Deciphering the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Keys
Related Articles: Deciphering the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Keys
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Keys. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Keys

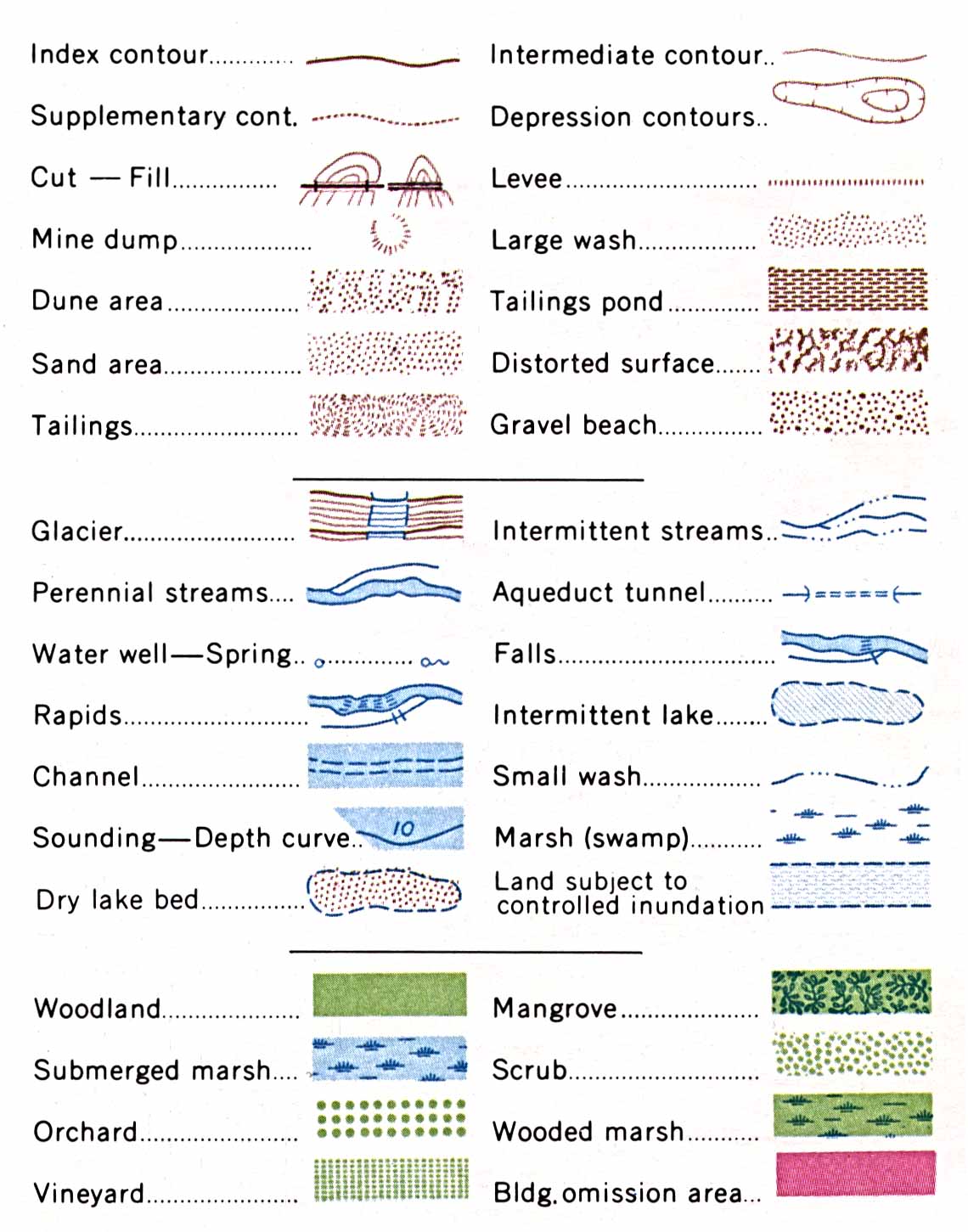
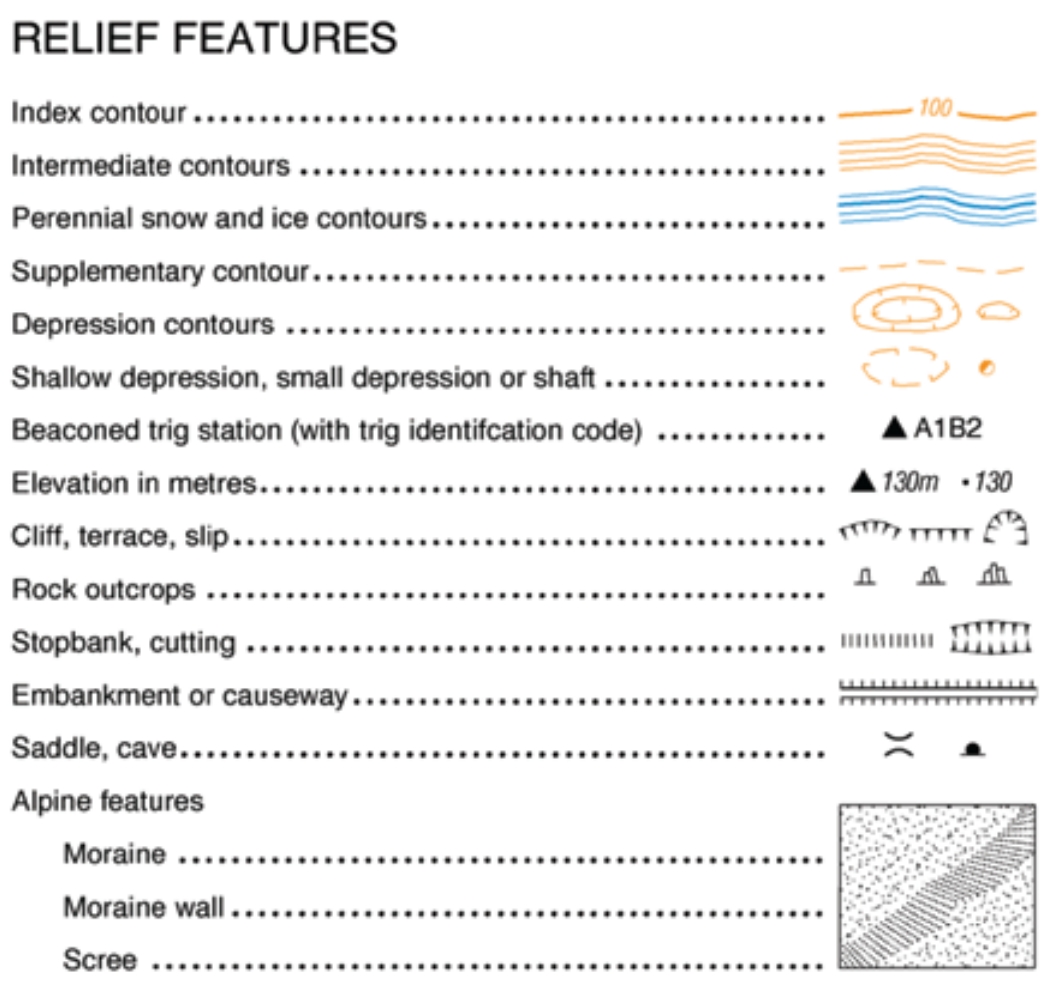
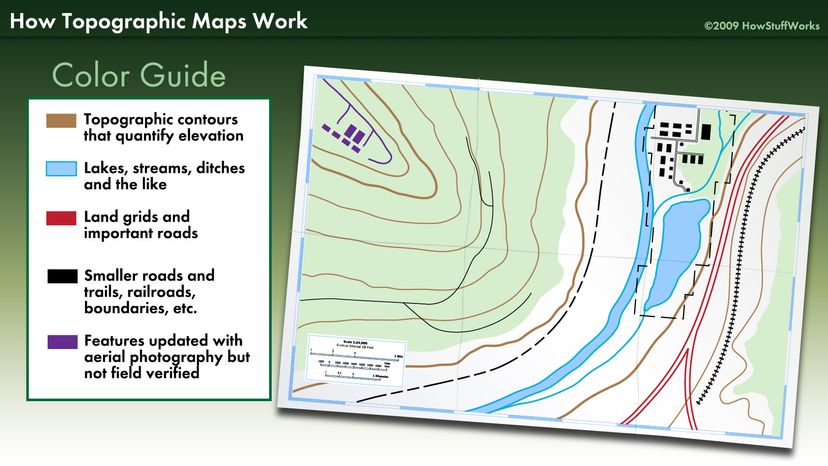
Topographic maps are essential tools for anyone navigating or studying the Earth’s surface. They provide a detailed visual representation of terrain, elevation, and geographical features, enabling users to understand the landscape’s three-dimensional form. The key to unlocking the information contained within these maps lies in understanding the symbols and conventions used, collectively known as the topographic map key.
Understanding the Basics: The Language of Topographic Maps
The topographic map key is a legend that translates the symbols and colors on the map into real-world features. It acts as a visual dictionary, guiding the user to interpret the information accurately.
Essential Elements of a Topographic Map Key:
- Elevation Contours: These lines connect points of equal elevation, providing a visual representation of the terrain’s shape. The closer the contours, the steeper the slope.
- Contour Interval: This value indicates the difference in elevation between adjacent contour lines. It is typically expressed in feet or meters and is crucial for determining the relative height of features.
- Spot Elevations: These numbers indicate the exact elevation of specific points on the map, often located at prominent peaks, depressions, or other significant features.
- Water Features: Rivers, lakes, streams, and other water bodies are depicted with specific symbols, including blue lines for streams and blue areas for water bodies.
- Cultural Features: Man-made elements like roads, buildings, bridges, and power lines are represented with distinct symbols, helping users understand the infrastructure and human impact on the landscape.
- Vegetation: Different types of vegetation, such as forests, grasslands, and wetlands, are represented with specific symbols and patterns, offering insight into the plant life present in the area.
- Symbols and Abbreviations: The key also includes a comprehensive list of symbols and abbreviations used on the map, representing various features like wells, mines, cemeteries, and more.
Navigating the Terrain with the Topographic Map Key:
The topographic map key empowers users to understand the landscape’s complexities and make informed decisions. It helps in:
- Determining elevation and slope: By analyzing contour lines and the contour interval, users can estimate the elevation of specific points and determine the steepness of slopes.
- Identifying potential hazards: The map key reveals the presence of cliffs, ravines, and other hazards that could pose risks during navigation or exploration.
- Planning routes: Understanding the terrain through the key helps users plan efficient and safe routes, avoiding challenging obstacles and maximizing the use of existing trails.
- Conducting environmental studies: The key provides valuable information about vegetation, water bodies, and other environmental features, aiding in ecological research and environmental management.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Topographic Map Key Features
Modern topographic maps often incorporate advanced features that enhance their utility and provide a more comprehensive understanding of the landscape:
- Digital Elevation Models (DEMs): These computer-generated models represent the terrain’s elevation in three dimensions, offering a more detailed and accurate depiction of the landscape.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software integrates topographic data with other spatial information, enabling users to analyze and visualize complex relationships between different features, such as population density, land use, and environmental factors.
- Remote Sensing Data: Satellite imagery and aerial photographs can be incorporated into topographic maps, providing additional visual information about the landscape, including vegetation cover, land use, and urban development.
FAQs about Topographic Map Keys
Q: What is the difference between a topographic map and a regular map?
A: While a regular map focuses primarily on political boundaries, roads, and major cities, a topographic map provides a detailed representation of the Earth’s surface, including elevation, terrain features, and vegetation.
Q: How do I read a topographic map?
A: Start by understanding the key. Familiarize yourself with the symbols and conventions used, particularly contour lines and the contour interval. Then, use the key to interpret the features and understand the terrain’s shape and elevation.
Q: What are the benefits of using topographic maps?
A: Topographic maps offer detailed information about the terrain, aiding in navigation, planning, environmental studies, and understanding the landscape’s complexities.
Q: Are there different types of topographic map keys?
A: Yes, the specific symbols and conventions used on topographic maps can vary depending on the organization or agency responsible for producing the map. However, the fundamental principles remain consistent.
Tips for Using Topographic Map Keys
- Practice makes perfect: Familiarize yourself with the symbols and conventions used by practicing reading different topographic maps.
- Start with a simple map: Begin with maps of familiar areas to gain confidence and build your understanding of the key.
- Use online resources: Numerous websites and tutorials offer guidance on reading topographic maps and understanding the key.
- Consult multiple sources: If you are unsure about a particular symbol or feature, consult multiple sources, including the map key, online resources, and expert advice.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding the Topographic Map Key
The topographic map key is a crucial tool for anyone seeking to understand and navigate the Earth’s surface. By deciphering the symbols and conventions used on these maps, users can gain valuable insights into the terrain’s shape, elevation, and features, making informed decisions about navigation, planning, and environmental studies. As technology advances and new data sources become available, the topographic map key will continue to evolve, providing even more comprehensive and insightful representations of our planet’s diverse landscape.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Keys. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!