Decoding the Lines: Understanding Isobars on Weather Maps
Related Articles: Decoding the Lines: Understanding Isobars on Weather Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Decoding the Lines: Understanding Isobars on Weather Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Decoding the Lines: Understanding Isobars on Weather Maps
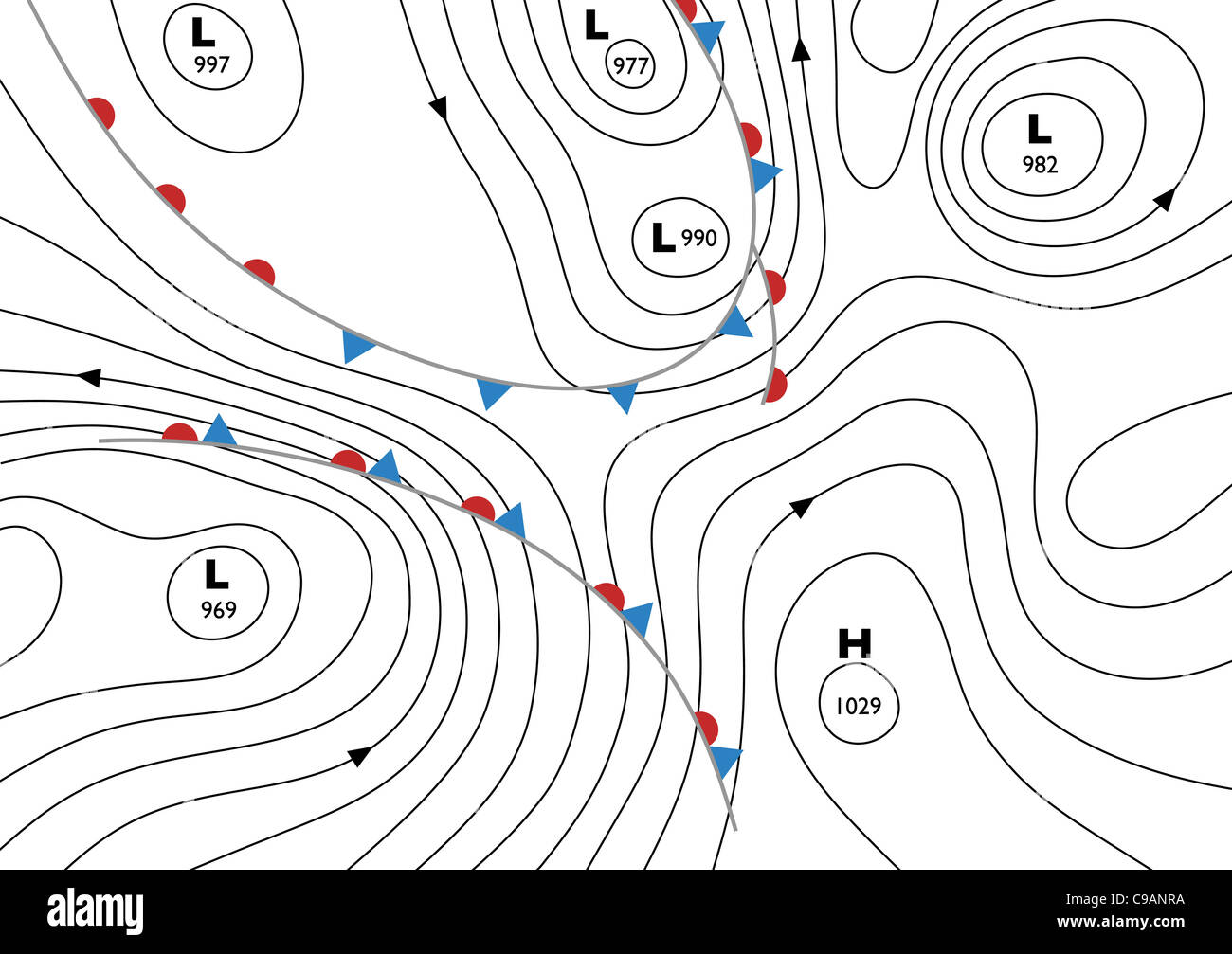
Weather maps, those colorful depictions of atmospheric conditions, are more than just aesthetic displays. They are powerful tools used by meteorologists to predict and understand weather patterns. Among the various symbols and lines on a weather map, one stands out as a key indicator of atmospheric pressure: the isobar.
Isobars: Lines of Equal Pressure
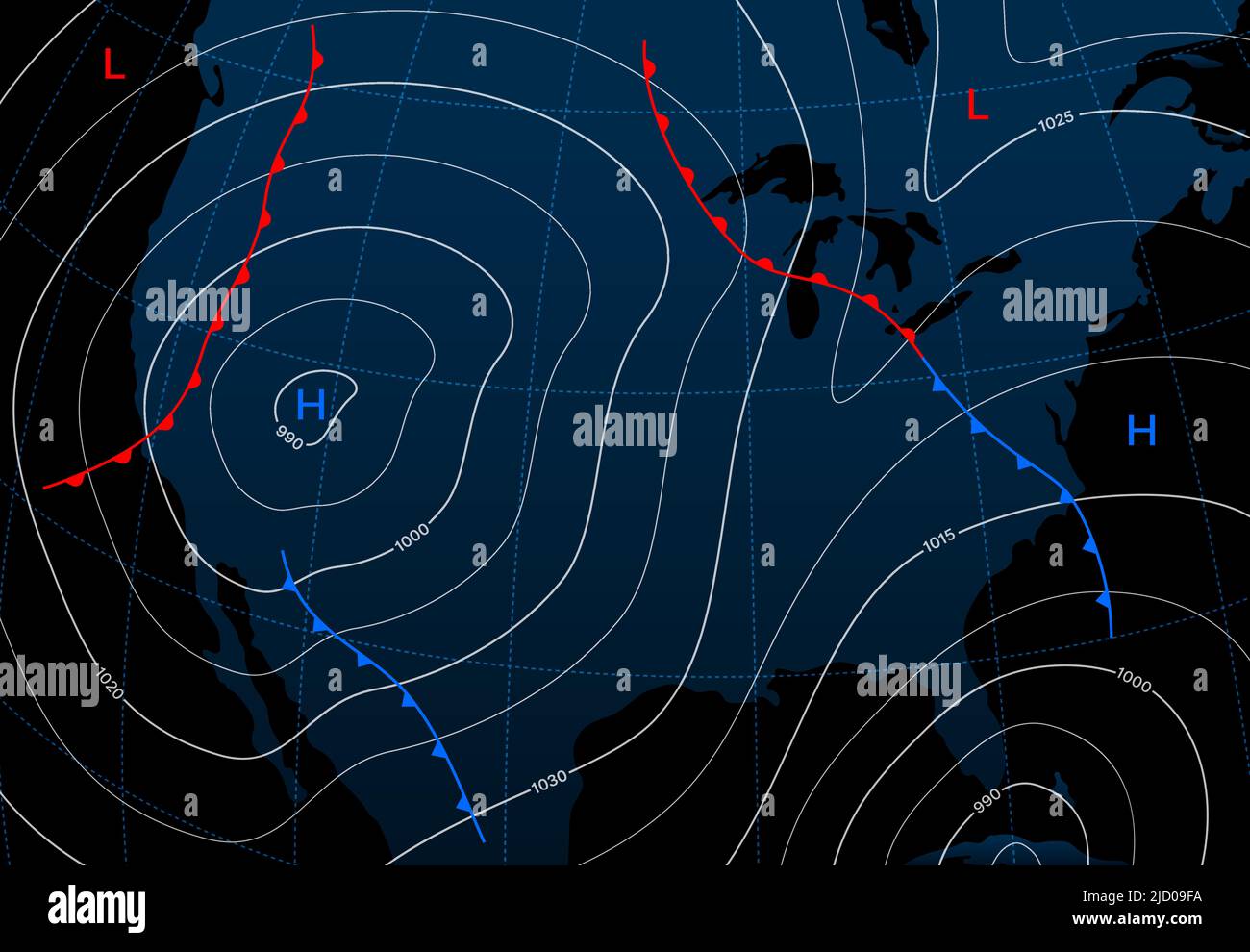
Isobars are lines drawn on a weather map connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure. The word "isobar" itself is derived from the Greek words "isos" (equal) and "baros" (weight), aptly reflecting their function. These lines, often depicted in shades of blue or red, provide a visual representation of pressure gradients, which are essential for understanding wind patterns and weather phenomena.
Pressure Gradients: The Driving Force of Wind
Atmospheric pressure is the weight of the air column above a given point. When pressure differences exist between two locations, a pressure gradient is created. This gradient acts as a driving force, causing air to move from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure. The steeper the pressure gradient, the stronger the wind.
Isobars: A Visual Guide to Wind Patterns
Isobars on a weather map reveal the strength and direction of wind. Closely spaced isobars indicate a steep pressure gradient and strong winds. Conversely, widely spaced isobars suggest a gentle pressure gradient and light winds. The direction of wind is perpendicular to the isobars, with wind blowing from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure.
Understanding Weather Systems with Isobars
Isobars play a crucial role in understanding various weather systems:
- High-Pressure Systems: High-pressure systems are associated with descending air, clear skies, and calm or light winds. On a weather map, these systems are represented by closed isobars with higher pressure values in the center.
- Low-Pressure Systems: Low-pressure systems are characterized by ascending air, cloud formation, and often precipitation. They are depicted on weather maps as closed isobars with lower pressure values at the center.
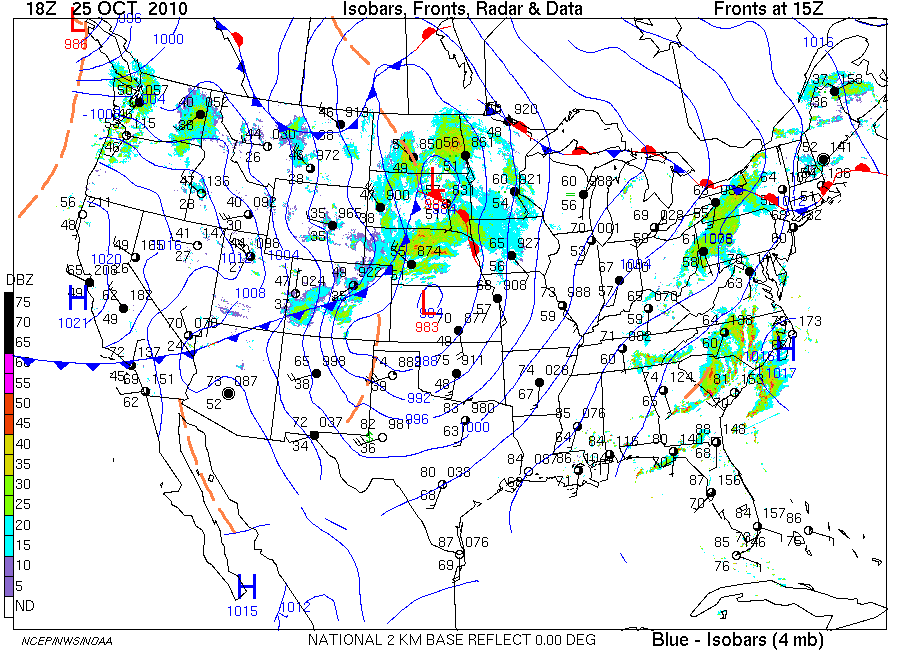
- Fronts: Fronts are boundaries between air masses with contrasting temperatures and densities. Isobars can help identify fronts by showing where pressure gradients are particularly steep. Cold fronts, where cold air displaces warm air, are often marked by a series of closely spaced isobars. Warm fronts, where warm air advances over cold air, tend to have more widely spaced isobars.
Isobars and Weather Forecasting
Isobars are essential tools for weather forecasting. By analyzing the distribution and patterns of isobars, meteorologists can:
- Predict wind direction and strength: The spacing and orientation of isobars provide valuable information about wind patterns.
- Identify areas of potential storms: Closely spaced isobars indicate strong pressure gradients, which can lead to the development of thunderstorms.
- Forecast temperature changes: High-pressure systems are associated with clear skies and warm temperatures, while low-pressure systems often bring cloudy skies and cooler temperatures.
- Track the movement of weather systems: Monitoring changes in the position and shape of isobars over time allows meteorologists to track the movement of weather systems.
Beyond the Basics: Isobaric Analysis
Isobaric analysis involves a deeper understanding of pressure patterns and their implications. Meteorologists may consider factors such as:
- Isobaric height: The height of a specific isobar above sea level can provide insights into atmospheric circulation and stability.
- Isobaric slopes: The slope of an isobar reveals the direction of airflow and can be used to predict the movement of weather systems.
- Isobaric thickness: The vertical distance between two isobars at different pressure levels can indicate the temperature difference between those levels.
FAQs About Isobars on Weather Maps
1. What are isobars used for?
Isobars are used to visualize atmospheric pressure and identify areas of high and low pressure. They help meteorologists understand wind patterns, predict weather systems, and forecast temperature changes.
2. How are isobars drawn on weather maps?
Isobars are drawn connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure. They are typically shown as lines on a weather map, with values indicating the pressure in millibars (mb) or hectopascals (hPa).
3. Why are isobars important for weather forecasting?
Isobars provide valuable information about pressure gradients, wind patterns, and the movement of weather systems. This information is crucial for accurate weather forecasting.
4. How do isobars relate to wind direction?
Wind blows perpendicular to isobars, from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure. The closer the isobars, the stronger the wind.
5. Can isobars be used to predict precipitation?
While isobars don’t directly predict precipitation, they can help identify areas where low-pressure systems are developing, which are often associated with cloud formation and precipitation.
Tips for Interpreting Isobars on Weather Maps
- Pay attention to the spacing of isobars: Closely spaced isobars indicate strong winds, while widely spaced isobars suggest light winds.
- Look for the direction of the isobars: Isobars curving clockwise indicate a high-pressure system, while counter-clockwise curves suggest a low-pressure system.
- Consider the location of fronts: Isobars can help identify fronts by showing where pressure gradients are particularly steep.
- Use online resources: Many websites and apps provide detailed weather maps with isobars and other weather information.
Conclusion: Isobars – A Vital Tool for Weather Understanding
Isobars are fundamental elements of weather maps, providing a visual representation of atmospheric pressure and its influence on wind patterns, weather systems, and temperature changes. By understanding the principles of isobaric analysis, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the complex dynamics of weather and make informed decisions regarding safety and planning. Whether you are a seasoned meteorologist or simply curious about the weather, understanding isobars is a crucial step towards deciphering the language of the atmosphere.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Pacific-Ocean_HLcenters-noaa-OPC-58b740303df78c060e196387.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/isobarmap-56a9e0d25f9b58b7d0ffa3cf.gif)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Decoding the Lines: Understanding Isobars on Weather Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!