Navigating the Complex Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Middle East and Israel Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Complex Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Middle East and Israel Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Complex Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Middle East and Israel Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Complex Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Middle East and Israel Map

The Middle East, a region often shrouded in geopolitical complexities, holds immense historical, cultural, and strategic significance. Understanding the intricate tapestry of its geography, particularly focusing on the position of Israel within this dynamic landscape, is crucial for navigating the region’s multifaceted challenges and opportunities. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the Middle East and Israel map, highlighting its importance in unraveling the region’s complexities and facilitating informed understanding.
A Geographical Overview
The Middle East, a vast and diverse region, encompasses a vast expanse of land stretching from North Africa to Central Asia. Its geographical boundaries are not definitively fixed, but generally include countries such as Egypt, Sudan, Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Oman, the United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Bahrain, Kuwait, Iran, Iraq, Jordan, Syria, Lebanon, and Turkey. This region is characterized by its diverse landscapes, ranging from vast deserts and fertile plains to towering mountains and coastal plains.
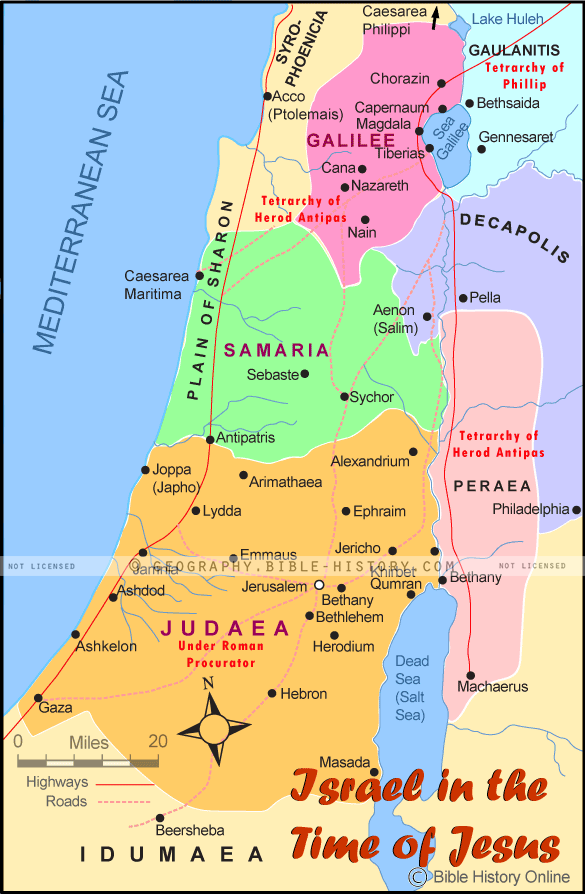
Israel, a relatively small country, occupies a strategically vital location in the eastern Mediterranean. It shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the southwest, and the Gaza Strip and West Bank to the west. The country’s unique geographical features, including the Jordan Valley, the Negev Desert, and the coastal plain, have shaped its history and continue to influence its present.
Historical Significance
The Middle East has been a cradle of civilization for millennia, witnessing the rise and fall of empires, the birth of religions, and the development of trade routes that connected the world. From the ancient Mesopotamian civilizations to the rise of Islam, the region has played a pivotal role in shaping human history.
Israel, specifically, holds immense religious significance for Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Jerusalem, considered holy by all three religions, has been a focal point of conflict and pilgrimage for centuries. The land of Israel has been a site of constant struggle and negotiation, reflecting the complex historical and religious ties that bind the region.
Political Dynamics
The Middle East is characterized by complex political dynamics, often marked by conflict and instability. The region has witnessed numerous wars, revolutions, and political upheavals, fueled by factors such as religious differences, territorial disputes, and resource scarcity.
Israel’s relationship with its neighbors, particularly with the Palestinian territories, remains a key source of tension and conflict. The ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict, rooted in competing claims to the same land, has been a major source of instability in the region for decades.
The map of the Middle East and Israel offers a visual representation of these intricate political realities. It helps us understand the geographical proximity of countries, the location of key conflict zones, and the potential for cooperation and conflict.
Strategic Importance
The Middle East holds immense strategic importance due to its vast energy reserves, particularly oil and natural gas. The region’s strategic location at the crossroads of continents makes it a vital hub for global trade and transportation. The Suez Canal, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea, is a critical waterway for international shipping.
Israel, despite its relatively small size, is a technologically advanced nation with a strong military. Its strategic position in the region, combined with its technological prowess, makes it a key player in regional security dynamics.
Economic Landscape
The Middle East’s economic landscape is diverse, ranging from oil-rich economies like Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates to countries like Lebanon and Jordan that rely heavily on tourism and agriculture. The region faces challenges such as poverty, unemployment, and economic inequality.
Israel, known for its technological innovation and entrepreneurial spirit, has a thriving economy. Its high-tech sector, particularly in areas such as cybersecurity and artificial intelligence, is globally recognized. The country also boasts a strong agricultural sector and a burgeoning tourism industry.
Cultural Diversity
The Middle East is a melting pot of cultures, with a rich tapestry of languages, religions, traditions, and art forms. From the vibrant souks of Marrakech to the ancient mosques of Istanbul, the region offers a unique and diverse cultural experience.
Israel, despite its relatively small size, is a culturally diverse nation. Its population comprises Jews of various backgrounds, as well as Arab citizens, Druze, and other minority groups. This cultural diversity enriches the country’s artistic landscape, cuisine, and social fabric.
Challenges and Opportunities
The Middle East faces a myriad of challenges, including political instability, armed conflict, economic inequality, and environmental degradation. These challenges require a multi-faceted approach, involving cooperation among regional actors, international support, and a focus on sustainable development.
Despite these challenges, the Middle East also presents significant opportunities for progress and development. The region’s rich cultural heritage, its vast energy reserves, and its strategic location offer potential for economic growth, technological advancement, and regional cooperation.
Understanding the Map: Key Insights
The map of the Middle East and Israel provides a vital tool for understanding the complexities of the region. By analyzing the geographical relationships, political boundaries, and historical context, we can gain valuable insights into the region’s dynamics:
- Proximity and Conflict: The map highlights the proximity of countries, particularly the close proximity of Israel to its neighbors. This proximity has often fueled conflict and tension, as territorial disputes and security concerns are magnified by geographical closeness.
- Resource Distribution: The map reveals the distribution of key resources, such as oil and water, across the region. This distribution has played a significant role in shaping economic development and political relationships, often leading to competition and conflict over scarce resources.
- Strategic Importance: The map illustrates the strategic importance of the region, particularly its location at the crossroads of continents and its control over vital waterways. This strategic significance has attracted global attention and influence, shaping the region’s political landscape and security dynamics.
- Cultural and Religious Diversity: The map reveals the cultural and religious diversity of the region, with different faiths and traditions coexisting within close proximity. This diversity has both enriched the region’s cultural landscape and presented challenges in navigating religious and ethnic tensions.
FAQs
Q: What is the significance of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict in the Middle East map?
A: The Israeli-Palestinian conflict is a central issue in the Middle East map. It represents the ongoing struggle over land and resources, rooted in competing claims to the same territory. The conflict has fueled instability, violence, and political deadlock in the region for decades.
Q: How does the map of the Middle East and Israel reflect the region’s historical and cultural significance?
A: The map highlights the historical and cultural significance of the region, showcasing the ancient civilizations that flourished in the area, the birthplaces of major religions, and the crossroads of trade routes that connected the world. It also reveals the cultural diversity of the region, with different languages, religions, and traditions interwoven within its geographical boundaries.
Q: What are the key challenges facing the Middle East in terms of its political and economic landscape?
A: The Middle East faces a multitude of challenges, including political instability, armed conflict, economic inequality, and environmental degradation. These challenges are often interconnected, fueled by factors such as resource scarcity, historical grievances, and political corruption.
Q: What are the potential opportunities for progress and development in the Middle East?
A: Despite the challenges, the Middle East also presents significant opportunities for progress and development. The region’s rich cultural heritage, its vast energy reserves, and its strategic location offer potential for economic growth, technological advancement, and regional cooperation.
Tips for Understanding the Middle East Map
- Study the geographical features: Pay attention to the location of major bodies of water, mountain ranges, and deserts. These features shape the region’s climate, resources, and strategic importance.
- Analyze political boundaries: Examine the borders between countries, identifying areas of potential conflict or cooperation. Understand the historical context behind these boundaries.
- Explore cultural and religious influences: Investigate the distribution of different religious and ethnic groups within the region. This will help you understand the cultural diversity and potential sources of tension.
- Consider economic factors: Analyze the distribution of resources and the economic development of different countries. This will provide insights into the region’s economic landscape and potential for growth.
- Stay informed about current events: Keep up-to-date on political developments, conflict zones, and economic trends in the region. This will help you understand the dynamic nature of the Middle East map.
Conclusion
The map of the Middle East and Israel serves as a powerful tool for understanding the region’s complexities and navigating its multifaceted challenges and opportunities. By analyzing the geographical relationships, political boundaries, historical context, and cultural influences, we gain a deeper appreciation for the region’s significance in shaping global affairs. It is crucial to approach the region with a nuanced understanding of its history, culture, and political dynamics, recognizing the need for dialogue, cooperation, and a commitment to peaceful resolution of conflicts. The Middle East map, while reflecting the region’s challenges, also holds the potential for a brighter future, one where peace, prosperity, and understanding prevail.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Complex Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Middle East and Israel Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!