A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography of China: Understanding the Land of the Dragon
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography of China: Understanding the Land of the Dragon
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography of China: Understanding the Land of the Dragon. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography of China: Understanding the Land of the Dragon

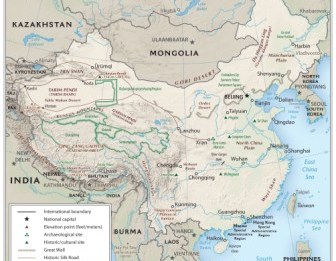
China, the world’s most populous nation, is a vast and diverse country with a rich history and culture. Its sprawling landscape, encompassing mountains, deserts, plains, and coastlines, has played a pivotal role in shaping its development and identity. Understanding the geography of China is essential for comprehending its history, culture, and contemporary challenges. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of China’s physical geography, highlighting its key features, regional variations, and the profound impact these have on its people and society.
A Land of Extremes: The Diverse Topography of China
China’s topography is characterized by its remarkable diversity, ranging from towering mountains to vast plains and from arid deserts to lush river valleys. This variety has led to a wide range of climate zones and ecological niches, contributing to the nation’s unique biodiversity and cultural tapestry.
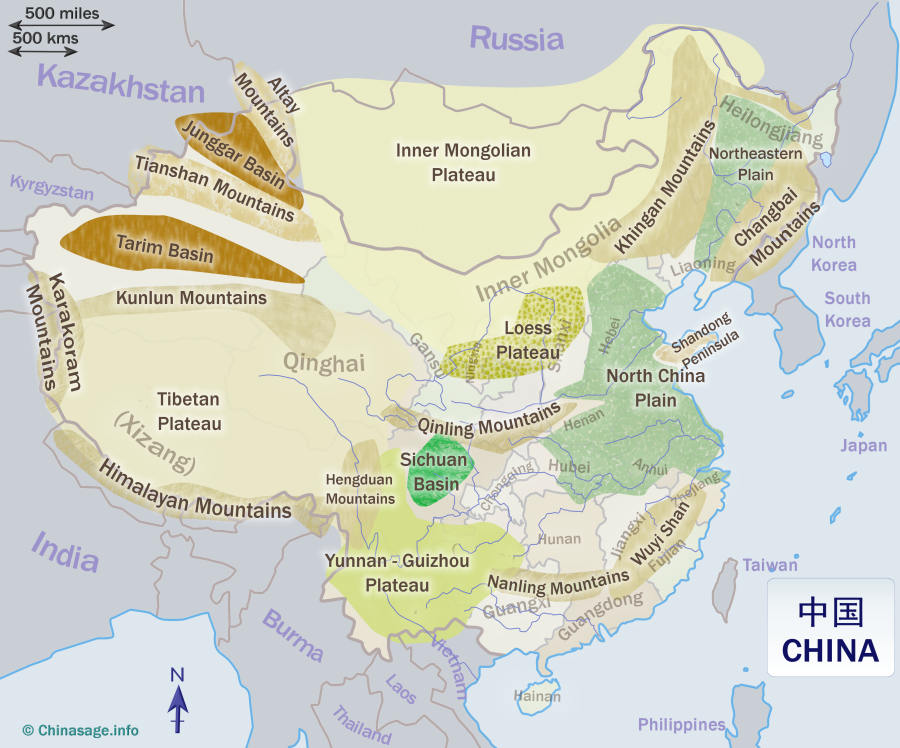
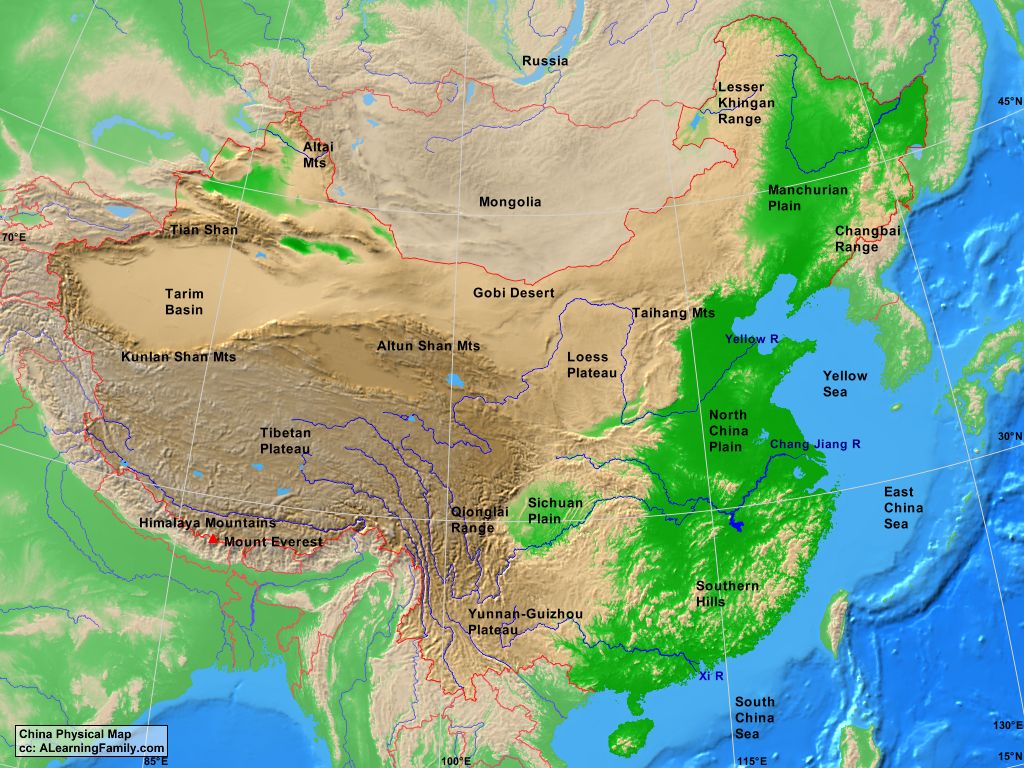
1. The Mighty Himalayas and the Tibetan Plateau:
The towering Himalayas, forming the world’s highest mountain range, dominate China’s southwestern frontier. The majestic Mount Everest, the world’s highest peak, stands as a testament to the immense geological forces that shaped this region. The Tibetan Plateau, often referred to as the "Roof of the World," lies to the north of the Himalayas, stretching across vast expanses of high-altitude plains and grasslands. This plateau, with its unique ecosystem and cultural heritage, plays a critical role in regulating regional climate and water resources.
2. The Vast Plains of Eastern China:
The eastern part of China is dominated by expansive plains, primarily the North China Plain and the Yangtze River Plain. These fertile lowlands, formed by the deposition of sediments from major rivers like the Yellow River and the Yangtze River, have been the cradle of Chinese civilization for millennia. These plains have supported a dense population and intensive agriculture, contributing significantly to China’s economic growth.
3. The Rugged Coastline and the Islands:
China’s coastline, stretching over 14,500 kilometers, is a mix of jagged cliffs, sandy beaches, and numerous islands. The eastern coast, bordering the Yellow Sea, East China Sea, and South China Sea, is home to major ports and coastal cities, playing a vital role in international trade and maritime activities. China also possesses numerous islands, including Taiwan, Hainan, and the Diaoyu Islands, which are subject to territorial disputes with neighboring countries.
4. The Arid Deserts and the Gobi:
China’s northwest is dominated by vast deserts, including the Taklamakan Desert and the Gobi Desert. These arid regions, characterized by extreme temperatures and scarce rainfall, present significant challenges for human habitation and development. However, they also hold immense ecological value, supporting unique plant and animal life adapted to harsh conditions.
5. The Diverse River Systems:
China’s river systems are essential for its economy and society. The Yellow River, known as "China’s Sorrow" due to its frequent floods, is the second-longest river in Asia, while the Yangtze River, the longest river in Asia, plays a vital role in irrigation, transportation, and hydroelectric power generation. Other significant rivers include the Pearl River, the Songhua River, and the Mekong River, which flows through Southeast Asia.
The Impact of Geography on Chinese Culture and Society
China’s diverse geography has profoundly influenced its culture and society, shaping its history, economy, and way of life.
1. The Influence of Mountains and Rivers:
The mountains and rivers have played a crucial role in shaping Chinese culture and identity. The majestic mountains have been revered as sacred spaces, inspiring awe and reverence. Rivers, like the Yellow River and the Yangtze River, have been seen as lifelines, providing sustenance and connecting communities. The natural barriers created by mountains and rivers have also contributed to the development of distinct regional cultures and dialects.
2. The Importance of Agriculture:
The fertile plains of eastern China have been the cornerstone of Chinese agriculture, supporting a large population and shaping the nation’s agricultural traditions. The reliance on agriculture has also influenced social structures and economic development, with farming communities playing a central role in Chinese society.
3. The Role of Geography in Historical Events:
China’s geography has played a significant role in its history, influencing military campaigns, trade routes, and political boundaries. The Great Wall of China, built to defend against invaders, is a testament to the importance of geographical barriers in shaping the nation’s history.
4. The Challenges of Climate Change:
China’s diverse geography makes it vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. Rising sea levels threaten coastal cities, while changes in precipitation patterns affect agricultural production and water resources. Addressing these challenges requires careful planning and sustainable development strategies.
FAQs about China’s Geography:
1. What is the highest point in China?
The highest point in China is Mount Everest, with a summit elevation of 8,848.86 meters (29,031.7 feet).
2. What are the major rivers in China?
The major rivers in China include the Yellow River, the Yangtze River, the Pearl River, the Songhua River, and the Mekong River.
3. What are the major deserts in China?
The major deserts in China include the Taklamakan Desert, the Gobi Desert, and the Badain Jaran Desert.
4. What is the climate like in China?
China’s climate varies significantly across its vast territory. The north is generally colder and drier, while the south is warmer and more humid. The eastern coast experiences a monsoon climate, with hot, humid summers and cool, dry winters.
5. What are the major geographic regions of China?
China is often divided into seven major geographic regions: Northeast China, North China, East China, South China, Southwest China, Northwest China, and Tibet.
Tips for Understanding China’s Geography:
- Use a detailed map: A comprehensive map of China is essential for understanding the country’s geography.
- Explore online resources: Websites and online databases offer valuable information about China’s geography, including maps, data, and articles.
- Read books and articles: There are numerous books and articles that provide insights into China’s geography and its impact on the country’s history, culture, and society.
- Travel to China: Experiencing China firsthand is the best way to appreciate its diverse geography and understand its significance.
Conclusion:
China’s geography is a remarkable tapestry of mountains, plains, deserts, and coastlines, shaping its history, culture, and economy. Understanding the country’s physical features, climate zones, and ecological diversity is essential for comprehending its past, present, and future. As China continues to develop and face global challenges, its geography will continue to play a vital role in shaping its destiny.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography of China: Understanding the Land of the Dragon. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!