Delving into the Boundaries of the Promised Land: A Geographical and Historical Exploration
Related Articles: Delving into the Boundaries of the Promised Land: A Geographical and Historical Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Delving into the Boundaries of the Promised Land: A Geographical and Historical Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Delving into the Boundaries of the Promised Land: A Geographical and Historical Exploration
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Delving into the Boundaries of the Promised Land: A Geographical and Historical Exploration
- 3.1 The Promised Land in Biblical Texts: A Shifting Landscape
- 3.2 Historical Evolution of the Promised Land’s Boundaries
- 3.3 The Promised Land in Different Cultural and Religious Contexts
- 3.4 The Enduring Significance of the Promised Land
- 3.5 FAQs Regarding the Boundaries of the Promised Land
- 3.6 Tips for Understanding the Boundaries of the Promised Land
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Delving into the Boundaries of the Promised Land: A Geographical and Historical Exploration

The concept of the "Promised Land" holds significant weight in both religious and historical contexts. For many, it signifies a place of refuge, prosperity, and divine favor. However, understanding the geographical boundaries of this land, as depicted in biblical texts and historical narratives, requires a nuanced exploration. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the Promised Land’s boundaries, examining its evolution throughout history, its significance in different cultural and religious contexts, and its lasting impact on our understanding of geography, history, and faith.
The Promised Land in Biblical Texts: A Shifting Landscape
The biblical narrative of the Promised Land begins with the covenant God made with Abraham, promising him and his descendants a land flowing with milk and honey. However, the exact boundaries of this land evolve throughout the biblical texts, reflecting the changing dynamics of the Israelites’ journey and their relationship with their neighbors.
The Book of Genesis: The initial promise to Abraham (Genesis 12:7) is broad, encompassing the land "from the river of Egypt to the great river, the river Euphrates." This vast territory encompasses a significant portion of the Near East, stretching far beyond the borders of modern Israel.
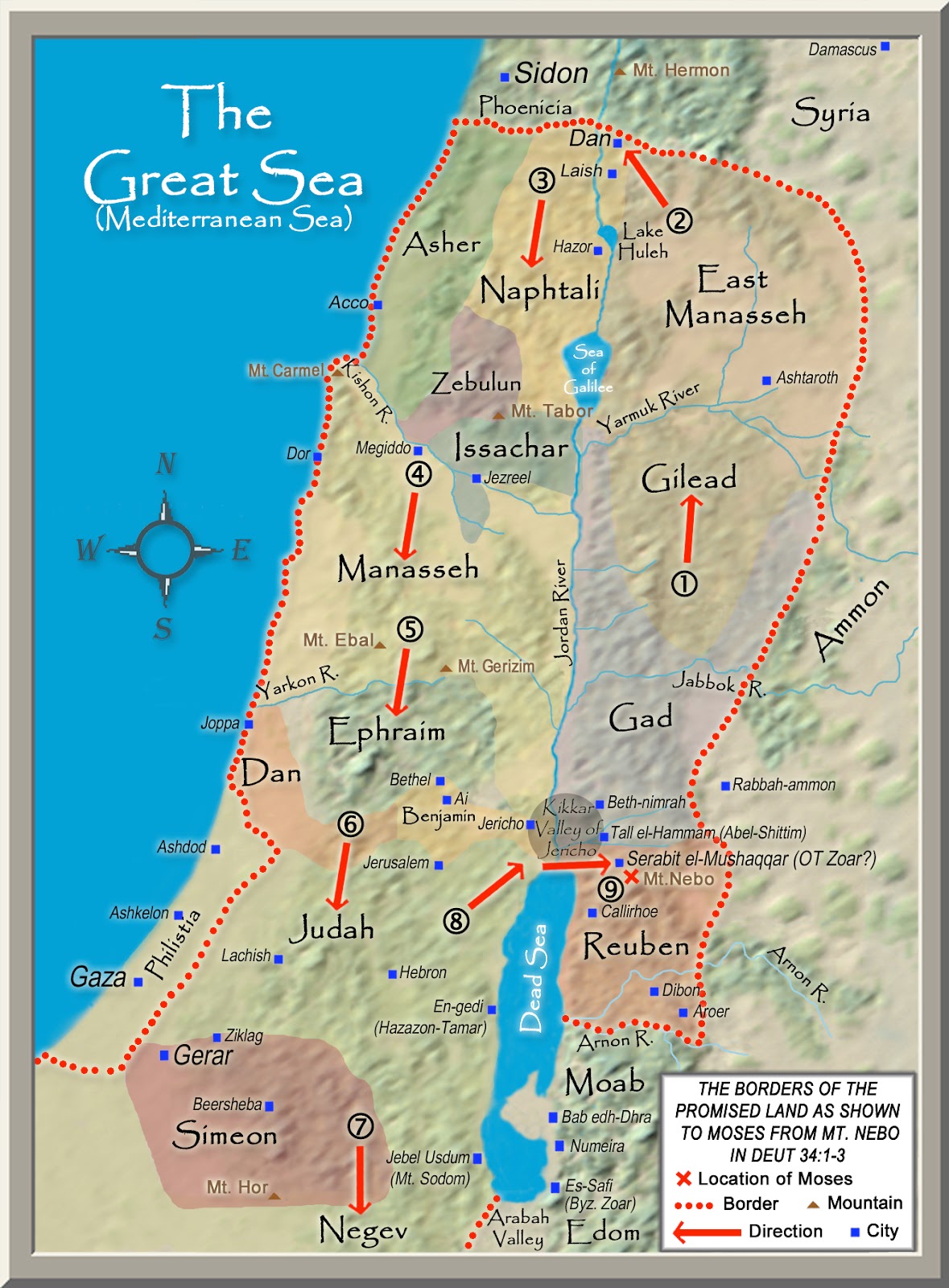
The Book of Exodus: The Promised Land becomes more defined in the context of the Exodus narrative. God reveals the land to Moses, outlining its boundaries as "from the Red Sea to the Sea of the Philistines, and from the desert to the river Euphrates" (Exodus 23:31). This description introduces the Red Sea and the Sea of the Philistines (Mediterranean Sea) as defining points, narrowing the focus to a more specific region.
The Book of Joshua: The conquest of Canaan under Joshua provides a more detailed account of the Promised Land’s boundaries. The land is divided into twelve tribes, each receiving a specific territory. The boundaries of these territories are described in detail, encompassing regions such as the Jordan Valley, the Negev Desert, the coastal plain, and the mountainous regions of Judea and Samaria.
The Book of Ezekiel: The prophet Ezekiel offers a vision of a restored Israel, with boundaries that stretch from the Mediterranean Sea to the Jordan River, and from the Dead Sea to Lebanon (Ezekiel 47:13-20). This vision emphasizes the importance of the land’s geographical features and its potential for prosperity and unity.
Historical Evolution of the Promised Land’s Boundaries
The biblical narratives provide a framework for understanding the Promised Land, but the actual historical development of its boundaries is more complex. Archaeological evidence and historical records reveal a changing landscape of empires, migrations, and conflicts, shaping the borders of the region throughout centuries.
Canaanite Period: Before the arrival of the Israelites, the land of Canaan was inhabited by various Canaanite tribes, each with its own territory and cultural identity. The archaeological evidence reveals a complex network of city-states and trading centers, indicating a flourishing civilization with diverse religious beliefs and practices.
Israelite Period: The arrival of the Israelites and their subsequent conquest of Canaan led to a significant shift in the region’s power dynamics. The establishment of the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah, with their respective territories, marked a new era in the region’s history. However, the boundaries of these kingdoms were constantly challenged by neighboring empires, leading to periods of expansion, conquest, and decline.
Roman Period: The Roman conquest of Judea in 63 BCE marked a turning point in the region’s history. The Romans established a province called Judea, which encompassed the region from the Mediterranean Sea to the Jordan River. This period witnessed a significant influx of Roman culture and administration, impacting the region’s social and political landscape.
Byzantine Period: After the fall of the Roman Empire, the region became part of the Byzantine Empire. The Byzantines continued the Roman tradition of administration and governance, fostering a period of relative stability and cultural exchange. However, the rise of Islam in the 7th century CE led to a new wave of conquest and change in the region.
Islamic Period: The Islamic conquest of the Levant in the 7th century CE resulted in the establishment of the Umayyad Caliphate, which ruled over the region for several centuries. The Islamic conquest brought about significant changes in the region’s religious and cultural landscape, with Arabic becoming the dominant language and Islam becoming the dominant religion.
Ottoman Period: From the 16th century onwards, the region came under the rule of the Ottoman Empire. The Ottoman Empire established a system of administration and governance, which lasted until the early 20th century. The Ottoman period was characterized by a diverse population, with a mix of Arab, Turkish, Jewish, and Christian communities living together under Ottoman rule.
British Mandate and the Creation of Israel: Following World War I, the Ottoman Empire collapsed, and the region came under British control. The British Mandate for Palestine was established in 1922, with the objective of creating a Jewish national home in Palestine. This period witnessed a significant influx of Jewish immigrants into the region, leading to growing tensions between the Jewish and Arab populations. In 1948, the British Mandate ended, and the State of Israel was declared, leading to the Arab-Israeli War.
The Promised Land in Different Cultural and Religious Contexts
The concept of the Promised Land has resonated across cultures and religions, influencing historical narratives, religious beliefs, and cultural practices.
Judaism: The Promised Land holds central importance in Judaism, representing the land promised to Abraham and his descendants. It is considered the land of their ancestors, a place of refuge, and a symbol of their identity. The return to Zion, the historical land of Israel, remains a core theme in Jewish theology and practice.
Christianity: The Promised Land is also central to Christian belief. Jesus Christ is often portrayed as fulfilling the promises made to the Israelites, bringing salvation and a new covenant with God. Christians believe that the Promised Land represents a spiritual reality, a place of eternal life and joy.
Islam: While the Promised Land is not explicitly mentioned in the Quran, the concept of a sacred land, often associated with Jerusalem, holds significance for Muslims. Jerusalem is considered a holy city in Islam, and the Dome of the Rock, built on the Temple Mount, is one of Islam’s most important mosques.
The Enduring Significance of the Promised Land
The concept of the Promised Land has had a profound impact on human history, influencing political movements, religious practices, and cultural identities. It continues to be a source of inspiration, conflict, and debate, reminding us of the complex interplay of faith, geography, and history.
The Promised Land’s significance lies in its ability to transcend geographical boundaries and historical events, embodying universal aspirations for freedom, security, and a place to call home. Its enduring influence on our understanding of faith, identity, and belonging underscores its importance in shaping human history and the ongoing pursuit of a just and peaceful world.
FAQs Regarding the Boundaries of the Promised Land
1. What are the different interpretations of the Promised Land’s boundaries throughout history?
The Promised Land’s boundaries have been interpreted differently throughout history, influenced by political, religious, and cultural factors. While biblical texts provide a framework, historical realities and changing power dynamics have led to variations in the perceived extent of the Promised Land.
2. How did the Promised Land’s boundaries evolve under different empires and rulers?
The Promised Land’s boundaries have shifted significantly under various empires and rulers. From the Canaanite period to the Ottoman Empire, the region witnessed a changing landscape of power dynamics, conquests, and migrations, influencing the borders of the land.
3. What is the significance of the Promised Land in different religious contexts?
The Promised Land holds profound significance in Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, representing a place of refuge, a symbol of faith, and a source of inspiration for followers of these religions.
4. How has the concept of the Promised Land influenced political movements and conflicts?
The concept of the Promised Land has played a significant role in shaping political movements and conflicts, particularly in the context of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Both Israelis and Palestinians claim the land as their own, drawing on historical and religious narratives to justify their claims.
5. What is the future of the Promised Land’s boundaries?
The future of the Promised Land’s boundaries remains a subject of ongoing debate and conflict. The complexities of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, coupled with the region’s geopolitical significance, make it difficult to predict the future of its borders.
Tips for Understanding the Boundaries of the Promised Land
-
Study biblical texts: Understanding the biblical narratives surrounding the Promised Land provides a foundational understanding of its significance and historical context.
-
Explore historical maps: Examining historical maps of the region can offer insights into the evolution of the Promised Land’s boundaries over time.
-
Engage with different perspectives: Recognizing the diverse interpretations of the Promised Land’s boundaries across different cultures and religions is crucial for fostering understanding and dialogue.
-
Consider the political and social context: Understanding the political and social dynamics surrounding the Promised Land’s boundaries is essential for appreciating the complexity of the region’s history and ongoing conflicts.
-
Embrace critical thinking: Approaching the subject of the Promised Land with a critical mindset, examining both historical and contemporary perspectives, allows for a more nuanced and informed understanding of its significance.
Conclusion
The Promised Land, with its shifting boundaries and enduring significance, continues to captivate our imaginations and challenge our understanding of history, faith, and identity. Its geographical expanse, as depicted in biblical texts and historical narratives, offers a glimpse into the complex interplay of human aspirations, cultural influences, and political realities. By delving into the historical evolution of the Promised Land’s boundaries and examining its significance in different cultural and religious contexts, we can gain a deeper appreciation for its lasting impact on our world.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into the Boundaries of the Promised Land: A Geographical and Historical Exploration. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!