A Journey Through Time: Exploring the African Continent in 1800
Related Articles: A Journey Through Time: Exploring the African Continent in 1800
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Time: Exploring the African Continent in 1800. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Time: Exploring the African Continent in 1800

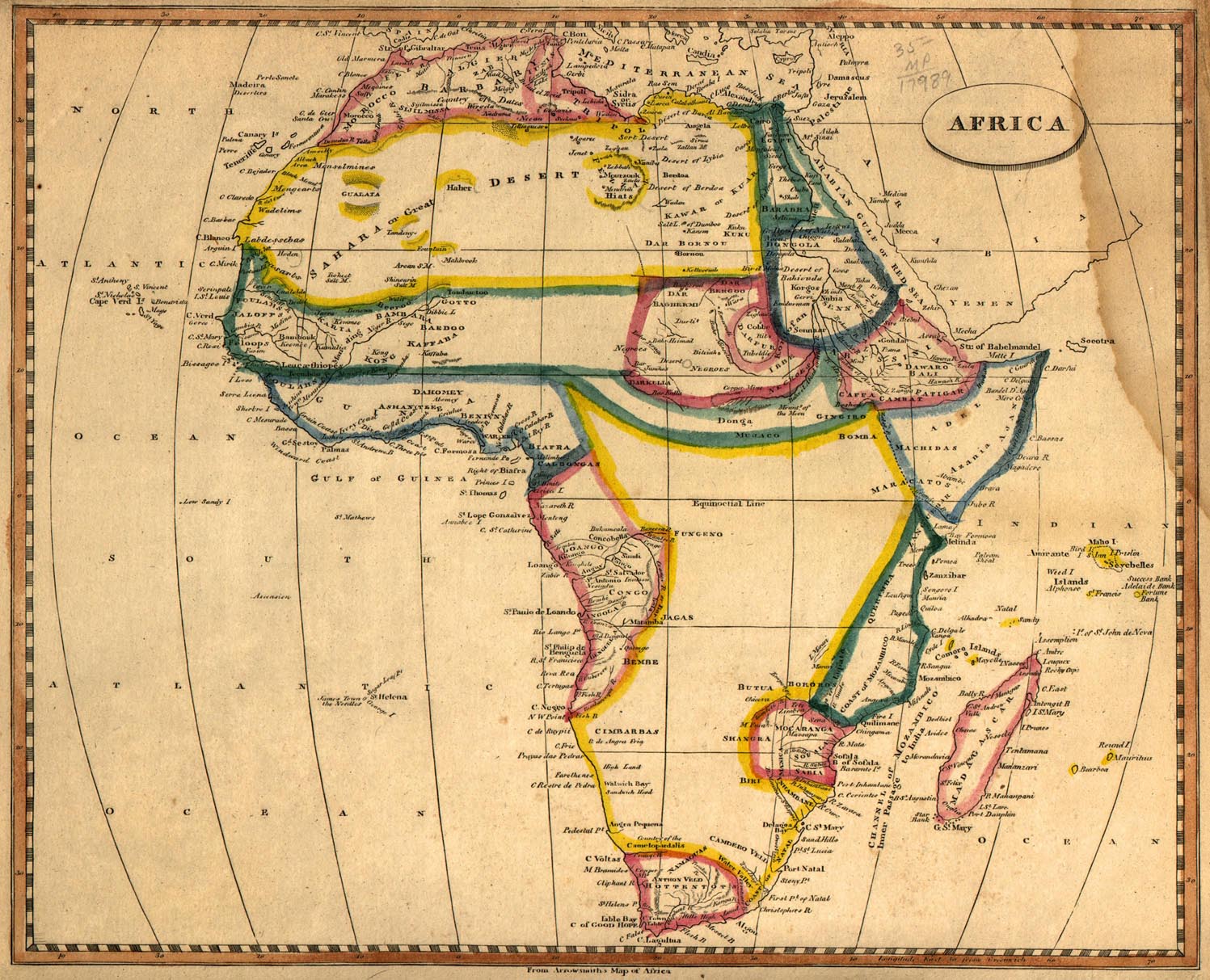
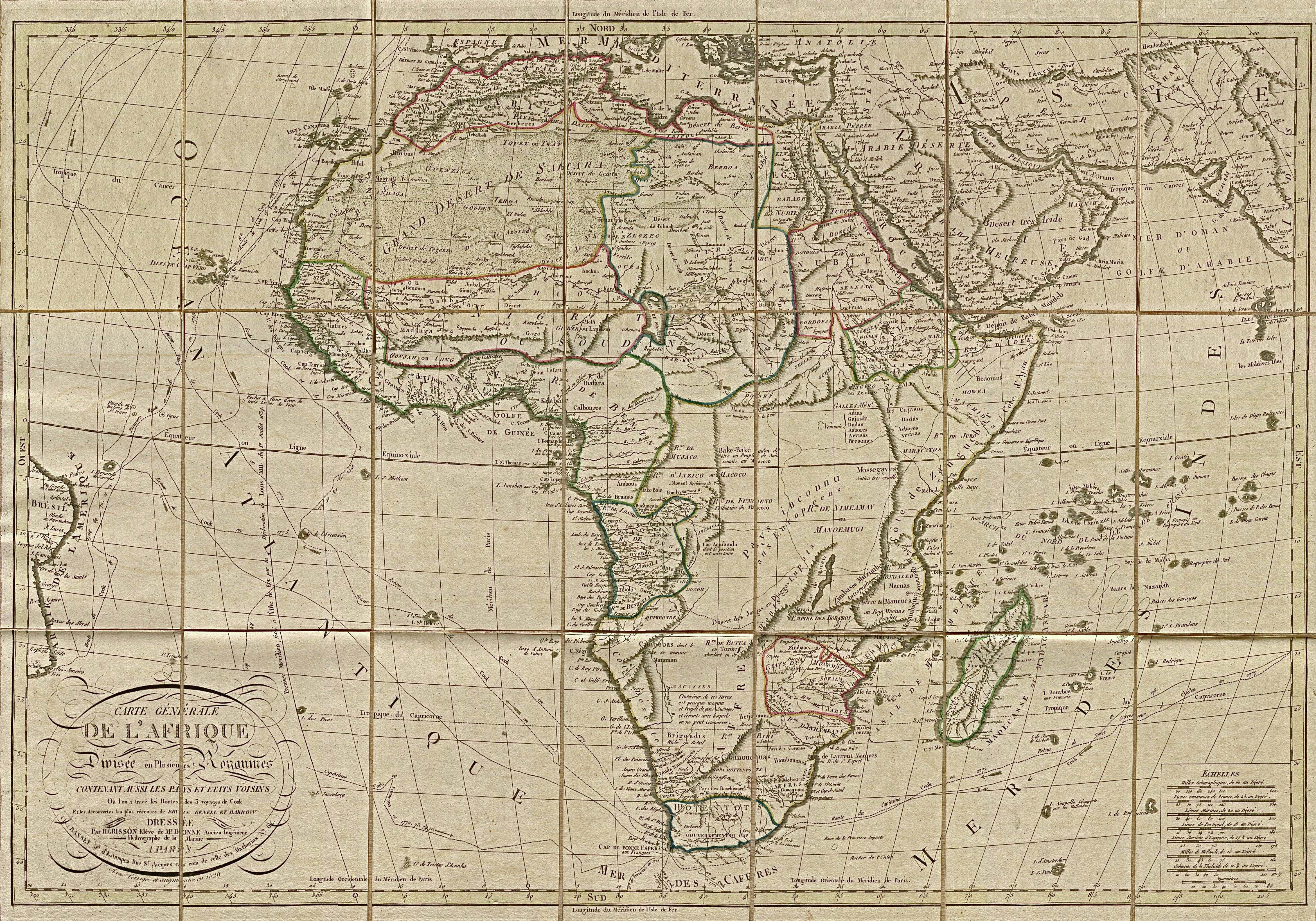
The African continent, a vast and diverse landmass, has witnessed centuries of change, both political and geographical. Understanding the Africa of 1800 is essential for grasping the complexities of the modern continent. Examining the map of Africa in this era provides a crucial window into the past, revealing the intricate tapestry of empires, societies, and trade networks that shaped the continent’s future.
A Continent of Empires and Kingdoms:
The Africa of 1800 was not a monolithic entity. Instead, it was a mosaic of diverse empires, kingdoms, and tribal societies, each with its unique history, culture, and political structure.
- The Great Empires: The 18th century saw the rise of powerful empires across Africa. The Ottoman Empire controlled much of North Africa, while the Kingdom of Dahomey in West Africa was known for its powerful army and sophisticated political system. In the south, the Zulu Empire under King Shaka Zulu was renowned for its military prowess and expansionism.
- The Kingdoms of the Interior: Within the interior of the continent, numerous smaller kingdoms flourished, each with its own distinct culture and traditions. The Ashanti Kingdom in Ghana, for example, was renowned for its gold trade and intricate social structure.
- Tribal Societies: Beyond the empires and kingdoms, numerous tribal societies thrived, often living in harmony with their environment. The San people of Southern Africa, for example, were skilled hunter-gatherers with a deep understanding of the land.
The Impact of European Colonialism:
The 18th century marked the beginning of a significant shift in Africa’s political landscape. European powers, driven by a desire for resources and trade, began to establish colonies on the continent. This colonial presence would have a profound and lasting impact on Africa’s future.
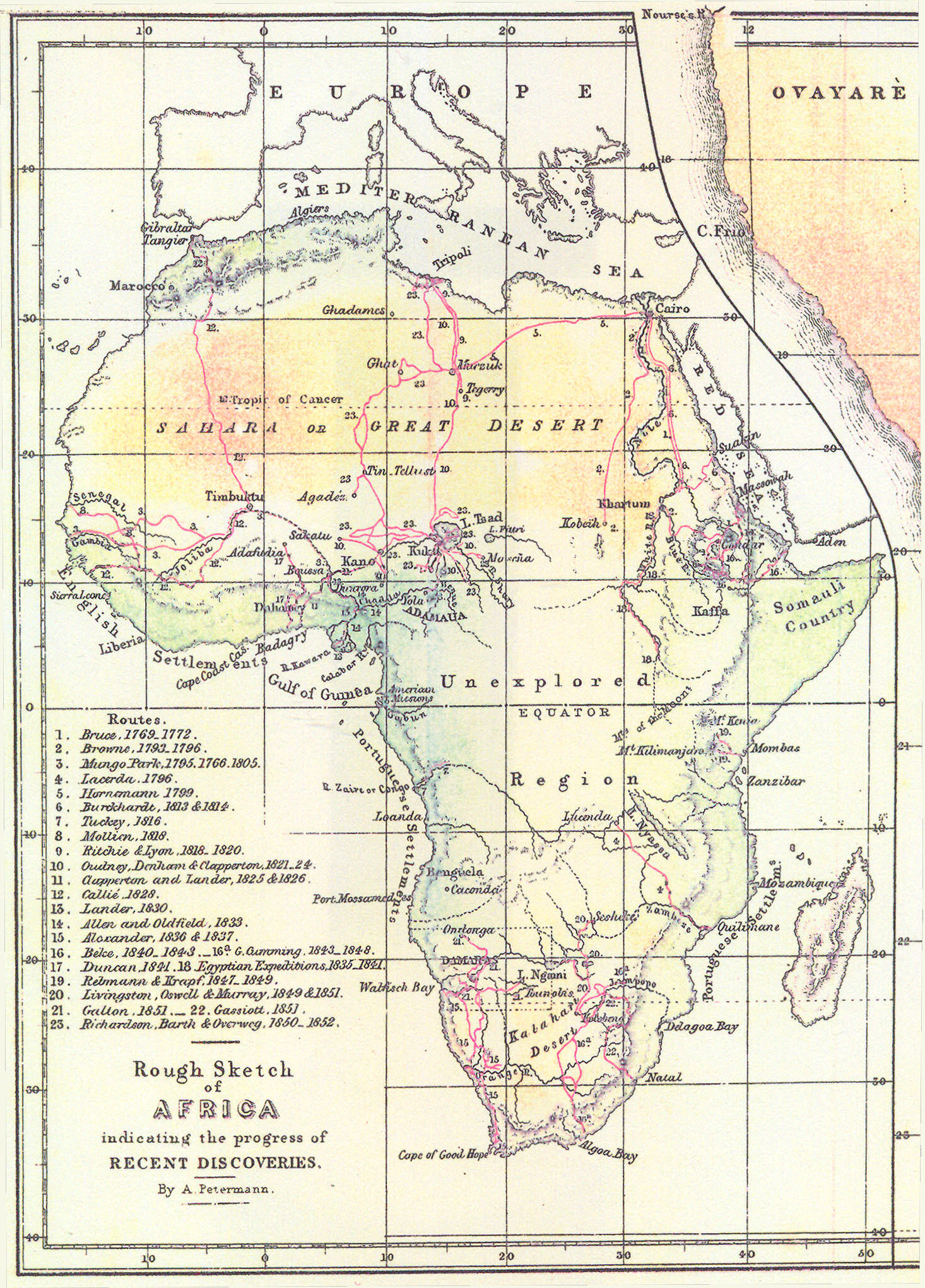
- The Scramble for Africa: The late 19th century witnessed the "Scramble for Africa," a period of intense competition between European powers for control of the continent. By 1914, almost all of Africa was under European control.
- The Impact of Colonialism: European colonization had a devastating impact on African societies. It led to the exploitation of resources, the disruption of traditional political structures, and the imposition of European laws and values.
The Importance of Understanding the Africa of 1800:
Understanding the Africa of 1800 is crucial for several reasons:
- Understanding the Roots of Modern Africa: The map of Africa in 1800 provides a foundation for understanding the historical forces that have shaped the modern continent. It helps explain the current distribution of languages, cultures, and ethnicities, as well as the ongoing challenges of post-colonial Africa.
- Appreciating the Diversity of African History: The Africa of 1800 was a vibrant and diverse continent, with a rich history of empires, kingdoms, and societies. Studying this period helps to challenge the often-narrow Eurocentric view of African history.
- Recognizing the Resilience of African Societies: Despite the challenges posed by colonialism, African societies demonstrated remarkable resilience and adaptability. Understanding the Africa of 1800 allows us to appreciate the strength and adaptability of African cultures.
FAQs about the Africa of 1800:
Q: What were the major trade routes in Africa in 1800?
A: The trans-Saharan trade route, connecting North Africa to the interior, was a major artery for the exchange of goods. Gold, salt, slaves, and other commodities were traded along this route. The Indian Ocean trade network also played a significant role, connecting East Africa with Asia and the Middle East.
Q: What were the main religions practiced in Africa in 1800?
A: Islam was prevalent in North and East Africa, while traditional African religions were dominant in much of the interior. Christianity was also present in some regions, particularly in areas with European influence.
Q: What were the major technological advancements in Africa in 1800?
A: Africa in 1800 was characterized by a diverse range of technologies, including ironworking, pottery, and textile production. The development of sophisticated agricultural techniques and the use of irrigation systems also played a crucial role in sustaining populations.
Q: What were the major challenges faced by African societies in 1800?
A: African societies faced numerous challenges in 1800, including inter-tribal conflicts, droughts, and disease outbreaks. The growing influence of European powers and the transatlantic slave trade also posed significant threats to African societies.
Tips for Studying the Africa of 1800:
- Explore Primary Sources: Historical maps, journals, and accounts from travelers and missionaries provide valuable insights into the Africa of 1800.
- Consult Academic Works: Numerous scholars have dedicated their research to the history of Africa in this period. Consulting their works can provide a comprehensive understanding of the complex political, social, and economic landscape of the continent.
- Engage with Visual Materials: Photographs, illustrations, and paintings from the 18th and 19th centuries offer a glimpse into the lives of people in Africa during this period.
Conclusion:
The Africa of 1800 was a continent brimming with diverse cultures, powerful empires, and vibrant trade networks. It was a period of significant change, marked by the growing influence of European powers and the emergence of new challenges. By studying this era, we can gain a deeper understanding of the complex history of Africa and the forces that have shaped the modern continent. Through careful research and a commitment to understanding the past, we can contribute to a more accurate and nuanced understanding of the African experience.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Time: Exploring the African Continent in 1800. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!