surrounding environment, its role in human development, and its potential for future conservation efforts. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a detailed exploration of the Roanoke River’s map, highlighting its key features, historical context, and contemporary relevance.
A River’s Journey: Tracing the Roanoke on the Map
The Roanoke River originates in the Blue Ridge Mountains of Virginia, specifically in Patrick County. Its journey begins as a small, meandering stream, gradually gaining volume and width as it flows eastward. The river’s course is marked by several significant features:
- Headwaters: The Roanoke River’s headwaters are nestled within the Blue Ridge Mountains, specifically in the vicinity of the Patrick Henry National Memorial and the Blue Ridge Parkway. This mountainous region provides the river with its initial source of water, often fed by snowmelt and rainfall.
- Dan River Confluence: The Roanoke River joins forces with the Dan River, a tributary originating in North Carolina, forming a larger waterway that continues eastward. This confluence is a significant point, marking the beginning of the Roanoke River’s journey through the Piedmont region.
- Fall Line: As the river descends from the Piedmont region to the Coastal Plain, it encounters the Fall Line, a geological feature characterized by waterfalls and rapids. This transition zone marks a significant shift in the river’s character, from a more mountainous and rapid flow to a wider, slower course.
- Tidal Influence: The Roanoke River’s lower reaches are subject to tidal influences from the Albemarle Sound, creating a unique ecosystem where freshwater and saltwater mix. This estuary is home to a diverse array of plant and animal life, including commercially important species like oysters and crabs.
- Mouth: The Roanoke River finally reaches its terminus at the Albemarle Sound, a large, shallow body of water connected to the Atlantic Ocean. This final destination marks the end of the river’s journey, a testament to its vital role in shaping the surrounding landscape and providing a critical habitat for numerous species.
Mapping the River’s History: A Journey Through Time
The Roanoke River’s map tells a story that stretches back centuries, reflecting the intertwining of human history and natural processes. Key historical moments are vividly etched into the river’s landscape:
- Native American Presence: The Roanoke River was a vital resource for the native tribes who inhabited the region long before European colonization. The river provided sustenance, transportation, and a source of fresh water. Archaeological evidence suggests that Native Americans had established settlements along the river’s banks, leaving behind remnants of their culture and way of life.
- Early European Exploration: European explorers, driven by the pursuit of new lands and resources, ventured into the Roanoke River’s territory in the 16th century. The river’s navigable waters facilitated their exploration and the establishment of early settlements. The Roanoke Colony, a failed attempt at English colonization, is directly linked to the river’s history, adding a layer of intrigue and mystery to the region.
- Industrial Development: The Roanoke River played a crucial role in the industrial development of the region, particularly during the 19th and 20th centuries. The river’s waterpower was harnessed to drive mills and factories, fueling economic growth and transforming the surrounding landscape.
- Transportation Hub: The Roanoke River served as a vital transportation artery, connecting inland communities to coastal markets. Boats and barges traversed the river, transporting goods and people, facilitating trade and communication between distant regions.
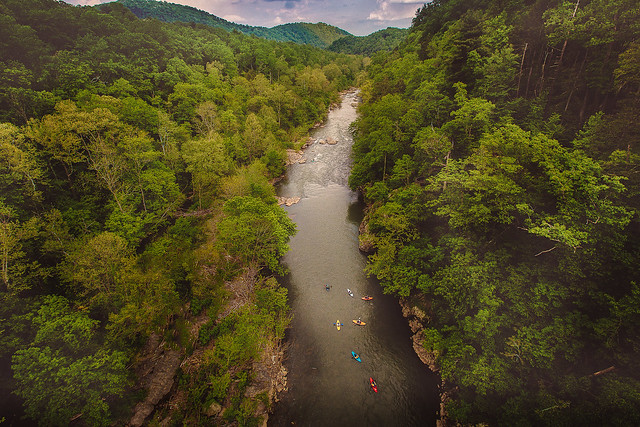
- Modern Recreation: Today, the Roanoke River is a popular destination for recreational activities, attracting visitors from near and far. The river’s scenic beauty, diverse wildlife, and ample fishing opportunities make it a prime destination for kayaking, canoeing, fishing, and birdwatching.
The River’s Significance: A Vital Ecosystem and Economic Resource
The Roanoke River’s map reveals a dynamic ecosystem that supports a diverse array of life. Its ecological significance is evident in the variety of habitats it provides:
- Water Quality: The Roanoke River serves as a critical source of fresh water for surrounding communities and industries. Maintaining its water quality is essential for human health, agriculture, and the overall health of the ecosystem.
- Wildlife Habitat: The river’s diverse habitats, ranging from forested wetlands to tidal marshes, support a rich tapestry of plant and animal life. Fish, birds, mammals, and reptiles rely on the river for food, shelter, and breeding grounds.
- Biodiversity: The Roanoke River’s ecosystem is home to a remarkable array of species, including endangered and threatened species. Protecting the river’s biodiversity is crucial for preserving the natural balance of the region.
- Economic Benefits: The Roanoke River contributes significantly to the regional economy. Recreation, fishing, and tourism generate revenue, while the river also provides essential resources for agriculture and industry.
Navigating the Future: Conservation and Sustainable Use
The Roanoke River faces a range of challenges, including pollution, habitat degradation, and climate change. Understanding the river’s map and its interconnectedness with the surrounding environment is critical for addressing these challenges:
- Water Quality Management: Protecting the river’s water quality requires a concerted effort to reduce pollution from agricultural runoff, industrial discharges, and urban development.
- Habitat Restoration: Restoring degraded habitats along the river’s banks, such as wetlands and forests, is essential for supporting biodiversity and providing natural buffers against pollution.
- Climate Change Adaptation: Addressing the impacts of climate change, including rising sea levels, more frequent droughts, and extreme weather events, requires proactive measures to protect the river’s ecosystem and its vital services.
FAQs About the Roanoke River Map
Q: What is the best map for exploring the Roanoke River?
A: There are several excellent map resources available for exploring the Roanoke River. Online mapping services such as Google Maps and ArcGIS provide detailed topographical maps, while specialized boating and fishing maps offer specific information for navigating the river’s waterways.
Q: What are some key landmarks along the Roanoke River?
A: Notable landmarks along the Roanoke River include the Roanoke Rapids Dam, the Weldon Falls, the Roanoke River Greenway, and the historic town of Roanoke Rapids, North Carolina.
Q: How can I contribute to the Roanoke River’s conservation?
A: You can contribute to the Roanoke River’s conservation by supporting organizations dedicated to its protection, reducing your own water usage, practicing responsible waste disposal, and advocating for sustainable land use practices.
Tips for Using the Roanoke River Map
- Explore Different Map Types: Utilize various map types, such as topographic, satellite, and street maps, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the river’s landscape.
- Focus on Specific Areas of Interest: Use the map to zoom in on specific areas of interest, such as historical sites, wildlife habitats, or recreational areas.
- Combine with Other Resources: Integrate the map with other resources, such as guidebooks, websites, and articles, to enhance your understanding of the river’s history, ecology, and cultural significance.
- Share Your Discoveries: Share your findings and experiences with others to promote awareness and appreciation for the Roanoke River’s beauty and importance.
Conclusion
The Roanoke River’s map serves as a powerful tool for understanding its rich history, diverse ecosystem, and ongoing challenges. By navigating its waters, both literally and figuratively, we gain a deeper appreciation for this vital waterway and its role in shaping the lives of those who live along its banks. Through conservation efforts and sustainable use, we can ensure that the Roanoke River continues to flow for generations to come, enriching the lives of people and wildlife alike.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Roanoke River: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Geography and Significance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!